
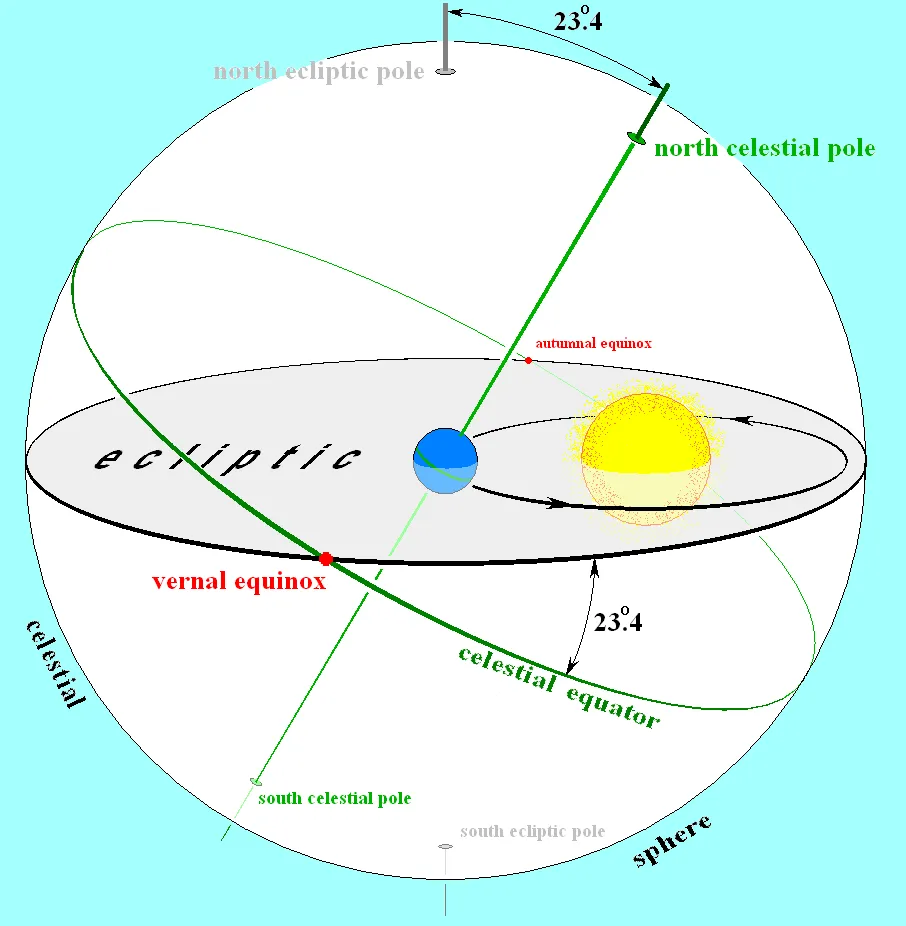
Equinox
The Equinox is the moment when the Sun crosses the celestial equator as seen in the celestial sphere. This corresponds to the moment in which the Sun reaches declination 0° in the Equatorial Coordinate System. This occurs twice in a year. One is the March Equinox and the other one is the September Equinox. In the March Equinox, the right ascension value of its location is 0h and in the September Equinox, the value of the right ascension is 12h. These moments are called also the Vernal (Spring) Equinox and the Autumnal (Autumn) Equinox, however, some confusion may arise due to the inversion of the seasons between the northern and the southern hemispheres.
The day when the equinox occurs is characterized by equal duration of day and night. It is also characterized by sunrise occurring almost exactly due East (azimuth 90° in the Topocentric Coordinate System)
It is also interesting to note that currently the star constellation that is harbors the point 0° Dec and 0h RA is the constellation of Pisces. Around the year 2600, this point would have entered the region of the constellation of Aquarius. This occurs due to an Earth's movement called precession, which we will explain in a later post
Previous Posts
Concepts in Astronomy #1. Introduction
Concepts in Astronomy #2. The Ecliptic
Concepts in Astronomy #3. The Celestial Equator
Concepts in Astronomy #4. Right Ascension
Concepts in Astronomy #5. Declination
Concepts in Astronomy #6. The Celestial Sphere
Concepts in Astronomy #7. Azimuth
Concepts in Astronomy #8. Altitude
Concepts in Astronomy #9. The Equatorial CoordinateSystem
Concepts in Astronomy #10. The Topocentric CoordinateSystem