Since you are reading this post I am going to assume that you are sitting down somewhere and that you also believe that your speed is zero (unless you are on a train or a subway).
What if I told you the answer to that question depends on who is observing and that it is all relative.
Relativity - There Are Two Types
When STEM types talk about relativity they are referring to one of two types, Galilean relativity or Einsteinian relativity.
Galilean relativity is easier to understand. You are sitting on a train and you throw a ball straight up in the air and it falls straight back down into your lap. So far so good but a person standing on the ground watching you through the train's window will actually see that ball follow a parabolic trajectory. So motion even in its simplest form depends on where you are.
Einstein's relativity is more complex but is concerned primarily with the fact that your perception of space and time are dependent on your local velocity. I have posted about it a few times over the past few months and if you are interested in it please feel free to read these posts:
- Intuitive Special Relativity - Why You Can't Go Faster Than The Speed of Light
- Intuitive Special Relativity - The Lorentz Transformation
- Intuitive Special Relativity - Time Is Relative
- Intuitive Special Relativity - Time Dilation
Earth - A Living Space Ship Hurtling Through The Void
Earth Spin
The Earth is a large spinning rock hurtling through the emptiness of space.
It is rotating once per day which means that everyone not at the North or South poles is moving. The equatorial diameter of the Earth is 12,756 km which gives us a circumference of 40,076 km. Someone living on the equator travels this 40,000 km once per day (24 hours) and so just sitting still they are moving at 1670 km/h or 460 metres per second.
In fact, this effect is taken advantage of when rockets are launched. The Europeans prefer to launch from Guiana in South America and the Americans prefer to launch from the southern most part of the contiguous USA which is the state of Florida. In general, the closer you are to the equator the faster your rocket is going right at lift-off.
Earth Orbit
In addition to spinning, the Earth is also in orbit around the Sun. The Earth's mean orbital diameter is about 150 million km giving us a circumference of about 942 million km. The Earth completes this circuit once per year (365.25 days) and we can work out that the orbital velocity to be about 107,500 km/h or 29.9 kilometres per second.
That's a fair clip.
The direction of the Earth's orbit looking down from the North pole is counter-clockwise and the spin of the Earth is also counter-clockwise. This means that if you lie down on the ground when the Sun is rising you are facing the void of space and all it contains and moving directly towards it at 30 kilometres per second.
Scary.
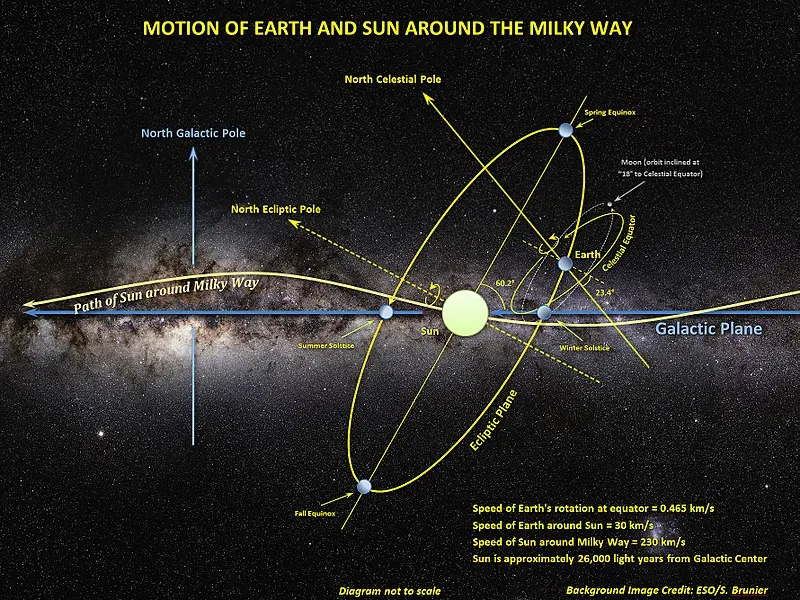
The Sun's Galactic Orbit
It seems that nothing sits still in this Universe not even the life-giving centre of our solar system. The Sun is positioned in the Orion arm of the galaxy about 25,000 from the galactic centre. The Sun and its attendant planets all orbit around the galaxy once every 225 to 250 million years.
Doing the math once again gives us a solar speed around the galaxy of about 190 kilometres per second.
The ecliptic of the solar system is tilted with respect to this motion so adding or subtracting the Earth's orbital velocity from this general velocity is not straightforward. It doesn't matter though; the answer is that we are all moving at a blistering speed through the galactic neighbourhood.
Milky Way vs Andromeda - The Big Galactic Smash Up
So the Sun is orbiting our galaxy at an impressively high speed but wait there's more.
We are also apparently on a collision course with the Andromeda galaxy which is currently about 2.5 million light years away from us. The collision is expected in about 4.5 billion years or so which means it is really nothing anyone needs to worry about.
As expected, I did the math for this and find that the Milky Way and Andromeda are approaching each other at a speed of about 170 km/s. Assuming the two galaxies are roughly equal in mass means that the Milky Way itself is moving at about half of the total approach speed or about 90 kilometres per second through space towards the Andromeda galaxy.
The Expansion of Space-Time
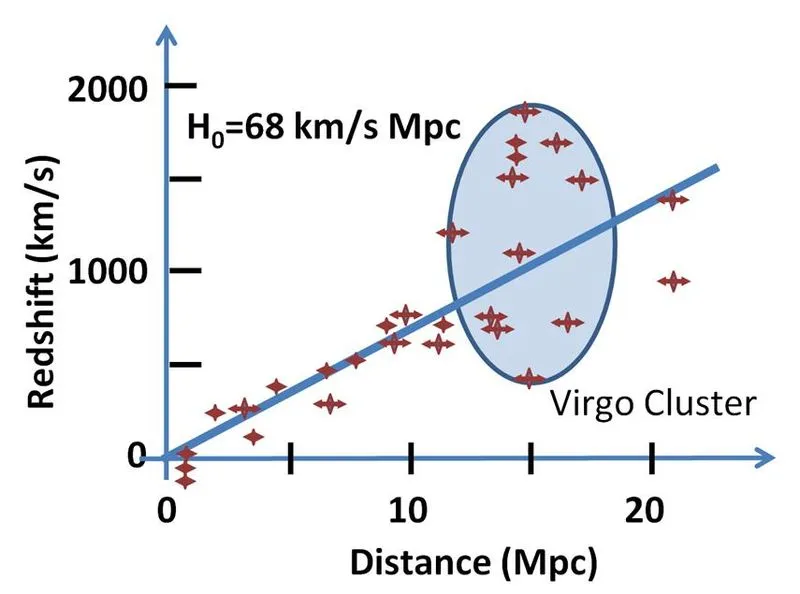
Edwin Hubble found that the redshift of light from distant galaxies increases with distance (i.e. the faster away a galaxy is the faster it is moving away from us). This is known as Hubble's Law and has been measured to be about 68 kilometres per second per megaparsec (a megaparsec is 3.26 million light years).
This means that aliens in very distant galaxies will see us moving away from them at high velocity. If they are 1 billion light years away it would look like we are moving away from them at about 21,000 kilometres per second.
There is a speed limit for massive objects known as the speed of light but there is no speed limit for the expansion of space-time (as far as I know).
So, all you have to do is move out to the edge of the Observable Universe and look back, we will be moving away at the speed of light (note: this does not violate the speed of light limit because we would not be moving faster than light through our local spacetime).
Closing Words
So if you are feeling like a slug-boy or slug-girl for just sitting around all day doing nothing but reading excellent blog posts on Steemit take heart.
You are actually moving at the speed of light (to someone).
Thank you for reading my post.
Post Sources
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Earth
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guiana_Space_Centre
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sun#Orbit_in_Milky_Way
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Andromeda_Galaxy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edwin_Hubble
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hubble%27s_law