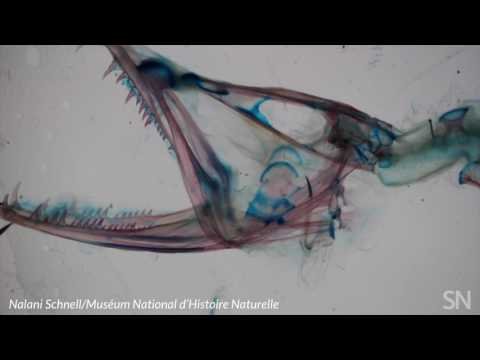
Dragon fish are a group of fish scattered in the ocean floor. According to a new study analyzing the physiognomy of the mandible, their small size is compensated with their "alien" appearance and the ferocity they shows. A group of researchers from the National Museum of Natural History in Paris and the National Museum of Natural History in Washington have analyzed nine-dragon fish species of the family (Stomiidae). Five had a flexible rod, called a notochord, covered by special connective tissue that bridged their vertebrae and skulls.
The researchers took into account that the physiognomy of mouth is more flexible joints due to the soft tissue that connects the skull and body. They also noted that this ability helps dragon fish species to swallow whole organisms, such as crustaceans and smaller fish.
In the video below we see that at the maximum opening, jaw detaches from the body and the only link is the soft tissue detachment whose flexibility allows it.
Flexible head joint found in dragonfish | Science News
Let's open the atlas of strange creatures:
Babirusa:
Is part of the family Suidae and can be found in the forests of Indonesia, specifically in the islands of Sulawesi, Togian, Sula and Buru. Called also pig deer, Babirusa is best known for its spectacular tusks. In males, the upper canines grow up penetrating the skin and curving back towards the forehead. Lower canines are quite developed and grow up. In contrast, among female canines are missing or reduced in size.
If males do not break their teeth, which can be done during daytime, they will continue to grow until they will be hurt or will penetrate the skull. In Indonesia, folklore inspired Babirusa's appearance and make up masks that resemble demonic. Although pig deer is protected by law, poaching continues to threaten its existence.
Pink-fairy-armadillo-cropped:
If we exclude the tail, the pet has a length of between 9 and 11.5 centimeters. Despite its fragile appearance, thanks to its large claws, he can bury in the ground in seconds. In fact, as a solitary nocturnal animal, he spends most of the time underground, preferably near ant mounds to receive continuous food sources. Besides the ants and the larvae, its diet also contains worms, snakes, roots and plants.
It is believed that pink-fairy-armadillo-cropped is endangered, but scientists know so little about it, that it is unclear in what state is the population.
Fossa:
Is an endemic mammal to Madagascar. In fact, Foss is the largest carnivorous mammal on the island. Males can reach a length of 70-80 cm and a weight of 5.5 to 8.6 kg, being slightly larger than females. Over 50% of its diet consists of lemurs, primates endemic lizards, rodents or birds.
Fossa is one of those animals that are active day and night and does not return to rest twice in the same place, except mother with cubs. They communicate using smell and sound or visual signals. They spin and produce cries when they feel threatened, the females meows during mating and the males emit a specificsound when they find the right partners.
Also, using the glands in the rear area, they mark their territory, the rocks and trees nearby. In addition, it was found that these animals communicate through body language and face, but scientists still conduct research in this field in order to unveil the mysteries behind this type of communication.
Snub-nosed monkeys :
These monkeys originate in Asia, and the new species in this genus is Rhinopithecus strykeri, which in local dialect is called "mey nwoah", meaning "monkey face pointing toward the sky." When it rains, residents easily identify monkeys because they stand head between his knees, to not get rain drops in the nose. If not disdain, rain enter in their nose and makes them sneeze.
Those monkeys live in large groups of up to 600 members, and lead lives in trees. As for communication, they use specific sound signals they produce either individually or in unison.