
INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING
I am collating my study notes as part of my education into Computer Programming. In an attempt to increase and improve my own learning, and to help others also (learn by teaching) I will be sharing my notes, as neatly presented as possible, for others to follow along with if they so wish. This is Lesson 6's notes.
EARLIER LESSONS
Lesson 1 Notes
Lesson 2 Notes
Lesson 3 Notes
Lesson 4 Notes
Lesson 5 Notes

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER PROGRAMMING – STUDY NOTES
LESSON 6
SWITCH STATEMENT
Switch statement = a selection statement whereby a certain expression or a variable is checked against a number of possibilities.
The switch statement does not exist in the Python language.
switch (expression)
{
case constant1:
Statements;
break;
case constant2:
Statements;
break;
case constant3:
Statements;
break;
default:
Default-Statements;
}
The switch statement example will first check case constant1. If that is true then that statement gets run. Then the break statement is applied and it jumps out of the switch at that point. If case constant1 is false then it moves on to case constant2 and checks that one. And so on until it runs through hall options, either finding a statement that is true, or reaching the default statement. If it reaches the default then it runs that one.
If there is no break statement then all of them will get run.
LINK: Switch Statement
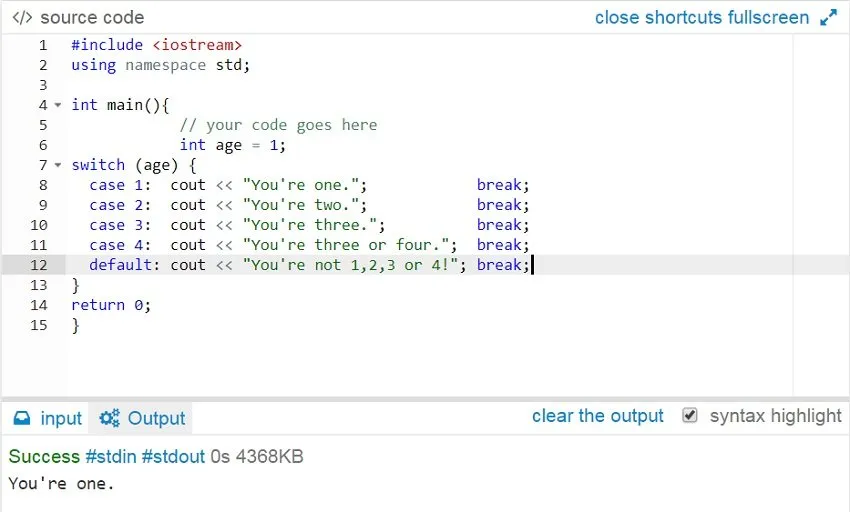
In the code example above, the switch statement looks for the correct answer. The variable age has already been set at 1, but in a real life example it would most like be input by the user. The switch rotates through each case constant until it finds the one that is true, and then runs the statement for that.
COMMENTS
Comments are lines in the code marked by // in C++ or something similar in the other programming languages. Comments do not affect code functionality (unless erroneously place into a non-comment line of code). They act as documentation in the source code.
RECAP OF EARLIER LESSONS
In Lesson 1 we briefly looked at:
- What is a programming language?
- Language Types – especially HIGH Level and LOW Level.
- Compiled vs Interpreted Languages
- Data Types: Strongly Typed vs Weakly Typed Languages.
- Data Types: The most common data types (characters, integers, floating-point, fixed-point, boolean, reference).
In Lesson 2 we looked briefly looked at:
- Variables
- Constants
These both flow on from Data Types and work with these.
In Lesson 3 we looked briefly at:
- Operators
Used to allow operations (such as multiplication) to be performed on variables or constants.
In Lesson 4 we looked briefly at:
- Conditional Statements
If, If-Else, If-Then Statements, which are used to control the flow of a program.
In Lesson 5 we looked briefly at:
- Loops
While, Do-While, and For loops.
- Break Statement.
- Continue Statement.

FURTHER DATA
cpp.sh - C++ shell website
Scratchpad - Shift + F4 on Firefox - Javascript shell
Dev C++ - A free, portable, fast and simple C/C++ IDE
Code::Blocks - A free C, C++ and Fortran IDE
Ideone - an online compiler and debugging tool which allows youto compile source code and execute it online in more than 60 programming languages.
My Posts
Introduction From a Newbie Programmer and Intro - part 2
Introduction to Computer Programming - part 1 (Lesson 1)
Introduction to Computer Programming - part 2 (Lesson 2)
Introduction to Computer Programming - part 3 (Lesson 3)
Introduction to Computer Programming - part 4 (Lesson 4)
Images from unsplash.com, except code screenshots, which are my own.
I welcome new followers, and thank you for your upvotes and comments.