
The practice of guaranteeing information and managing risks associated with its use, processing, storage, and transmission is known as information assurance. The integrity, availability, authenticity, non-repudiation, and confidentiality of user data are all aspects of information assurance.
Components Information Security Assurance?
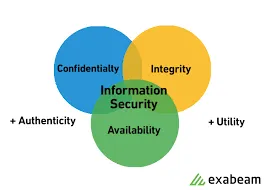
1.Confidentiality
Keeping sensitive data private using safeguards like data encryption is an extremely important function of IA professionals. Confidentiality involves protecting private information from disclosure to any unauthorized users, systems, or other entities. Confidentiality must be considered in terms of the data, not just in terms of access or permissions. Only those who are authorized can access the data, the devices or the processes that contain the data. Prioritizing information confidentiality helps companies defend themselves from having their ideas stolen while protecting their customers from the exploitation of their personal information.
2. Availability
Availability means that users can access the data stored in their networks or use services that are featured within those networks. Without easy data access, the system’s users are limited in their ability to access important information or perform critical tasks. Threats to availability are becoming more complex because more of the world’s information is online and vulnerable to hackers. For instance, if a cybercriminal renders an automated car’s operation system inoperable, the car could cause an accident. Businesses have the same risk. If a company’s leaders can’t access important data when making business decisions, the company could lose revenue as a result. IA professionals must know how to avoid threats that could block data availability using tools like firewalls and implement other, more complex security measures.
3.Integrity
Upholding an information system’s integrity involves keeping its network intact and uncompromised; thus, the primary goal of this pillar is to set up safeguards that deter threats. For example, viruses and malicious code are the most common threats to a system’s integrity. To prevent viruses from deleting or damaging files, IA professionals use antivirus software and other tools to stop them before they enter the computer system. They also develop policies to keep users in their organizations from mishandling data and run penetration testing to simulate system attacks. These tests ensure that their networks are strong; if the IA professionals detect weaknesses, they work to repair and secure the system and protect the integrity of the data therein. Having the right IA rules and practices in place helps keep organizations’ information and systems secure.
Differentiate the certification programs to Common body language?

Differentiate the Governance and Risk management?

The whole set of rules, policies, and standards that guide a firm is known as governance, or corporate governance. Risk management, often known as enterprise risk management, is the process of recognizing potential company risks and taking steps to mitigate or eliminate their financial impact.
Different between Security Architecture to Design?
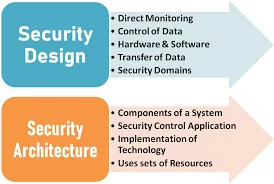
A security system's security architecture is the set of resources and components that enable it to function. The approaches and procedures that place those hardware and software parts to promote security are referred to as security design. Handshakes and authentication are examples of network security design elements.
Different between Business Continuity Planning to D-i-s-a-s-t-e-r Recovery Planning?
Disaster recovery focuses on recovering data access and IT infrastructure after a disaster, whereas business continuity focuses on keeping businesses running during a disaster. Meanwhile, a disaster recovery strategy ensures that an organization may resume normal operations following a crisis.
What is Physical Security Control?

Physical control refers to the application of security measures inside a defined structure to dissuade or prohibit unwanted access to sensitive information. Closed-circuit surveillance cameras are one example of physical controls. Alarm systems based on motion or temperature. Security personnel.
** What is Operations Security?**

Operational security (OPSEC) is a security and risk management procedure that guards against sensitive data falling into the wrong hands. OPSEC is a strategy and a method that encourages IT and security professionals to look at their operations and systems through the eyes of a possible attacker.
What is Law?

The law is legislation that regulates behavior and is developed and implemented by social or political institutions, with its precise meaning a source of long-standing disagreement. It's been called a science and an art, among other things.
What is Investigation?

Criminal investigation is an applied science that entails the examination of evidence in order to inform criminal proceedings. Searching, interviews, interrogations, evidence collecting and preservation, and numerous kinds of investigation can all be part of a thorough criminal investigation.
What is Ethics?

The area of philosophy known as ethics, or moral philosophy, "involves systematizing, defending, and endorsing conceptions of good and bad action." Ethics, like aesthetics, is concerned with considerations of worth; together, these fields make up the area of philosophy known as axiology.
What is Information Security?

The technique of securing information through limiting information risks is known as information security, or InfoSec. It falls within the category of information risk management.