E' un insieme organizzato di informazioni che aggiornato costantemente e gestito da un computer.
Queste informazioni hanno le seguenti proprietà fondamentali:
•Connesse logicamente(argomento comune)
•Formato specifico(tracciato record)
•Memorizzate su uno specifico supporto consultabile nel tempo
•Facilmente consultabili
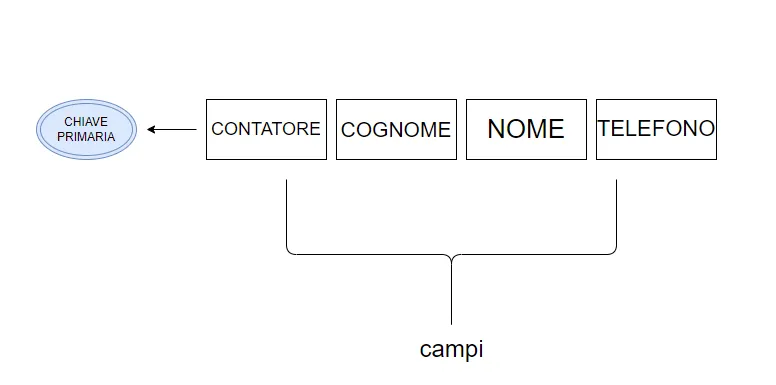
Le informazioni in un archivio sono organizzate secondo uno specifico tracciato record
Il tracciato record è l'insieme dei campi(singole informazioni) che identificano un record di un archivio
Un file è una collezione di record, ossia informazioni logicamente omogenee che descrivono i singoli elementi di un archivio
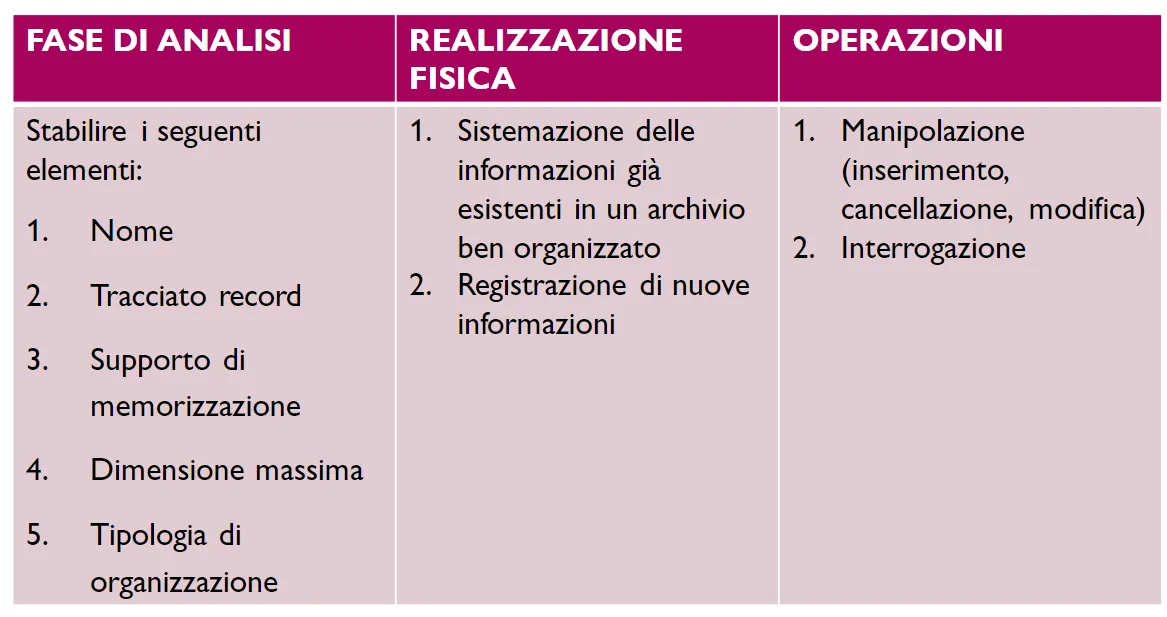
Per la creazione di un archivio abbiamo 3 fasi, nella prima fase chiamata analisi inseriamo tutte le informazioni, quindi il nome, il tracciato record e la dimensione.
Nella seconda fase chiamata realizzazione fisica inseriamo tutte le nostra informazioni all'interno di un archivio fisico e nell'ultima eseguiamo tutte le operazioni, quindi inserimento, modifica ecc...
L'aumento dei dati da gestire ha segnato il passaggio da archivi basati su supporti cartacei ad archivi basati su memorie di massa .Le memorie di massa hanno i seguenti parametri:
•Tipo di accesso
•Capacità
•Tempo medio di accesso
•Velocità di trasferimento
I dati vengono memorizzati in formato binario ed hanno dei bit chiamati bit di parità che servono per controllare eventuali errori.
Il componente del Sistema Operativo che gestisce i file è detto File System
In un file con organizzazione ad indici, la ricerca di un record avviene con una ricerca binaria (accesso a chiave)...vediamo un esempio.
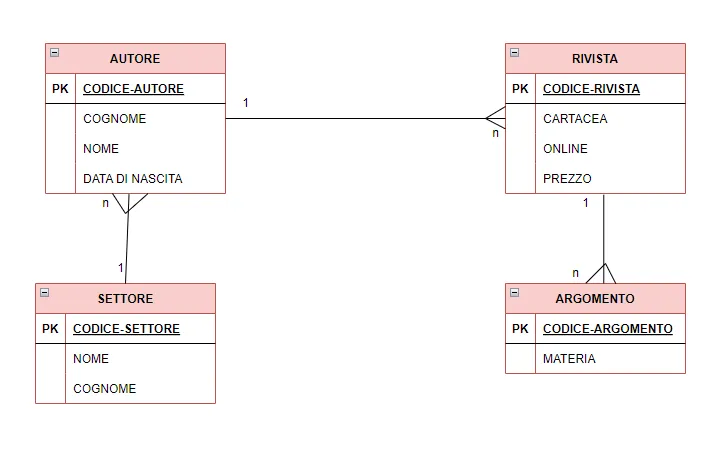
Sono degli Archivi di dati organizzati in modo integrato e Progettati con tecniche specifiche, vengono Gestiti tramite specifici software e cosa molto importante superano i limiti degli archivi tradizionali, Da come si può capire, il termine base di dati si ha poiché tratta argomenti del mondo reale.
Tra le caratteristiche più importanti abbiamo:
Efficienza e produttività: ovvero cercare in modo facile e veloce dati con diversi criteri
•Misure di sicurezza: si ha più sicurezza gli accessi
•Integrità e consistenza: garantire una modifica dei dati in tempo reale
Il DBMS è un software per la gestione dei database, svolge varie operazioni come la creazione, l'inserimento e modifica...L'utente non si preoccupa dell'organizzazione fisica e a differenza degli archivi è presente un amministratore.
Utilizza 3 linguaggi principalmente:
-DDL: serve per la creazione e definizione di una base di dati.
-DML: serve per la manipolazione dei dati
-QL: serve per l'estrazione delle informazioni
Il dbms ha vari vantaggi...per primo viene eliminata la ridondanza, si ha una maggiore facilità all'acceso ai dati, integrità dei dati, sicurezza dei dati, e come più importante maggiore concorrenza.
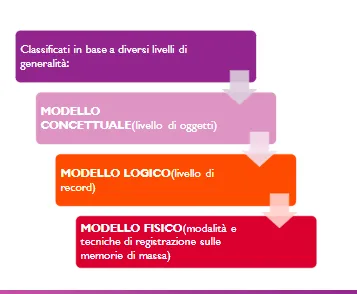
Il modello concettuale è basato su Entità/Associazioni(E/R) ed è formato da 3 Elementi:
•Entità
•Attributi
•Associazioni
Il modello logico deriva dal modello concettuale e applica una serie di regole, abbiamo 3 Tipologie:
•Gerarchico
•Reticolare
•Relazionale
Mentre il modello fisico ci descrive come viene rappresentato un database, attraverso vari linguaggi, come sql.

Gli utente come potrete intuire sono coloro che usufluiscono dei database, abbiamo 3 tipi di utenti:
•AMMINISTATORI sono coloro che gestiscono i database,quindi controllano gli accessi e aggiornano i database,dopo di che abbiamo gli UTENTI FINALI che accedono ai dati mediante linguaggio di interrogazione (QL)

It is an organized set of information that is constantly updated and managed by a computer.
This information has the following basic properties:
•Logically connected(common topic)
•Specific format(record layout)
• Stored on a specific medium that can be consulted over time
•Easily consultable
The information in an archive is organized according to a specific record layout
The record layout is the set of fields (individual information) that identify a record in an archive
A file is a collection of records, i.e. logically homogeneous information describing the individual elements of an archive

For the creation of an archive we have 3 phases, in the first phase called analysis we enter all the information, then the name, the record layout and the size.
In the second phase called physical implementation we insert all our information in a physical archive and in the last one we carry out all the operations, therefore insertion, modification, etc...
The increase in data to manage has marked the transition from paper-based archives to archives based on mass memories. Mass memories have the following parameters:
• Type of access
•Capacity
•Average access time
•Transfer speed
The data is stored in binary format and has bits called parity bits which are used to check for errors.
The component of the operating system that manages files is called the file system
In a file with index organization, the search for a record takes place with a binary search (key access)... let's see an example.

They are data archives organized in an integrated way and designed with specific techniques, they are managed using specific software and, very importantly, they exceed the limits of traditional archives. As you can understand, the term database is used because it deals with real world topics.
Among the most important features we have:
Efficiency and productivity: that is, searching for data with different criteria quickly and easily
• Security measures: access is more secure
•Integrity and Consistency: Ensure real-time data change
The DBMS is a database management software, it performs various operations such as creation, insertion and modification ... The user does not care about the physical organization and unlike archives there is an administrator.
It uses 3 languages mainly:
-DDL: it is used for the creation and definition of a database.
-DML: It is used for data manipulation
-QL: it is used for the extraction of information
The dbms has various advantages... first redundancy is eliminated, there is greater ease of access to data, data integrity, data security, and most importantly greater concurrency.

The conceptual model is based on Entities/Associations (E/R) and consists of 3 Elements:
•Entity
•Attributes
•Associations
The logical model derives from the conceptual model and applies a series of rules, we have 3 Types:
•Hierarchical
•Reticular
•Relational
While the physical model describes how a database is represented, through various languages, such as sql.

As you can guess, users are those who use the databases, we have 3 types of users:
• ADMINISTRATORS are those who manage the databases, therefore they control accesses and update the databases, after which we have the END USERS who access the data via query language (QL)