
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

05-08-2025 - Operations Research - Branch-and-Bound Algorithm [EN]-[IT]
With this post, I'd like to provide a brief introduction to the topic mentioned above.
(code notes: X_77)
Branch-and-Bound Algorithm

Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Introduction
Let's start by saying that this ingenious yet complex algorithm was created by two women...
Now let's get started.
In operations research, we have a branch of programming called linear programming, which in turn has a unique aspect when it can be classified as integer linear programming. I discussed it a few posts ago. The Branch and Bound algorithm is an optimization technique used to solve integer programming problems.
How the Branch and Bound Algorithm Works
The algorithm works by systematically exploring all possible solutions (branches), but avoiding fully exploring those that cannot lead to better solutions (pruning, or bounding).
How the Branch and Bound Algorithm Works
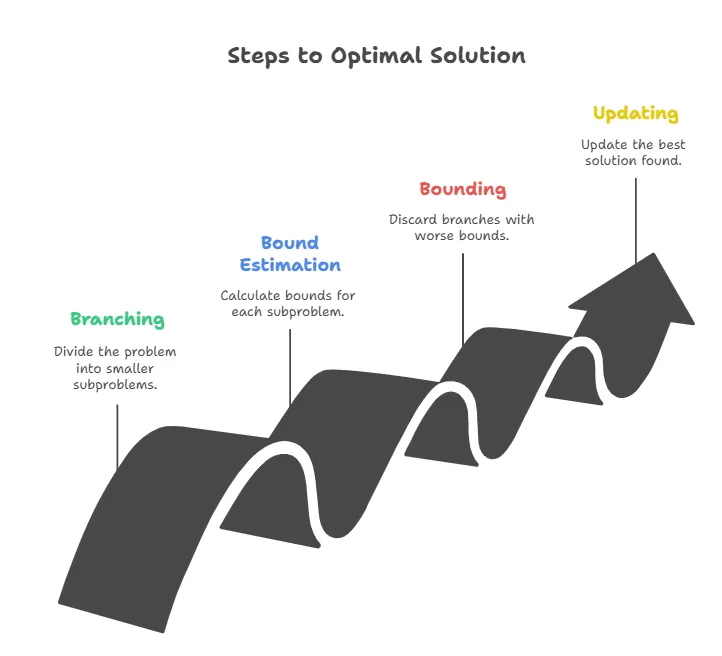
Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Napkin.ai
This algorithm is developed in 4 phases:
-Branching: the problem is divided into smaller subproblems.
-Bound Estimation: for each subproblem, an upper or lower bound is calculated for the optimal possible solution in that portion of the solution space.
-Bounding: If the bound calculated on a branch is worse than the best solution found so far, that branch is discarded. This avoids wasting time on operations to perform on solutions.
-Update: Each time a new, better feasible solution is found, the value of the last optimal solution found is updated.
The Branch and Bound Algorithm Explained Technically
Branch and bound is a technique for finding feasible solutions
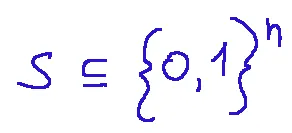
and cost vector

This method partially explores the set S; this type of exploration is Also called implicit exploration, it evaluates the objective function on a subset of S.
The strength of this algorithm is that it excludes subsets of solutions from the enumeration that can easily be demonstrated to be non-optimal.
In the branch-and-bound method, it happens that...
-1-
When the approximate solution of the current subproblem has integer components, the upper bound is updated if the value of the solution is less than the previous one.
-2-
When the value of the approximate solution of the current subproblem is greater than the upper bound, the problem is eliminated from the list of open subproblems.
-3-
The possible solution strategies of the branch-and-bound method solve the current subproblem exactly.
-4-
The current subproblem is decomposed when the value of the approximate solution of the subproblem is less than the upper bound and the solution does not have integer components.
-5-
The algorithm stops when the list of open subproblems is empty.
-6-
The possible selection strategies of the branch-and-bound method determine how to manage the list of open subproblems.
-7-
The possible separation strategies of the branch-and-bound method determine how to partition the set of feasible solutions into two or more subsets.
-8-
The main elements of the branch-and-bound method are exact solutions of the recursively generated subproblems.
Conclusions
The branch-and-bound method is an exact solution method for LP01 problems.
This method implicitly (partially) explores the set of feasible solutions to a LP01 problem and evaluates the objective function on limited subsets of feasible solutions.
Question
Did you know that in 1960, a famous article was published by the London School of Economics, titled "An Automatic Method of Solving Discrete Programming Problems," which introduced the branch-and-bound method for the first time? The article was written by Ailsa H. Land (British mathematician) and Alison (G.) Doig (Australian researcher).

ITALIAN

05-08-2025 - Ricerca operativa - Algoritmo branch and bound [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_77)
Algoritmo branch and bound

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Introduzione
Diciamo subito che questo algoritmo geniale quanto complesso fu ideato da due donne...
ora partiamo.
In ricerca operativa abbiamo un ramo di programmazione definito programmazione lineare, che a sua volta ha un'aspetto particolare quando si può classificare come programmazione lineare intera. Ne avevo parlato qualche post fa. Ecco, l'algoritmo Branch and Bound è una tecnica di ottimizzazione usata per risolvere problemi di programmazione intera.
Come funziona l'algoritmo branch and bound
L’algoritmo funziona esplorando sistematicamente tutte le soluzioni possibili (rami), ma evitando di esplorare completamente quelle che non possono portare a soluzioni migliori (potatura, o bounding).
Funzionamento dell'algoritmo branch and bound

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Napkin.ai
Questo algoritmo si sviluppa in 4 fasi:
-Suddivisione (Branching), il problema viene suddiviso in sotto problemi più piccoli.
-Stima dei limiti, per ogni sotto problema si calcola un limite superiore o inferiore della soluzione ottima possibile in quella porzione dello spazio delle soluzioni
-Potatura (Bounding): se il limite calcolato in un ramo è peggiore della miglior soluzione trovata finora, quel ramo viene scartato. Questo evita di perdere tempo su operazioni da effettuare su soluzioni.
-Aggiornamento, ogni volta che si trova una nuova soluzione ammissibile migliore si aggiorna il valore dell'ultima soluzione ottima trovata.
L'algoritmo branch and bound spiegato in maniera tecnica
Il branch and bound è una tecnica per trovare soluzioni ammissibili
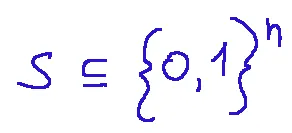
e vettore dei costi

Questo metodo esplora in maniera parziale l'insieme S, questa tipologia di esplorazione viene chiamata anche esplorazione implicita, e valuta la funzione obiettivo su un sottoinsieme di S
Il punto di forza di questo algoritmo è che esclude dall'enumerazione sottoinsiemi di soluzioni di cui si può facilmente dimostrare la non ottimalità.
Nel metodo branch and bound avviene che...
-1-
Quando la soluzione approssimata del sottoproblema corrente è a componenti intere, l'upper bound viene aggiornato se il valore della soluzione è minore del precedente
-2-
Quando il valore della soluzione approssimata del sottoproblema corrente è superiore all'upper bound il problema viene eliminato dalla lista dei sottoproblemi aperti
-3-
Le possibili strategie di soluzione del metodo branch and bound risolvono in maniera esatta il sottoproblema corrente
-4-
Il sottoproblema corrente viene decomposto quando il valore della soluzione approssimata del sottoproblema è minore dell'upper bound e la soluzione non è a componenti
intere.
-5-
L'algoritmo si arresta quando la lista dei sottoproblemi aperti è vuota
-6-
Le possibili strategie di selezione del metodo branch and bound determinano come gestire la lista dei sottoproblemi aperti.
-7-
Le possibili strategie di separazione del metodo branch and bound determina come partizionare l'insieme delle soluzioni ammissibili in due o più sottoinsiemi
-8-
Gli elementi principali del metodo branch and bound sono soluzione esatta dei sottoproblemi generati ricorsivamente
Conclusioni
Il metodo branch and bound è un metodo esatto di soluzione per problemi di PL01.
Questo metodo esplora in maniera implicita (parziale) l'insieme delle soluzioni ammissibili di un problema di PL01 e valuta la funzione obiettivo su sottoinsiemi limitati di soluzioni ammissibili.
Domanda
Lo sapevate che nel 1960 uscì un articolo, diventato poi famoso, della London School of Economics intitolato "An Automatic Method of Solving Discrete Programming Problems" in cui si parlò per la prima volta del metodo branch and bound? L'articolo fu scritto da Ailsa H. Land (matematica britannica) e Alison (G.) Doig (ricercatrice australiana)
THE END