ENGLISH VERSION
Source
Since the irruption of Ethereum in the blockchain world, several projects have appeared that start from or are inspired by EVM as an essential part of their proposal, one of the ways that seems to me the most practical and simple to identify this type of networks, is to verify their use in wallets that we normally use for the Ethereum network, for example, the Metamask. The reason this is so is that the dapp wallet is using the same Virtual Machine environment, which makes it compatible with all those that have it as part of their architecture.
One of the main reasons for working on this basis is to facilitate integration and adoption by a large community, both developers and users in general, who already use the ethereum network, which although it was the first to demonstrate the potential of a programmable blockchain, now has a lot of competition, one of such magnitude that some are said to be the new ethereum or, more commonly, the ethereum killer.
Within this group is fantom which despite being more than two years old since it was launched, it was only a couple of years ago that it began to be noticed more strongly, with a rise from $0.15 to $3.48 in just over two months, between July and September 2021. Even in the current market period it has been one of the cryptocurrencies that has not only made gains since the beginning of the year, but has held up relatively better in price than the others. So, without further ado we are going to share a little bit about it in this post.
What is Fantom?
As we referenced above, Fantom has been working on its proposal for a few years now, in fact its whitepaper dates back to August 2018 and the official launch of the mainnet in late 2019. If there is one thing that we can very clearly state about this blockhain, it is its work from the academic and experience bases in the cryptographic sector.
Thus, it is associated with Yonsei University in Seoul and University of Sydney in Australia. Similarly, its CEO was Dr. Ahn Byung, a computer engineer who, although he later left the project, left behind a committed team, including Andre Cronje, founder of Yearn.Finance, therefore an important figure in the DeFi world. All these things significantly drive the researchń and ddevelopment of the underlying technology in Fantom which as we have noted from the title of this post is very particular, in fact it is presented as the next generation of blockchain-based solutions.
Before considering these technologies, which are behind the functioning of the network, let's consider the tokenomics of its main native token, $FTM, which consists of a supply of 3.175 trillion, of which 2.791 trillion are already in circulation, may seem a lot, more if we consider that it has an initial inflation rate of 5%. However, let's not be scared off by the numbers, because the token has several use cases, in addition to the projects they propose to build, which largely revolve around DeFi, where a good and sufficient circulation of money is merited. It is the game between the suply and demand of assets that Fantom is betting on winning.
Therefore, among the use cases of the token we can mention the payments of the transactions made on the network, the participation and construction in the government through its DAO and the staking of the cryptocurrency, with which we already started to touch the topic of its functioning.

Source
How does it work?
Let's start by mentioning, following the narrative of the previous point, that the consensus protocol for block validation that Fantom uses is the PoS, so each node validator needs to stak a minimum of 1M $FTM tokens to be eligible as block producer, which obviously generates a reward, in which we all have the opportunity to participate as well, since, we have the option to stak the token and delegate them to a validator node for it.
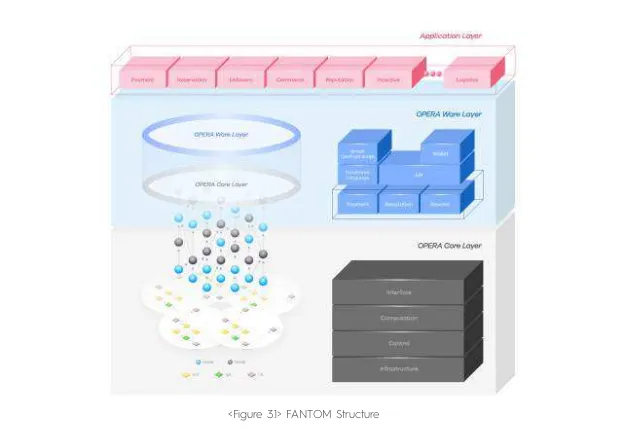
At first glance it seems that nothing changes, that there is nothing new in the approach, but if we get closer, even a little, we begin to realize that it is quite the opposite. In fact, Fantom's proposal is based on its Opera Chain, which is composed of several layers and makes possible both compatability with the EVM, facilitating the interoperability of several blockchains, and a stupendous speed and scalability of transactions.
To do this the participating nodes of the network are governed by the Lachesis Protocol which is a technology that applies the resilience algorithm to the Byzantine Generals Problem, but in an asynchronous way (that is why its abbreviation is ABFT), i.e., another way to solve the Satoshi Nakamoto dilemma and PoS limitations . Moreover, this protocol also allows block validation between 1 and 2 seconds. For all this, it is totally valid that it is presented as the new generation of blockchain solutions.
If we want to go a little more in depth about how Fantom works, we have to consider that the way to keep track of the blocks is not following the structure of traditional blockchains, since it works with what it calls "block events", which is nothing more than a set of transactions backed up in the form of DAG, which allows nodes to process transactions at various times and confirm them very quickly, since the completion time per transaction is 1 second. To get an idea of this let's think about the [Hive OBI] rule (/@@leoglossary/leoglossary-one-block-irreversibility-hive "one block irreversibility hive"), which makes each block irreversible for about 3 seconds, so in the end we can be talking about two blockchains with similar speed and speed of completion.
Source
Features to highlight
Fantom is positioned, along with Solana, as a very good competitor to ethereum, especially because being compatible with EVM, in a way it improves it, with the particular technologies it uses. It solves the blockchain trilemma, providing the network with scalability, security and decentralization at the same time. Thanks to its proposals it is a network not only fast but with very cheap transactions, for example a payment made here can cost us in fee around $.0000001.
For this reason, in its ecosystem we can find a large number of dapps, benefiting in a special way the DeFI projects, as can be seen in its web page. But in addition to this, the network already natively provides its users with several services under the Fantom Defi label. We can, as mentioned above, do token staking, with an APR rate of around 12% and a minimum blocking period of 14 days.
Other services that we can find are to put as collateral our FTM tokens that we have in staking to request a loan, mint synthetic assets using FTM tokens as collateral, so for example we can block the amount of tokens required to obtain a stablecoin, so if it is the dollar we would have the $FUSD. Finally, the use of its DEX, which is distinguished by being multi-chain, that is, it facilitates us to exchange tokens between EVM-based blockchains.
In its mission to make the use of blockchain technology closer, Fantom has approached to work with universities, as well as with governments, offering them the ideal platform for the improvement of many of their infrastructures, as well as a suitable environment for the construction of their CBDCs.
Source
Conclusions
Its characteristics make it an attractive network for a large adoption of businesses, companies and developers, who seek to be able to process large volumes of transactions, and not only this because the cost of their transactions is also extremely economical. At the same time, it saves its compatibility with Ethereum through the use of its virtual machine, which at the same time facilitates interoperability, which is one of the aspects where we are heading in all this development of blockchain technology.
Personally, I think it is a proposition that moves between two major contenders, which can be a disadvantage, and they are Ethereum and Solana. However, its strength and/or advantage lies in what distinguishes it from both. For, in the case of the former, it does not remain only in its compatability with EVM but goes beyond, and with respect to the latter, although it achieves its same goal, it does so using a different methodology, where the use of DAGs is fundamental. In the words of a Fantom lover we could say that Solana still works in the first generation blockchain (synchronous set of blocks), while Fantom does it in another way (asynchronous set of transactions), that is why it calls itself "Opera Chain".
Among the limits or disadvantages of the project we can consider its token inflation. Well, the truth is that it does not yet burn enough, its use is to pay fees that are super cheap, as we have already seen, staking and participate in governance, where to make proposals you have to pay 100 FTM and votes are counted according to the coins we own.
Another limitation is its technology, because, although great I consider that it is still difficult for us to understand what they call the first generation blockchain, to digest these new concepts and applications. The positive thing is that there is no total rupture, for example, its compatibility with EVM is an example of this.

Source

VERSIÓN EN ESPAÑOL
 Source
SourceDesde la irrupción de Ethereum en el mundo de la blockchain, han aparecido diversos proyectos que parten o se inspiran de la EVM como parte esencial de su propuesta, una de las maneras que me parece más práctica y sencilla para identificar este tipo de redes, es verificar su uso en las wallets que normalmente usamos para la red de Ethereum, por ejemplo, la Metamask. La razón de que esto sea así es que la dapp wallet está usando un mismo entorno de Máquina Virtual, que lo hace compatible con todos los que la tengan como parte de su arquitectura.
Uno de los motivos principales de trabajar sobre esta base es facilitar la integración y adopción por parte de una gran comunidad, tanto de desarrolladores como de usuarios en general, que ya usan la red de ethereum, que si bien fue la primera en demostrar las potencialidades de una blockchain programable, ahora cuenta con mucha competencia, una de tal magnitud que de algunas se dice son la nueva ethereum o, más comúnmente, la ethereum killer.
Dentro de este grupo está fantom que a pesar de tener más de dos años que se lanzó, fue hace un par de años que se empezó a notar con más fuerza, con un alza de 0.15$ a 3.48$ en poco más de dos meses, entre Julio y septiembre del 2021. Incluso en el perido actual del mercado ha sido una de las criptomonedas que no solo ha tenido ganancias desde inicios del año, sino que se ha mantenido relativamente mejor en su precio que las demás. Por eso, sin más preámbulos vamos a compartir en este post un poco sobre ella.
¿Qué es Fantom?
Como hicimos referencia arriba, Fantom lleva unos cuantos años trabajando en su propuesta, de hecho su whitepaper data de agosto del 2018 y el lanzamiento oficial de la mainnet a finales del 2019. Si hay algo que muy claramente podemos afirmar de esta blockhain es su trabajo desde las bases académicas y de la experiencia en el sector criptográfico.
Así tenemos que está asociada con la Universidad de Yonsei en Seúl y la Universidad de Sidney en Australia. De igual menra, su CEO fue el Dr. Ahn Byung, ingeniro en computación que aunque luego se apartó del proyecto dejó un equipo comprometido con el mismo, entre los que se encuentra Andre Cronje, fundador de Yearn.Finance, por lo tanto, un personaje importante dentro del mundo DeFi. Todas estas cosas impulsan de manera significativa la investigaciń y dsarrollo de la tecnología subyacente en Fantom que como hemos hecho notar desde el título de este post es muy particular, de hecho se presenta como la nueva generación de soluciones basadas en blockchain.
Antes de considerar estas tecnologías, que están detrás del funcionamiento de la red, consideremos el tokenomics de su principal token nativo, $FTM, el cual consta de un supply de 3.175 billones, de lo cuáles ya están en circulación 2.791 billones, puede parecer mucho, más si consideramos que tiene una tasa de inflación inicial de 5%. No obstante, no nos dejemos espantar por los números, porque el token tiene varios casos de uso, además de los proyectos que proponen para construir, los cuáles giran en gran parte en torno a DeFi, donde se amerita que haya una buena y suficiente circulación de dinero. Es el juego entre el suply y la demanda de los activos que Fantom apuesta a ganar.
Por eso, entre los casos de uso del token podemos mencionar los pagos de las transacciones que se hacen en la red, la participación y construcción en el gobierno a través de su DAO y el staking de la criptomoneda, con lo cual ya empezamos a tocar el tema de su funcionamiento.
 Source
Source¿Cómo funciona?
Empecemos por mencionar, siguiendo la narrativa del punto anterior, que el protocolo de consenso para la validacón de los bloques que Fantom utiliza es el PoS, pues, cada nodo validador necesita poner en staking un mínimo de 1M de $FTM tokens para ser elegible como productor de bloque, lo cual genera obviamente una recompensa, en la cual todos tenemos la oportunidad de participar también, pues, tenemos la opción de realizar staking del token y delegarlos a un nodo validador para ello.
En un primer acercamiento parece que nada cambia, que no hay novedad en el planteamiento, pero si nos acercamos más, aunque sea un poco, nos empezamos a dar cuenta que es todo lo contrario. En efecto, la propuesta de Fantom se basa en su Opera Chain, que compuesta por varias capas hace posible tanto la compatabilidad con la EVM, facilitando la interoperabilidad de varias blockchains, como una estupenda velocidad y escalabilidad de las transacciones.
Para hacer esto los nodos participantes de la red se rigen por el Protocolo Lachesis que es una tecnología que aplica el algorítmo de resistencia al problema de los generales bizantinos, pero de manera asíncrona (por eso, su abreciación es ABFT), es decir, otra manera de resolver el dilema de Satoshi Nakamoto y las limitaciones de la PoS . Por otra parte, este protocolo también permite la validación de bloques entre 1 y 2 segundos. Por todo esto, es totalmente válido que se presente como la nueva generación de las soluciones blockchain.
Si queremos ir un poco más en profundidad sobre el funcionamiento de Fantom tenemos que considerar que la menera de llevar el registro de los bloques no es siguiendo la estructura de las blockchains tradicionales pues trabaja con lo que llama "eventos de los bloques" que no es más que un conjunto de transacciones respaldadas en forma de DAG, lo cual permite permite que los nodos procesen transacciones en diversos momentos y la confirmen muy rápidamente, pues, el tiempo de finalización por transación es de 1 segundo. Para tener una idea de esto pensemos en la regla del OBI de Hive, que hace que cada bloque sea irreversible alrededor de 3 segundos, por lo que al final podemos estar hablando de dos blockchains con velocidad y rapidez de finalización semejantes.
 Source
SourceCaracterísticas a resaltar
Fantom se posiciona, junto con Solana, como un muy buen competidor para ethereum, sobre todo porque siendo compatible con la EVM, en cierta forma la mejora, con las particulares tecnologías que utiliza. Resuelve el trilema blockchain, proveyendo a la red de escalabilidad, seguridad y descentralización al mismo tiempo. Gracias a sus propuestas es una red no sólo rápida sino con unas transacciones muy baratas, por ejemplo una pago hecho por aquí puede costarnos en fee alrededor de $.0000001.
Por esta razón, en su ecosistema podemos encontrarnos con un gran númerode dapps, beneficiándose de manera especial los proyectos DeFI, tal como se puede apreciar en su página web. Pero además de esto, de manera nativa ya la red provee a sus usuarios de varios servicios bajo la etiqueta de Fantom Defi. Podemos, como ya hemos mencionado arriba, hace staking del token, con una tasa de APR alrededor del 12% y un mínimo de bloqueo de 14 días.
Otros de los servicios que podemos encontrarnos son poner como garantía nuestros tokens FTM que tengamos en staking para solicitar un prestamo, mintear activos sintéticos usando los tokens FTM como colateral, así por ejemplo podemos bloquear la cantidad de tokens que se requieran para obtener una stablecoin, así si es el dólar tentríamos al $FUSD. Finalmente, el uso de su DEX, que se distingue por ser multi-cadena, es decir, nos facilita intercambiar tokens entre blockchains basadas en EVM.
En su misión de hacer cercana el uso de la tecnología blockchain, Fantom así como se ha acercado a trabajar con universidades, también lo ha hecho con gobiernos, ofreciéndoles la plataforma ideal para el mejoramiento de muchas de sus infraestructuras, así como un entorno adecuado para la construcción de sus CBDCs.
 Source
SourceConclusiones
Sus características le convierten en una red atractiva para una gran adopción de negocios, empresas y desarrolladores, que buscan poder procesar grandes volumenes de transacciones,y no sólo esto porque el costo de sus transacciones es también sumamente económico. Al mismo tiempo, guarda su compatiblidad con Ethereum mediante el uso de su máquina virtual, lo cual facilita al mismo tiempo la interoperabilidad, que es uno de los aspectos hacia donde nos dirigimos en todo este desarrollo de la tecnología blockchain.
Personalmente, creo que es un propuesta que se mueve entre dos grandes contendientes, lo cual puede ser una desventaja, y son Ethereum y Solana. No obstante, su fortaleza y/o ventaja está en lo que le distingue de ambas. Pues, en el caso de la primera, no se queda sólo en su compatabilidad con la EVM sino que vá más allá, y respecto a la segunda, aunque alcanza su mismo objetivo, lo hace usando una metodologia diferente, donde el uso de los DAG es fundamental. En palabras de un Fantom lover podríamos decir que Solana todavía trabaja en la blockchain de primera generación (conjunto sincrono de bloques), en cambio Fantom lo hace de otra manera (conjunto "asíncrono" de transacciones), por eso, se autodenomina "Opera Chain".
Entre los límites o desventajas del proyecto podemso considerar su inflacion de tokens. Pues, la verdad es que no quema aún lo suficiente, su uso es para pagar tarifas que son súper económicas, como ya hemos visto, hacer staking y participar en la gobernanza, donde para realizar propuestas hay que cancelar 100 FTM y los votos se contabilizan según las monedas que poseamos.
Otra limitación es su tecnología, pues, aunque grandiosa considero que todavía nos cuesta comprender lo que ellos denominan la primera generación blockchain, como para pasar a digerir estos nuevos conceptos y aplicaciones. Lo positivo es que no hay ruptura total, por ejemplo, su compatiblidad con la EVM es una muestra de ello.
 Source
Source


