
Knowing programming languages and their types can help to choose a good language. Also, by better understanding the levels of programming languages, we write better codes. In this post, I will review 3 common categories for programming languages. In particular, I'm talking about the levels of languages and we learn programming levels.
Programmers write the instructions of a computer program with the help of programming languages. These statements must finally be executed on the computer hardware. Since hardware only understands 0's and 1's, a comprehensive classification is defined for languages.
Of course, you may see different categories from different perspectives; For example, children's programming language or educational languages. At the beginning of the post, I will give a brief explanation about the two categories of user and field, and then I will talk about the levels of programming languages.
programming languages
Different categories for programming languages can be considered. The three common categories are:
- Classification based on the use of each language
- Classification based on the field of use
- Classification based on programming language level
First, I will mention the first two cases so that you understand their meaning. But since each of these two may require separate reviews, after their brief explanation, I will talk about the third category, the types of programming languages levels.
Types of usage of programming languages
usage means the use and place of use of the codes we write. Some languages may be specific to Windows or Linux applications. Some of them are only for mobile software development and others are only for web development.
Of course, with many and good developments in the field of information technology, there are also programming languages that have multiple applications. For example, with cross-platform programming, you will be able to output your program for different operating systems.
In a general case, the following four uses for programming languages can be considered:
- Desktop programming languages are used to develop software under computer operating systems such as Windows, Linux or Mac.
- Web programming languages are used for web development and implementation of online systems. These types of languages are divided into two categories: user side (front end) and server side (back end).
- Mobile programming languages are used to develop mobile applications.
- Multipurpose languages that may be used for two or all three of the previous uses.
domain-specific and general purpose languages
Another category is in terms of implementation or use of programming languages. Some languages are only used for a specific task. For example, HTML is only used to structure web pages. But we can use some other languages in different ways. For example, Python can be used for data analysis, server side development, etc.
Languages that are created and used only for one purpose are called domain-specific programming languages. Among these languages are languages such as HTML for creating the structure of web pages, SQL for working with relational databases, and VHDL for describing hardware.
Languages that are used to write software in various fields are called general purpose languages. Commonly used languages usually fall into this group; Such as C, PHP, Python and Java.
In general, general-purpose programming languages do not have a specific structure for a specific software field, but domain-specific languages are used for use in a specific field.
Levels of programming languages
If we want to look at the category of programming languages from another point of view, they can be divided into two main levels:
- Low Level Languages
- High Level Languages
Low level programming language
Low-level programming languages are languages that are very close to the machine level. Coding in these languages is done as strings of zeros and ones or codes with low understanding for humans.
Because these languages are implemented close to the hardware, in writing the program algorithm in them, we must also pay attention to the hardware details. For example, how to manage memory, recall information from memory on the processor, and how to work with values in registers (storage houses on the CPU) is up to the programmer.
Features of low-level languages
Because in low-level languages we have to think like machines, programming and understanding the algorithm of a program is more difficult. Also, if we don't need to change the process of memory management and their processing, using low-level languages can create additional difficulty in running programs.
On the other hand, because we talk almost directly with the computer and program the management and processing processes ourselves, the speed of execution of such programs is much higher than the high-level languages that we will learn about later.
In total, three important features of low-level programming languages are:
- Not having the ability to abstract (abstraction) in analyzing and writing the program
- It is close to machine language and it is difficult for humans to understand them.
- In low-level language, we need memory management and direct processor management.
High level programming language
In high-level programming languages, we code with the help of words and signs that are more readable for humans. High-level languages are written similarly to human thinking. Even in some languages that exist at this level, if we read the code sentence by sentence, it is as if we are talking to another human being.
As a rule, these languages are not directly understood by the machine. These codes must be converted into low-level codes and then run on the machine. This work is called code translation.
Features of high-level languages
In most high-level languages, we don't need memory management. We only write the algorithm and logic of the program and we have nothing to do with how to execute the codes. In fact, when we code with a high-level programming language, we are concerned with the implementation of a software, and how it is processed and managed is less important to us.
The simplicity of understanding high-level code is one of the main features of these languages. In many cases where we don't need how to manage memory, high-level languages can speed up our coding. In this case, we can implement our algorithm without paying attention to unnecessary details.
But because the translation process must be done once on these codes and the memory management or processes in that language may not be suitable for the algorithm we wrote, usually the programs written with high-level programming languages are more efficient than low-level languages. They have a lower speed.
Three important features of high-level languages are:
- They have much more abstraction capabilities.
- It is close to human language and is not directly processed by the machine.
- Usually, in high-level language, we do not need memory management and direct processor management.
Types of programming languages in terms of execution level
So far, we have learned that programming languages fall into two main levels, upper and lower. If we want to have a more detailed view of the levels of programming languages, we have three execution levels.
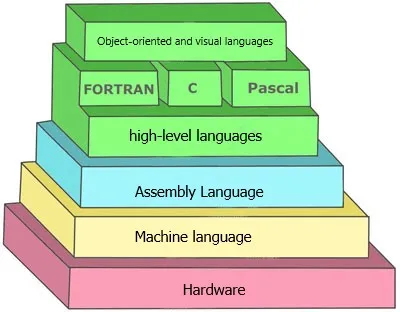
As you can see in the image below, high-level code is converted to assembly language and assembly code is converted to machine code. Finally, the machine codes that are zero and one will be executed on the computer hardware.
Machine code or zero and one language
We said that the computer only understands 0 and 1 or binary code. Machine code is long binary strings that are executed by a computer. These codes are not directly understandable by humans unless you are a binary code expert!
Although machine codes are binary (zero and one), they are usually written in base 16. The following code is a machine code:
10110000 01100001This command is for an x86 processor. The instruction code (10110) means that it should place the next byte value into a register specified after the code. The next three bits (000) specify the register, which in this processor is known as AL. The second 8 bits are the value that should be placed in the register. (Equivalent to 97 in base 2)
We write this binary code in base 16 to improve its readability:
B0 61In this instruction, B0 means to transfer the next number to register AL. 61 is also equivalent to 97 in base 16 representation.
Assembly programming language
Assembly languages are one level above machine language. Of course, it is still known as a low-level language. Assembly language instructions are human-readable, but the execution of the program is difficult to understand.
If we want to write the command we wrote above as machine code in assembly language, we will have the following programming statement:
MOV AL , 61hThe word MOV is the command and the value AL is the name of the processor register. The value 61h also specifies that the number 61 in hexadecimal (hex) should be placed in this register.
As you can see, assembly code is much more readable than machine code. But if we have a program with several thousand lines, it will be difficult to understand and analyze the codes.
The difference between machine code and assembly code is that machine code is directly executed by the CPU and contains only binary values 0 and 1. Each series of processors has its own set of machine code instructions, and all programs (whether assembly or high-level) must be converted to these instructions to run.
High level programming language
High-level languages are very diverse. In these languages, we usually code similar to human conversations; Of course, with a little difference and special symptoms.
For example, in most high-level programming languages, if we want to define a variable with a value of 97, it is enough to write the following command:
x = 97simply! Of course, this definition has functional differences with the assembly code above, which are out of our discussion.
High-level languages are improving day by day. If you look carefully in the image of the order of levels, you will see that the High Level programming languages, marked in green, are themselves divided into different sections.
Several high level languages (High Level)
We have countless high-level languages with different capabilities and applications! Just do a search in your field of interest to find out how many different programming languages exist in your field of interest.
C is considered the mother of many programming languages because many high-level languages are modeled after C. Python, PHP, Java, JavaScript, C#, R, Ruby, Basic (Basic and VB) languages are among the popular and relatively popular high-level languages.