
List in Python is one of the most used data type that we use in almost all our programs. If we can get enough skill in working with Python list, our programming process will be faster. We will also be able to do some extraordinary things! In this post, we will review the List data type in Python, how to work with it, important functions and practical techniques for working with lists.
If you have ever written even a single line of programming, you must have been asked how to store a large amount of data in a program. Suppose we want to enter the grades of a student in our program and perform processing on them.
If we want to consider a variable for each lesson of this student, the program will be very complicated! On the other hand, the number of student courses isn't known and we don't know how many variables we should consider.
With the help of lists, we'll be able to keep a large number of values in one variable and even perform various operations on them.
If you've worked with different programming languages, you're probably familiar with arrays. In a very general definition, a list can be considered a type of array in Python; An array whose length is variable and its elements can be of different data types.
List in Python
A list is an important data structure in Python. With the help of lists, we can store a sequence of data in a variable and perform various operations on them.
The list data type is one of the Collections data types in this popular language. The list contains a set of elements in order and can be changed. The list in Python is marked with brackets in the form of []; So that the list starts with [ and continues until ]. Each element in the list is separated from each other by a comma (,) and can be of any desired data type.
hive = ["peakd", 217, 22.5, "Albro"]In a line of code above, we have created a list named hive. Then we have put four values with different data types inside it. So easily!
Usage of the list
You can use the list anywhere you want! Wherever you have a meaningful or meaningless sequence of data, lists are your fastest and perhaps best choice.The advantage of lists in Python is that they are easily defined and their members can be added or subtracted. It is also very simple and fast to apply between lists. In the following, I introduce functions and techniques to easily do whatever you want with lists!
Accessing list members in Python
As mentioned earlier, the simplest way to define a list in Python is to use two square brackets next to each other.
With this definition, you will notice that it is also possible to create an empty list. As a result, it is not necessary to have all the values in the list at the beginning of the work; Rather, we will be able to add or subtract our desired values during the program.
Access to the members of the list is based on its indices. Indices are numbers that specify the position of each element in the list. The first element of a list will have index zero (0) and generally the nth element will have index n-1.
index list
Suppose we have a list of different $Hive platforms in our list.
platforms= ["hive.blog", "peakd.com", "leofinance.io", "ecency.com"]To access each element of the list, by having the position or index of that element and bringing the index in front of the variable name of the list, we will access the desired element.
That is, the following piece of code outputs the element located at index number 3; It means the fourth element in the list which is equivalent to ecency.com.
platforms[3]In this simple way, we'll be able to access all the elements in a list.
Note that the index is an integer value. As a result, calling the decimal or string index will give us an error.
In the above list we have four elements. The range of our indexes will be from 0 to 3. Entering a number greater than 3 will result in an index error (IndexError: list index out of range).
Negative list index in Python
Python programming language makes it possible to define an index for the members of a list. In such a way that the last element of each list has an index of -1, the last element has an index of -2, and so on until the first element...
With the help of negative index in Python, we can access the elements of a list from its end.
In general, the indices of the elements of a list in Python are considered as shown in the image below.
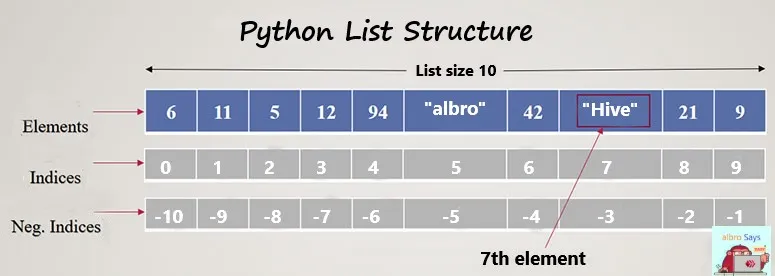
Therefore, to print the name of ecency.com in our assumed list, we will have a code similar to the code below.
print( platforms[-1] )
# Output: ecency.com
Question: According to these explanations, what do you think is the allowed negative index range in Python in a list with n members?
Accessing a part of the list (slicing the list)
One of the attractive features and functions of lists in Python is the ability to slice the list.
Let me explain this with an example. Suppose we have created the following list in our program.
lst = ['b', 'l', 'o', 'c', 'k', 'c', 'h', 'a', 'i', 'n']A list of size 10. How should we act if we want to access only a part of this list?
The list slicing feature allows us to access only a part of a list.
Access the list by defining the index range
To define an index range when calling list elements, it is enough to specify the range instead of entering an index number. Specifying the interval is done with a colon (:).
lst[3:7]
# Output: ['c', 'k', 'c', 'h']
In the code above, the elements whose index was in the range 3 to 7 were returned to us. Notice how the index range is defined:
If the range is defined as i:j, this definition will include element i to element j-1, and element j will not be included in the call.
If we don't specify any range boundary, it will default to the end. That is, to call the members of the list from the second element onwards, we act as follows.
lst[2:]
# Output: # ['o', 'c', 'k', 'c', 'h', 'a', 'i', 'n']
In the code above, the elements from the second index to the end of the list are displayed to us.
Also, in order to access a part of the list from the beginning to a specific index, you can do the following.
lst[:-2]
# Output: # ['b', 'l', 'o', 'c', 'k', 'c', 'h', 'a']
Here I have called all the elements in the list from the beginning to the last two (index -2).
Technique: Accessing between lists in Python
As you've probably picked up by now, we can use positive and negative indices when trimming a list.
If we use these two types of indices at the same time, we will be able to get interesting and surprising outputs from our list!
For example, let's say in our custom list, we want to remove the first two elements and the last two elements of the list and show the rest. For this, we will easily execute the following code. This way you can cut the list however you want!
lst[2:-2]
# Output: # ['o', 'c', 'k', 'c', 'h', 'a']
Technique: Sequential access to list elements (with step)
Suppose you have a list of numbers from 1 to 20 and you want to remove the middle two numbers from it. The first way that probably comes to mind is to use Python loops (such as for) to traverse the list.
I will look into this further. But here we will learn an interesting feature when defining the range of the list in Python.
As you learned, a colon (:) can be used to define a range of list indices. If, after defining the index interval, we put two points once more, we will be able to specify our movement step.
For a better understanding of the issue, pay attention to the following image:
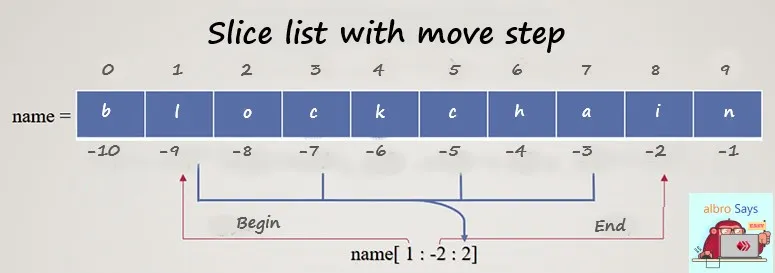
As it is clear in the picture, at first we have defined the start and end of the movement and then we have told what step to move on them and give us the output.
We create a list called numbers and put the numbers 1 to 20 in it. Then we move one by one, from the beginning to the end.
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20]
numbers[::2]
# Output: # [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19]
In this way, we have called all the odd numbers in the list. simply!
Now what if we want to start from the fifth element and move three by three? Its code will be something similar to the following code:
numbers[4::3]
# Output:
# [5, 8, 11, 14, 17, 20]I hope you are well acquainted with how to slice the list and its techniques and use it when necessary.
Nested list or multidimensional list in Python
The elements of lists can be anything; From number and string to another list! Therefore, if the elements of one list are another list, we will have nested lists.
Suppose we have a list that stores the information of a student. We want to have his id, name and all his grades.
student = [6214, "albro", ['A', 'B', '+A', 'F', '-C', 'A', '-B']]The third element of this list is a list itself. In the same way, you can create multi-level lists.
Definition of matrix in Python
As you know, a matrix is a nested list whose members have the same size.
By default, we do not have a matrix data structure in Python. Of course, with the help of some libraries and tools, such a data structure can be created and used.
Here we will review the simplest way to create a matrix in Python.
To create a matrix, it is enough to create a list where each element is another list.
mtrx = [[], [], []]It is better to always check during our program that the size of the internal lists does not exceed the specified size. An alternative solution to check the size of lists is to use the list size function (or the len() function), which is introduced in the utility functions section.
For example, we have stored the total working hours of employees on three days of the week in the matrix below.
logs = [['Mon', '06/22', 'albro', 12],
['Tue', '06/23', 'ecency', 7],
['Wed', '06/24', 'peakd', 10],
['Wed', '06/24', 'leofinance', 5 ]]Work with list elements
In addition to accessing the elements of a list, we will need to insert, remove or change the data in the list.
For each of these tasks, there are different methods or functions in Python. In the following, we will examine the most important and practical of them.
Add a new element to the list
There are three ways to add a new element to the current list. In the first two methods, the element is added to the end of the list; But with the help of the third method, we can place the element in our desired index.
We create a list of nums with three initial values and then add elements to it.
nums = [32, 15, 20]1. Adding a new element to the list with the append function
By calling the append() function on the list, it inserts its input value as a new element at the end of the list. This method just takes an input and its data type is not important.
nums.append(11)# Output: # [32, 15, 20, 11]
print(nums)
nums.append(73)# Output: # [32, 15, 20, 11, 73]
print(nums)
2. Quickly add an element to the Python list with a plus sign (+)
This method, which is a way of connecting two lists to each other, can be one of the fastest ways to add a new element or elements to our desired list.
In the utility functions section, I talk more about connecting two lists together.
For better understanding, I will give an example before explaining how to do it. Consider the following example:
nums = [32, 15, 20]
nums = nums + [25]Just like that, we added the number 25 to the end of the nums list!
If we print the list, we see that our list has been updated with the new value.
print(nums)
# Output:
# [32, 15, 20, 25]Now if there were multiple different values in the second list we are closing, all of them will be added to the end of the list.
nums = nums + [68, 23, 8] print(nums)
# Output: # [32, 15, 20, 25, 68, 23, 8]
Technique: summarizing addition operations
As you probably know, instead of the expression x = x + 3 we can write: x += 3. This theorem also holds for addition between two lists.
That is, the following two lines of code are equivalent to each other.
nums = nums + [25]
nums += [25]3. Insert function
The insert() function is called on the list and takes two inputs:
- The first argument: the index number we want (in the form of an integer)
- Second argument: the desired element to add to the list
There are two modes for the entered index number:
- The index is out of range and the size of the list; In this case, the element will be added at the end of the list.
- The index is within the current index range; The element is inserted in the desired house and the current element of this house and the houses after it are shifted to the right.
nums = [32, 15, 20]
nums.insert(1, 45)
print(nums)
# [32, 45, 15, 20]
nums.insert(100, 65)
print(nums)
# [32, 45, 15, 20, 65]Removing an element from a list in Python
When we want to remove a value from the list, there are two situations.
- We know the index of the desired element.
- We know the value of the desired element.
I introduce two different statements for each of these situations. You can use each of them in your appropriate place and remove the desired element from the list.
Delete the element with the index using the del statement
The del statement in Python is used to delete variables. In this way, whenever we put this keyword before the name of the variable, that variable will be completely removed from our program.
With the help of this statement, you can delete the entire list or an element from it.
If we put the name of the list or the indexed list in front of the del keyword, the list or element will be completely deleted.
lst = ['b', 'l', 'o', 'c', 'k', 'c', 'h', 'a', 'i', 'n'] del lst[3] print(lst)# ['b', 'l', 'o', 'k', 'c', 'h', 'a', 'i', 'n']
del lst print(lst)
# Traceback (most recent call last): # File "<pyshell#79>", line 1, in # print(lst) # NameError: name 'lst' is not defined
In the 2th line of the code above, I tried to delete the element in index 3 of the list (equivalent to element c). As you can see in the result, this element has been removed from the list.
In the 6th line, I have removed the entire list variable. After trying to print the list, I face the error of not defining the variable in Python.
Use the remove method to remove an element from the list
This method is called on the list and takes an input. Searches the list for what it takes as input and deletes the first one that matches.
In the list below, we have the letter a twice. By calling the remove('c') method, the first item found in the list (i.e. index 3) will be removed.
lst = ['b', 'l', 'o', 'c', 'k', 'c', 'h', 'a', 'i', 'n']
lst.remove('c')
print(lst)
# ['b', 'l', 'o', 'k', 'c', 'h', 'a', 'i', 'n']Change the element in the list
To change the value in the desired index, we can change it after calling that house from the list. This is done with the assignment sign or =.
lst = ["$HIVE", "$HBD", "albro", "leofinance" ,"ecency"]
lst[2] = "peakd"
print(lst)
# ['$HIVE', '$HBD', 'peakd', 'leofinance', 'ecency']If the element of our list is a numerical value and we want to increase or decrease it, it will be done in a similar way.
nums = [15, 24, 60]
nums[1] += 2
print(nums)
# [15, 26, 60]
Search the list
When working with lists in Python, there are many times when we want to search for an element in a list. Usually this type of search is used for a conditional expression.
Checking the existence of an element in the list with the word in
One of the keywords used to search for an element in a Python list is the term in.
As it is clear from the meaning of this keyword, it checks if there is a specific value in the list we want or not. And it gives us the result as True and False.
The method of using it is very simple and convenient. Just say what you want in Python!
Suppose we have the following numerical list:
nums = [15, 24, 60, 55, 74, 33]We want to check if the numbers 24 and 77 exist in this list or not?
If any of those numbers exist, we will print a corresponding message in the output.
if 24 in nums: print("24 is in python list!")
if 77 in nums: print("77 is in python list!")
# output: # 24 is in python list!
simply!
If we had a list with string values; Again, the way of work was the same.
colros = ["red", "purple", "green", "blue", "yellow", "orange"]
if "red" in colors and "blue" in colors: print("A mix of these colors can be Violet!")
# output: # A mix of these colors can be Violet!
Search the index of the element in the list
Sometimes it is necessary to get the index number of the element in the list. Or at the same time as searching for a value, if it exists, to have its index.
To do this, you can use the index() method in the Python list.
This method takes an input value and searches it in our list.
- If the value in the list is found, it will give us the index number of the desired house as output.
- If the desired value of the list does not exist, we will encounter a
ValueErrorerror.
With runtime error handling in Python, we will be able to easily find the index of the searched house in addition to the search.
names = ["albro", "peakd", "leofinance", "hive" ,"ecency"]
try: target = names.index("peakd") except ValueError: print("name not found!")
# result: # target = 1
Important functions for working with Python lists
When working with lists in Python, you are faced with a lot of functions! Functions that do many things for you.
In this part of the post, I will introduce some of the most important and most used Python list functions.
List size with the len function
One of the most important features of a list is its size. Among the most used functions is the len() function.
This function takes the list as input and gives us its size. Size refers to the number of elements in the list.
names = ["albro", "peakd", "hive", "leofinance" ,"ecency"] print(len(names))
# output: # 5
Remove the last element from the list with the pop method
With the help of the pop() function that is called on the list, we can remove the last element (the element in house -1) from it.
At the same time as we remove this element, the pop() function returns it to us. As a result, we will be able to put the last element into a variable or do something else with it before discarding it.
You can see the process of working with this method in the following code. First, we throw out the last member in the names list and print it. Then print the list to see the result of the operation.
names = ["albro", "peakd", "leofinance", "ecency" ,"$HIVE"] print( names.pop() ) print( names )
# output: # $HIVE # ['albro', 'peakd', 'leofinance', 'ecency']
Reverse the list with the reverse method
Sometimes we need to reverse a list! It means that the first member becomes the last member and the last member becomes the first member!
Perhaps the first solution is to create a new list and add elements from the end of the previous list to the new list.
By calling the reverse() method on the Python list, you can easily reverse the list.
names = ["ecency", "hive", "leofinance", "peakd" ,"albro"] names.reverse() print( names )
# output: # ['albro', 'peakd', 'leofinance', 'hive', 'ecency']
The reverse() function reverses the list and, in other words, the original list is destroyed. If you just want to have the list upside down or store the current list upside down in another variable, use the following method.
Technique: Reverse the list professionally with a negative step
Now, it was discussed about inverting or reversing the list in Python; Let me tell you a very interesting method with the help of my previous knowledge.
In the section of accessing list elements, we learned a method to move with a specific step in the list. If we set the step of movement in the list equal to -1, our movement will be reversed!
In this case we will only access the reversed list but not reverse it.
names = ["albro", "peakd", "ecency", "hive" ,"leofinance"] print( names[::-1] ) print( names )
# output: # ['leofinance', 'hive', 'ecency', 'peakd', 'albro'] #["albro", "peakd", "ecency", "hive" ,"leofinance"]
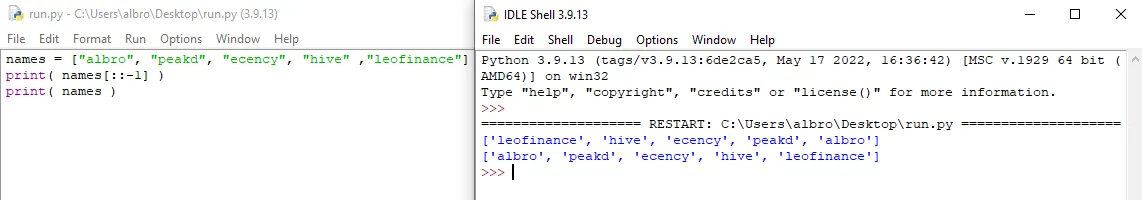
As you can see, with the help of this technique, I printed the reverse list in the second line; But the main list has not changed.
Delete all list elements with clear
If you are tired of the members of your list and want to remove all its members from the scene of your application, the clear() method is for you! 😉
By calling the clear() method on a list, all its members will be deleted and you will have an empty list.
names = ["albro", "peakd", "leofinance", "ecency" ,"hive"] names.clear() print( names )
# output: # []
List traversal in Python
List traversal in Python is one of the most important topics in list review. We have two ways to navigate the elements in the list.
In the following, we will explain both cases with examples.
List traversal with for loops and indexes
In this method, we use the index of each house to access the elements of the list.
The way of working is that we change the desired changes in the allowed interval and every time, we access the desired house.
names = ["albro", "peakd", "ecency", "leofinance" ,"hive"]
count = range(0, 5)
for i in count:
print( names[i] )In the above example, we set variable i to 0 to 4 and in each round of the loop, we printed the value in houses 0 to 4 of the list.
If the size of the list is not fixed, we will use the len() function to specify its size. The following code snippet shows a better structure for this type of list traversal.
names = ["albro", "hive", "peakd", "leofinance" ,"ecency"]
count = range(len(names))
for i in count ):
print( names[i] )Move through the list with for in
If you don't need the index of each house and just want to access the values in the list, there is an easier way.
With the help of the for in keyword, we will be able to scroll through a list.
For better understanding, consider the following example:
names = ["albro", "peakd", "hive", "leofinance" ,"ecency"]
for name in names:
print("Hello " + name)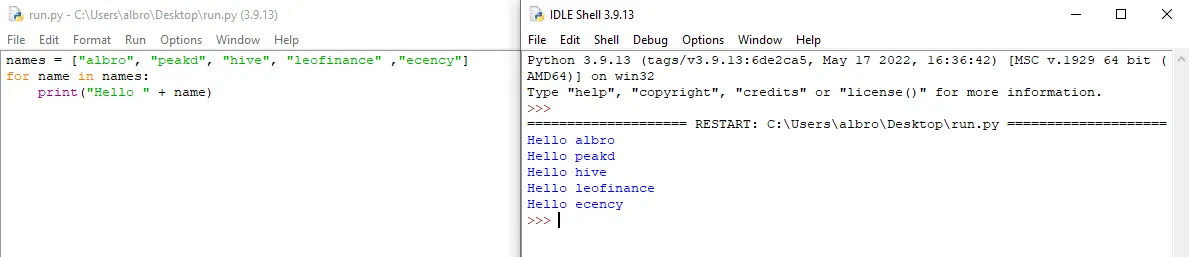
In the loop in this piece of code, in each round of loop execution, the value in each house of the list is poured into the name variable.
We can use this variable during the loop; Print it, compare it, or perform special operations on it.
Summary: List data type in Python
List in Python is one of the most used data structures that we use in our programs. If you are familiar with another programming language, it is better to say that a list is a kind of array in Python; Amazing array with many features. Lists are not sensitive to the data type of their elements and can contain elements of different data types.
In this post, I first discussed how to define the list. Then we reviewed the methods of accessing the elements of the list and learned how to add or remove an element from the list. We were able to search in a list and got to know its important functions and methods; Functions such as calculating the size of the list, reversing the list and emptying the list.
We learned how to navigate through a list in Python. There are two main and widely used methods for this work; The first is to use indexes and the second is to use the keyword for in in Python.
Hope you enjoyed this post!