
Post content list
- String definition in Python
- Multiline string definition
- String cutting in Python
- Commonly used Python string operators and functions
- Working with strings in Python
- Separate the string with a special character
- String search in Python
- Creating a structured string (string formatting)
- Iterate over String in Python
- Important Python string functions
- Replacing words in a Python string
- Convert list to string in Python
- Summary: Strings in Python
Strings are one of the most widely used data structures in programming languages that we deal with in almost all projects. Strings in Python are no exception to this! In Python, there is a default data structure called str, which can be used to create English or special character strings and do interesting things with them.
String in Python is an immutable type. That is, after defining a string, we cannot change it. For example, if we have a string as test, we cannot convert it to te3t!
To apply changes to a string, you need to create a new string. As a result, by applying changes to a string, we will have a new string.
In this post, we will comprehensively examine the topic of strings in Python and learn about its methods, functions and tricks.
String definition in Python
In the Python programming language, like many other languages, a text string is defined by double or single quotation marks.
"This is a String in Python!"
'This is another String in this code!'
"What is the result of 2 + 2 ?"It can almost be said that these two types of definitions don't have any particular difference. But where you want to use one of these symbols in your text, it is better that the string identifier is of the other type. (one " and the other ")
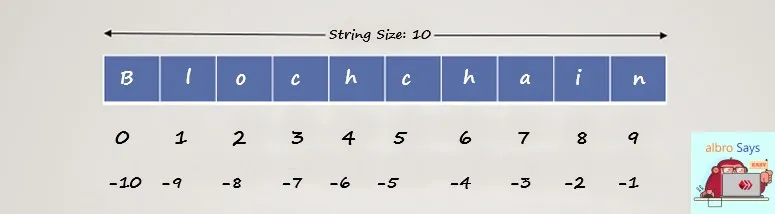
Strings, like lists in Python, are indexed. String indices are exactly the same as lists, starting with 0 and ending with -1.
Usually, the print() statement is used to print a string in Python. In its simplest form, this statement takes an input and prints it in the program console. (More detailed learning: print Python)
print( "Hello World!" )In the code below, we have defined a text string in Python and assigned it to a variable called name. Then we have displayed this value in the output. (Read more: Variables in Python)
name = "albro"
print( name )Multiline string definition
To define a multi-line text string in Python, we use the " or " three times at the beginning and end of the string.
Similar to the code below, we have defined a four-line message with three double quotes and put it in the txt variable.
txt = """Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,
consectetur adipiscing elit,
sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt
ut labore et dolore magna aliqua."""String cutting in Python
I said earlier that you can access the string like a list. All the features and tricks that exist for accessing lists also apply to strings.
With the help of the symbol [] in front of the name of the string variable, you can call the character that is in the desired house.
If our variable (variable s) contains the string 'albro', s[2] will return the value b and s[-1] will return the character o.
To cut a part of a string in Python, we also use Python list tricks. In the following code snippet, we have stored an expression in the txt variable but only printed the 4th, 5th and 6th house characters.
txt = "blockchain"
print( txt[ 4:7 ] )If the entered index value is outside the range of the string, we will encounter the error IndexError: string index out of range.
Commonly used Python string operators and functions
In the following, we will introduce various functions for working with strings in Python; But four of the most used ones are:
len() | It takes the string as input and gives us its size. |
str() | It converts its input into a string and outputs it. |
+ | It is used to connect two strings in Python. |
== | It is used to check the equality of two strings. (string comparison) |
Working with strings in Python
We programmers use strings a lot in our programs. From taking input in Python from the user to processing text data and heavier and larger tasks!
In the following, you will get to know four tricks of working with strings in Python. After that, we will check the functions of the string.
Separate the string with a special character
Suppose you have received information from the user and you want to convert a string to a list in Python. This work may seem very difficult and difficult at first glance!
If we have separated these data by a special character, our work is very simple. It is enough to call the split() method on the string...
Suppose we have the grades of a student in the form of a string as follows.
grades_str = "A,B,-B,C,B"The split() method takes an input known as a delimiter. The delimiter is the character or string that separates our data from each other. In our string, the comma (,) will separate the grades.
grades_str = "A,B,-B,C,B"
grades_list = grades_str.split(',')
print( grades_list )The output of this piece of code will be a list containing all scores.
['A', 'B', '-B', 'C', 'B']The separator can be anything, an English letter, a symbol, a number or even another string! For example, in the code snippet below, the target string is separated by "step" string.
string = "step 1: hello step 2: world step 3: run step 4: python" print( string.split("step") )
# ['', ' 1: hello ', ' 2: world ', ' 3: run ', ' 4: python']
The reason for creating an empty string at the beginning of the list is that the separator word is placed at the beginning of the string.
String search in Python
Sometimes we want to search for a character, word or string inside another string. We use the find() method to search the string.
This function takes three inputs, the first one is mandatory and the other two are optional.
- The first input is the character or string we are looking for.
- The second entry specifies the starting index of the search operation.
- The third entry also specifies the end index of the search field.
The output of this function is a number. If the defined character exists in the string, the index of the first occurrence (the first place the character is seen in the string) is returned to us. Otherwise, we will have the number -1 as output.
string = "Hello and Welcome to Albro Blog on Hive Blockchain!"
print( string.find("e") ) # 1
print( string.find("c") ) # 13
print( string.find("Albro") ) # 21If you want to limit your search to a part of the desired string, you can also define the second and third arguments; Otherwise, the search is performed on the entire string. Also, if you are searching for more than one character in the text, the output value of the function specifies the starting point of the match in the text.
Creating a structured string (string formatting)
Sometimes we need to format strings in Python or format them. Suppose we want to display a string and a number together. For example, let's print the student's grade in the output, something like the following text:
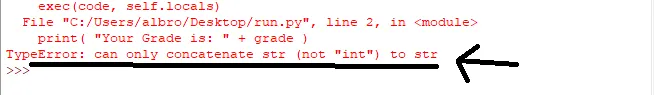
Your Grade is: 90The first thing that comes to mind is to use the operator + to add a score to the message string and finally print it. For this, we write and execute the following code.
grade = 90
print( "Your Grade is: " + grade )By executing the above code, the following error is obtained!
The error text is clear! It's not possible to join a string and a numerical value! We have two solutions:
The first solution: use the str function to convert a number to a string in Python
The first solution is to convert the score (number) into a string using the str() function. This function takes an input and returns a string as an output.
grade = 90
print( "Your Grade is: " + str(grade) )The second solution: format the string with the format method
But the second solution will be more standard and professional. For this, instead of the variable values that are supposed to be included in the string, we put the sign {}.
Then, by calling the format() method on the desired string, we give it our variable values and create the final string.
Take a look at the code below for a better understanding of the process.
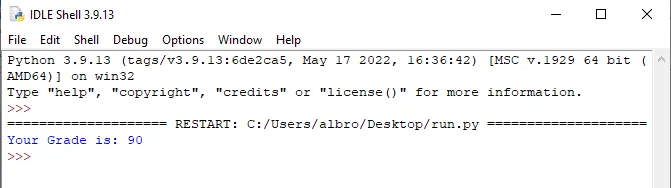
grade = 90 msg = "Your Grade is: {}" print( msg.format(grade) )
# Result: Your Grade is: 90
The format() function can take any number of inputs. In fact, you can define as many variables as you need within a single string.
Iterate over String in Python
Loops in Python can be used to iterate through a string. The first idea that probably came to your mind is to use indices to access each character of the string.
txt = "A test text from Albro"
count = range(len(txt))
for i in count:
print( txt[i] )In this piece of code, we scroll through a text using a for loop and print each of its characters. The same code with a while loop will be as follows.
txt = "A test text from Albro"
count = len(txt)
i = 0
while i < count:
print(txt[i])
i += 1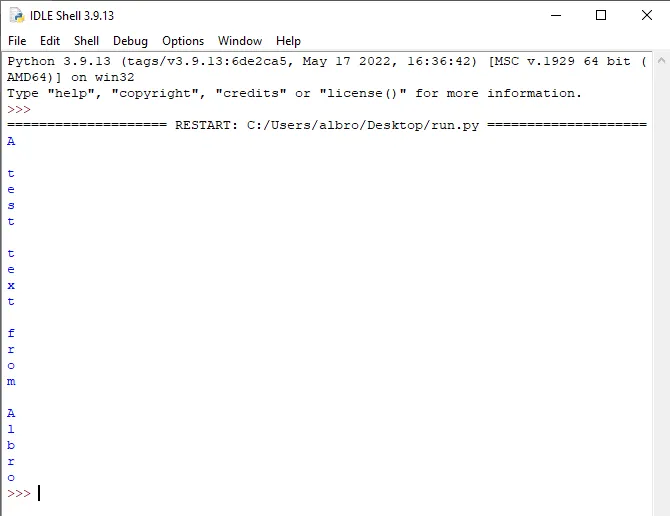
A nice and simple trick to iterate through the string characters one by one is to use in in the for loop. The structure of this iteration is as follows.
for char in string:
# Do something with charThis type of iteration is very simple and is also very suitable in terms of the coding concept. (to any character in the string...)
The piece of code for iteration within the string in Python will be as follows.
txt = "A test text from Albro"
for char in txt:
print( char )Important Python string functions
Since strings have many uses in programming, there are relatively many different functions for them. In this section, I introduce 8 of the most important functions that you may deal with more.
All these functions are called as methods and on strings. That is, if the function name is func() and our string variable is s, it will be called as s.func().
lower(): convert the letters in the string to lowercase letters (in English)upper(): Convert string letters to uppercase lettersstrip(): remove empty space (extra spaces) at the beginning and end of the stringcount(): Calculates the number of repetitions of the word or character taken as input in the string.isdigit(): Returns True if all the characters in the string are numbers and False otherwise.index(): Specifies the index of the beginning of the word or character taken as input in the string. Its difference with the find method is that if it does not find the desired value, the program will encounter an error.
Replacing words in a Python string
If we want to replace a word or character with another word or character in the string, we use the replace() method.
This function is called on the target string and takes two inputs:
- First entry: old value
- Second input: new and replacement value
In the code below, I have changed all letters e to o.
txt = "Hello Dear Albro Followers!"
print( txt.replace('e', 'o') )
# Hollo Doar Albro Followors!If we substitute a word or phrase instead of characters, the substitution operation will be executed without any problems.
txt = "Hello Dear Albro Followers!"
print( txt.replace('Followers', 'Friends') )
# Hollo Doar Albro Friends!Convert list to string in Python
If you have a list of strings or words that you want to join to create a string, you should use the join() method.
The join() function takes an input, which must be of the iterable type in Python. Lists and tuples are also iterable.
This function concatenates each member of the iterable taken as input with the string or character it was called on.
Let me make it easier to understand with an example. Suppose we have a list of people's names that we want to put all of them in a string and separate them with ,. For this, we run the second line of the following code.
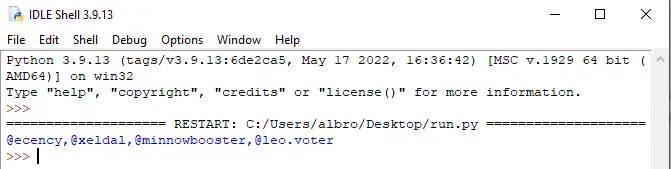
lst = ["@ecency", "@xeldal", "@minnowbooster", "@leo.voter"] string = ','.join( lst )
print(string)
# @ecency,@xeldal,@minnowbooster,@leo.voter
Summary: Strings in Python
In this post, I discussed the comprehensive training of Python. We learned how to define a string and saw how to work with strings in Python. We have identified at least 13 commonly used functions and learned how to use them.
We know that by using the + operator between two strings, they can be connected to each other. We used the split() function to convert a string to a list in Python, and we used the join() method to convert a list to a string in Python.
In your opinion, what other function in working with Python strings is widely used that I have not introduced? Please share it with everyone in the comments section.