Our primordial instinct dictates us to be adept at changes and reform ourselves to suit the environment. Technology evolves to fit our needs to ease the routines we have. Likewise, buildings need to transform to sought our needs. Architects developed a flexible design that enables structures to move in real-time without compromising the structure's integrity which is kinetic architecture. The building is capable of adapting to adverse environmental conditions when needed.
Kinetic architecture is not a new concept. It existed in the Middle Ages or earlier in the drawbridges. To date, architects explored ways to infuse movement in building superstructures. It may be shifting windows or transforming houses. There are three themes commonly adapted in kinetic architecture: retractable roofs or folding bridges, shape-shifting structures with impressive aesthetics, and surface movement.
The kinetic architecture provides a different sense of functionality to a building or structures. We often see kinetic architecture applied in functional edifices such as bridges and stadiums. Some bridges open up their midsection to allow the passage of vessels, which have a higher elevation than the bridge's clearance.
Wembley National Stadium
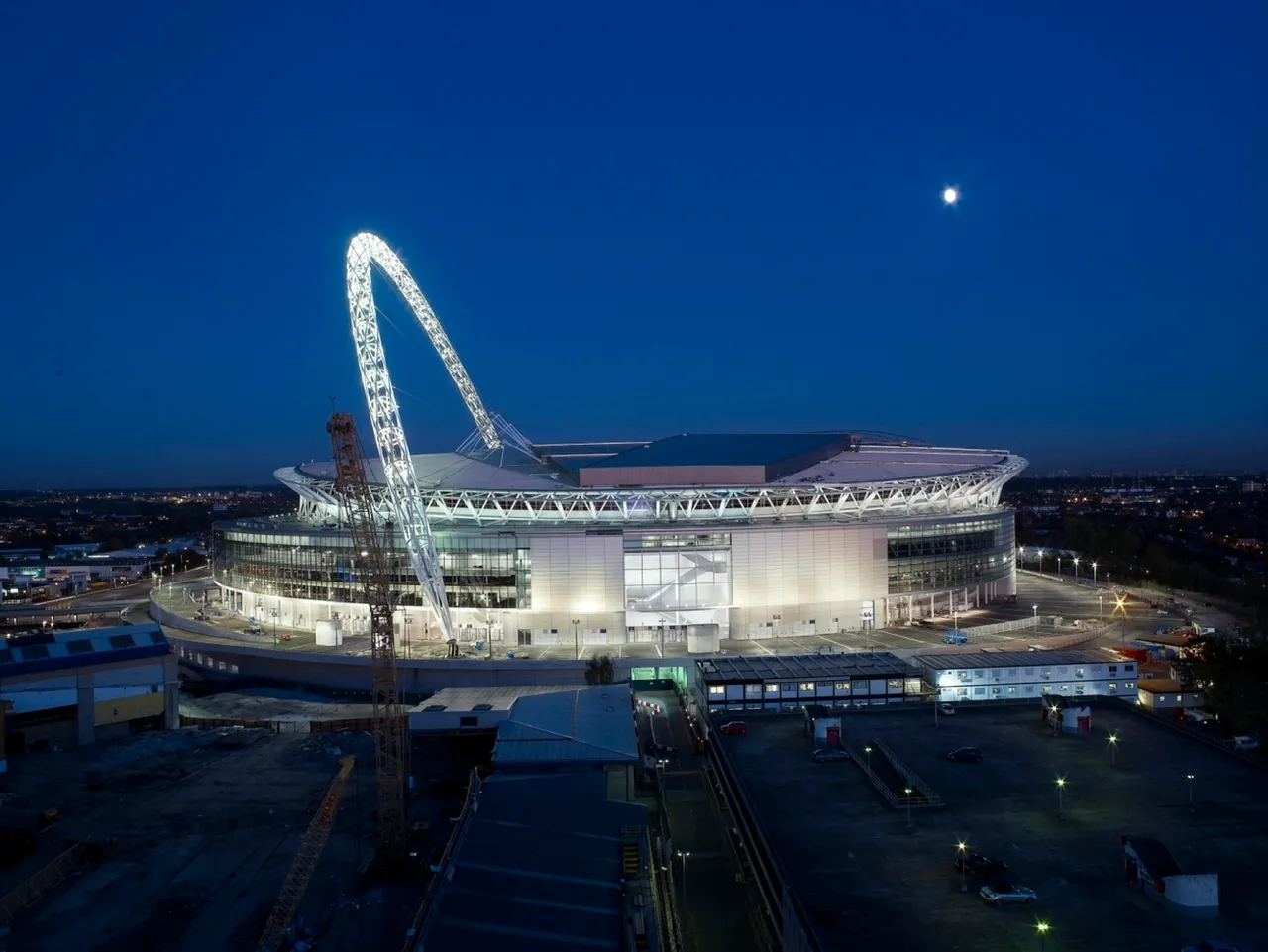

Wembley National Stadium
The old Wembley Stadium was an iconic sporting venue in Britain. In 1966, it is where they held the Football World Cup finals. They reinvented the stadium and opened it for use in 2007. It houses 90,000 seats. With 90,000 seats, it is almost four times elevation and covering twice the area as compared to the old stadium. The new stadium is the largest covered arena in the world. The new stadium has a relatively high steel arch that supports its sliding roof.
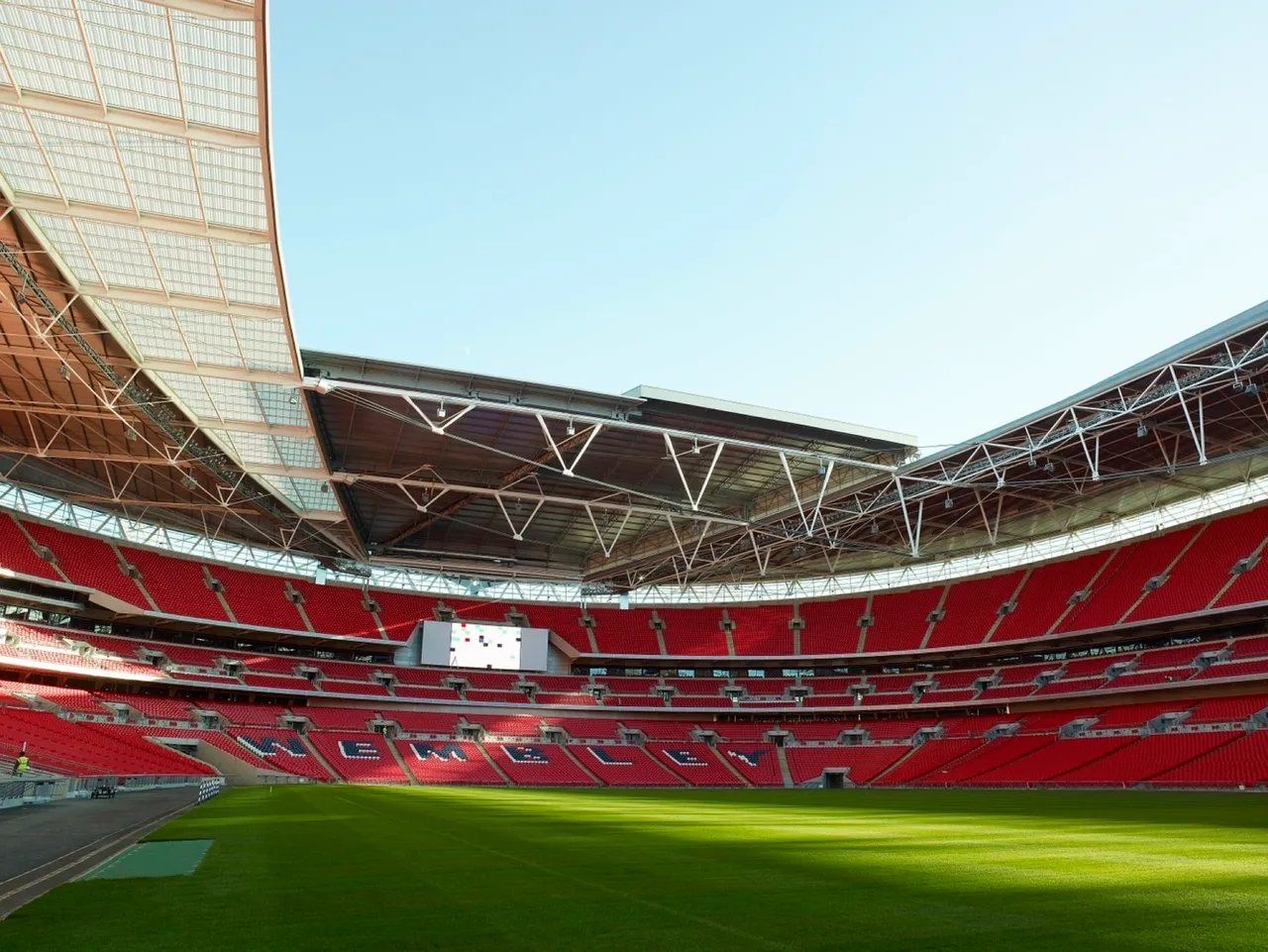

Wembley National Stadium
The stadium wants all spectators to enjoy the experience, which the designer designed larger seats with much legroom. The higher tier can It has escalators to be access using escalators. A concourse wraps around the premises that provide catering to at least 40,000 people at once.
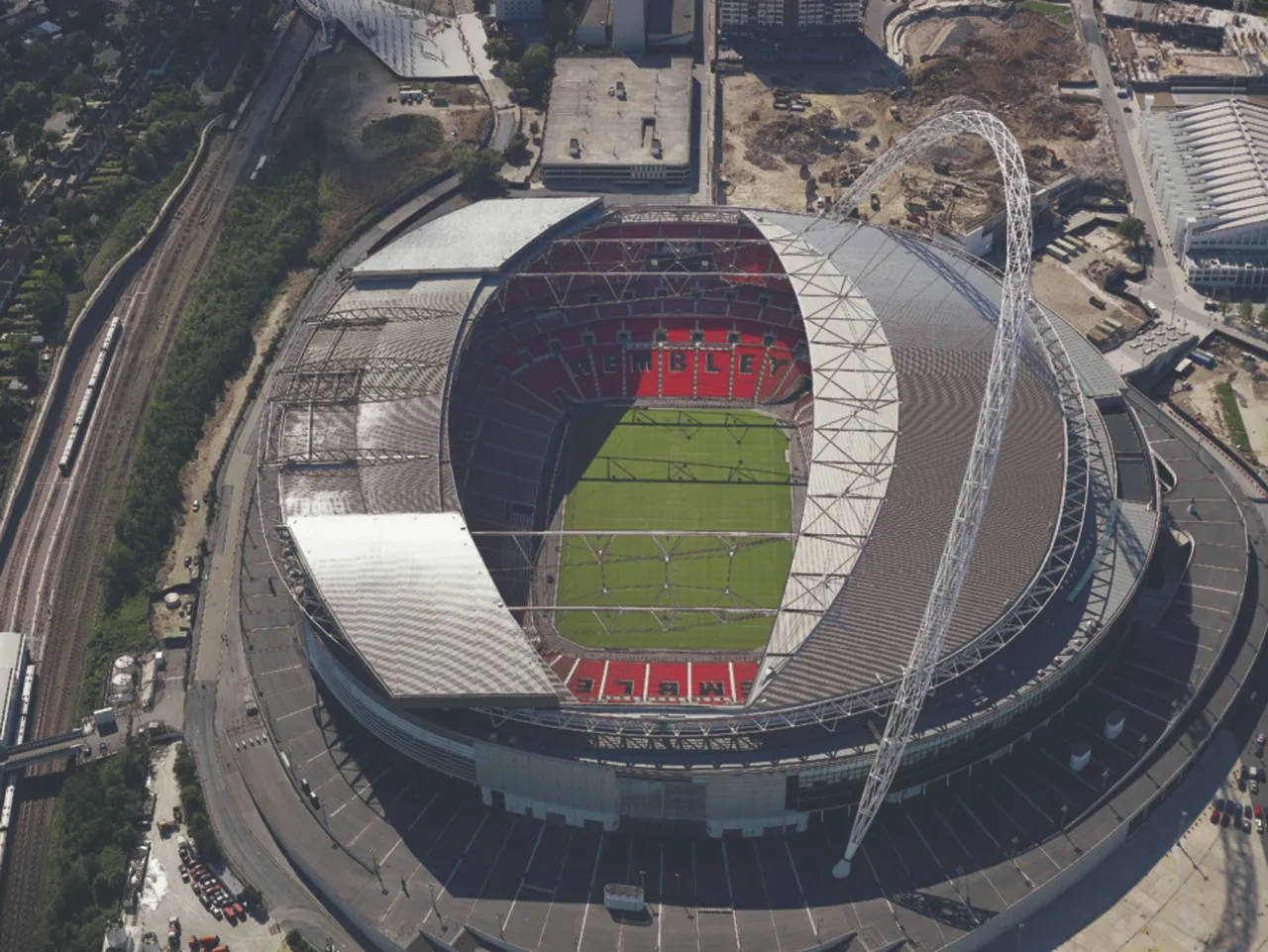

Wembley National Stadium
The stadium has a retractable roof, which ensures everyone experience comforts in all weather. When the canopy is open, it ensures that the turf receives sufficient sunlight. It also airs the stadium for the spectators to be comfortable. It closes when there is poor weather and covers the entire seating bowl.
The kinetic architecture enables aesthetically appealing transformations. This theme revolves around fantastic structures that have shape-shifting capability to produce impressive visuals. A famous building that uses it is the Milwaukee Art Museum.
Milwaukee Art Museum
The world-renowned architect Santiago Calatrava was one of the designers of the museum with an exceptional pavilion. Calatrava designed the Quadracci Pavillion to create a new image for the museum. It depicts a modern white structure that looks like a ship jutting out the water. It gains fame due to its movable sun-shield that folds and unfolds according to the time of the day.
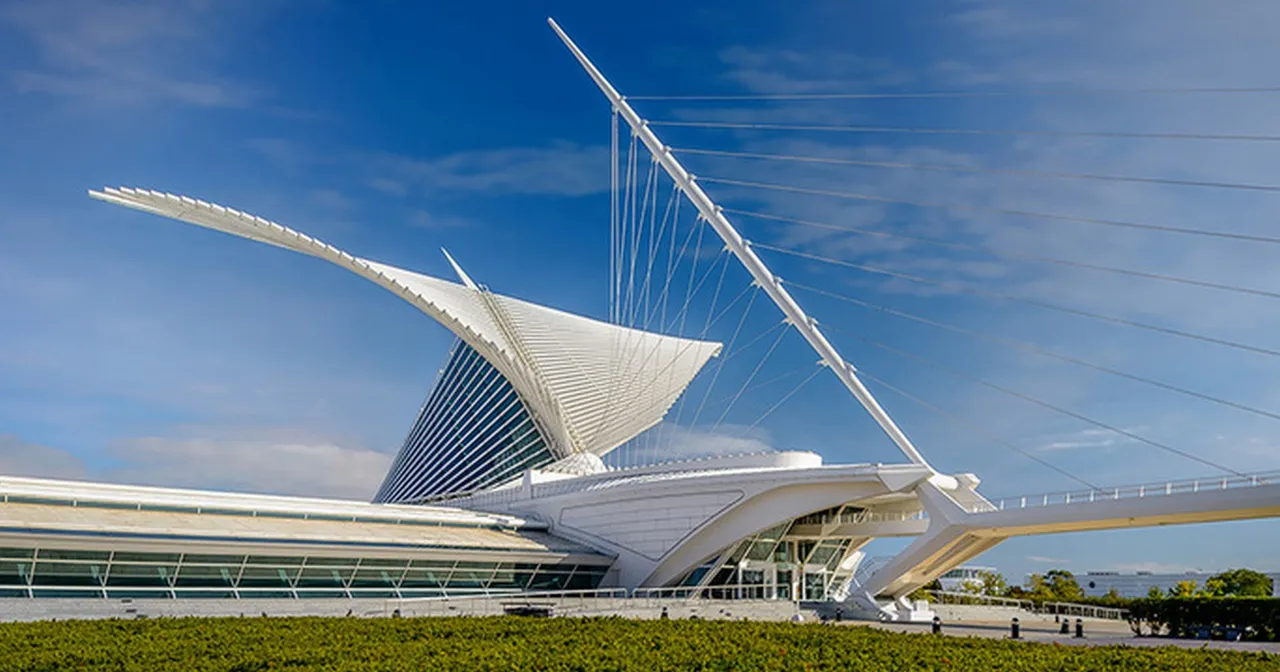

Milwaukee Art Museum
The pavilion's kinetic structure is a delight. It has a wing-like brise-soleil with louvers that open and close depending on the time of the day. It has 72 steel fins that weigh about 90 tons each. The wings take 3.5 minutes to open or close. It has sensors that measure wind speed and direction. When the structures opened, the shape becomes a sign. It is set against the lake to serve as a backdrop. It depicts that there is an inauguration of new exhibitions.
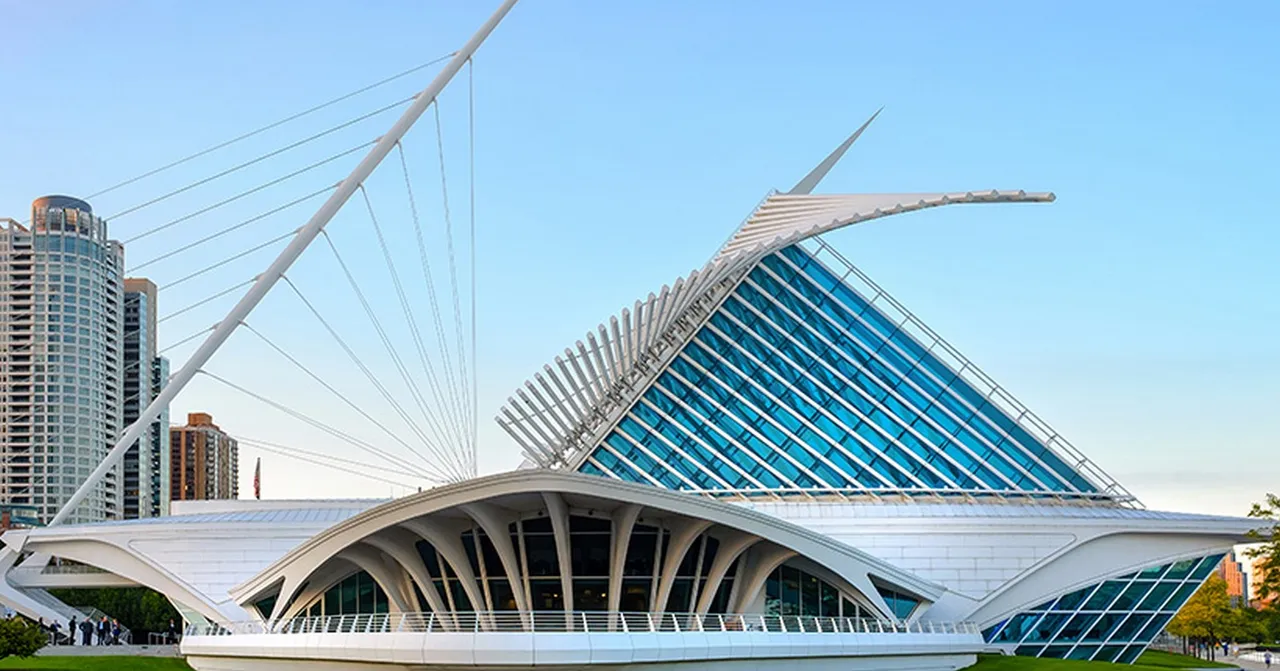

Milwaukee Art Museum
The Milwaukee Art Museum houses an atrium at the shore level. It has a gallery space for temporary exhibitions. Aside from that, it houses a 300 seat capacity lecture hall for the education center. In the pavilion, people can have a good meal at the restaurant, which has panoramic views of the lake.
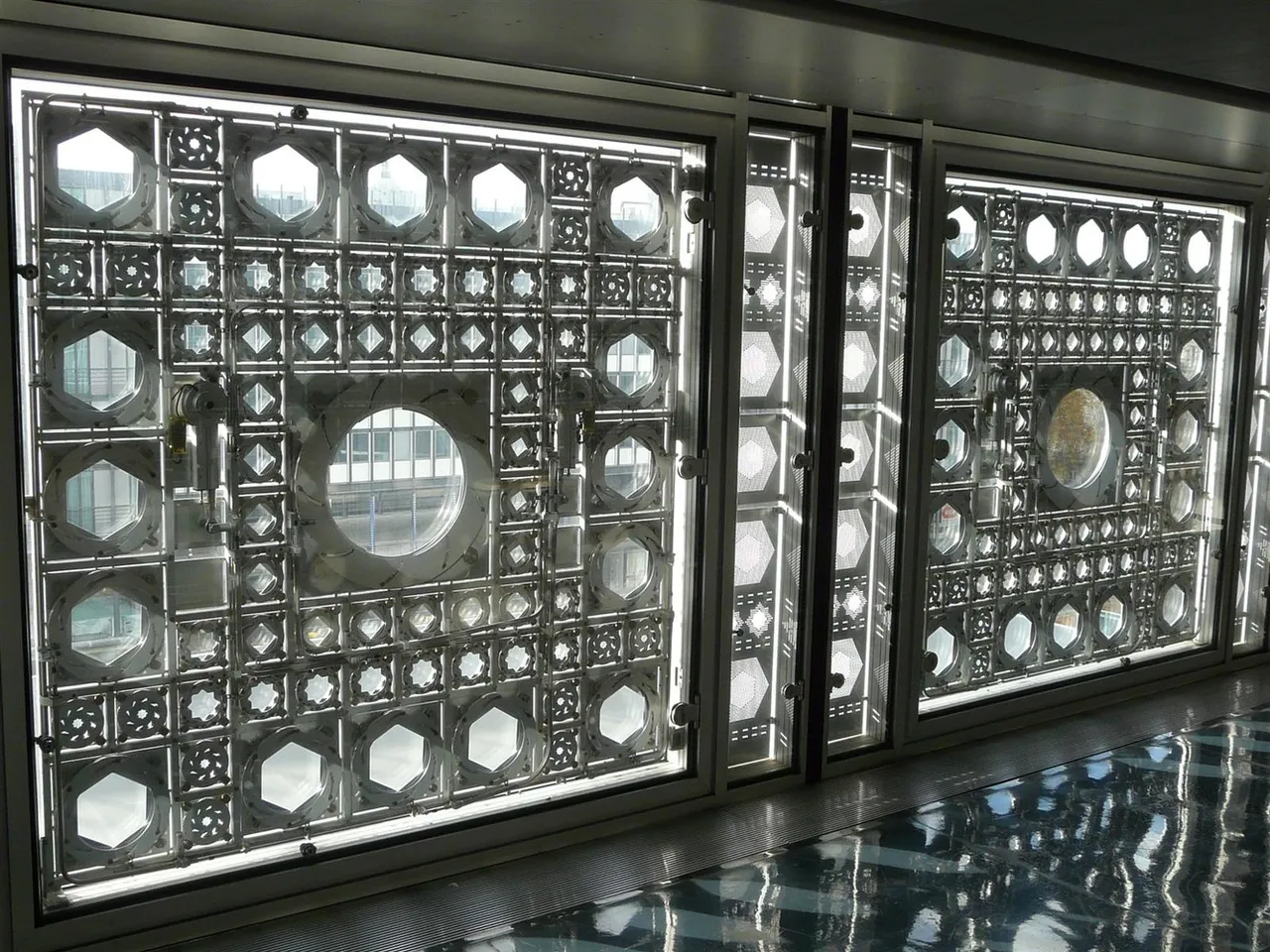
The last theme in kinetic structure is surface transformation. Buckminster Fuller called it skin-like articulation. It often uses robotics in transforming edifice. The Institute du Monde Arabe in Paris exhibits this theme. The building has a metallic screen that unfolds with moving geometric motifs. It has a high-tech brise soleil that regulates the level of light and heat exposure when it opens and closes.
Institute du Monde Arabe
They constructed the institute to serve as a devotion to the relationship of the Arab culture with France. Jean Nouvel designed the Institute du Monde Arabe. His attention to detail prevails with the facade detailing of Institute du Monde Arabe. It used advanced responsive brise soleil on the south façade that protects from the sun and privacy. He gets a lot of its design from Arabic architecture, which is the mashrabiyya.
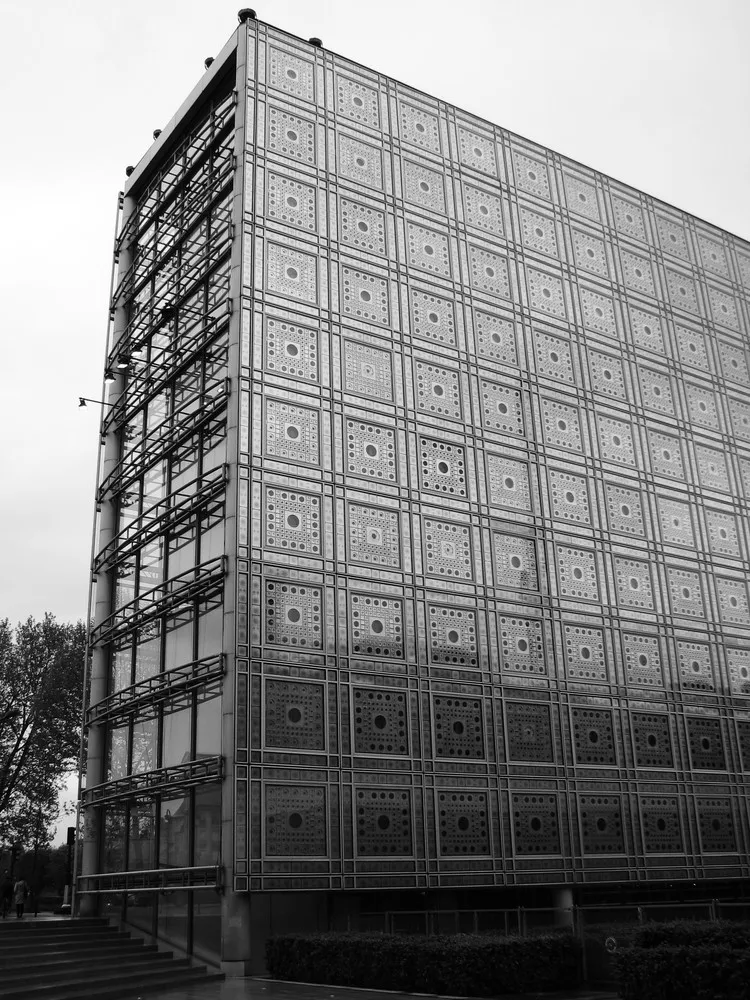

Institute du Monde Arabe
Institute du Monde Arabe
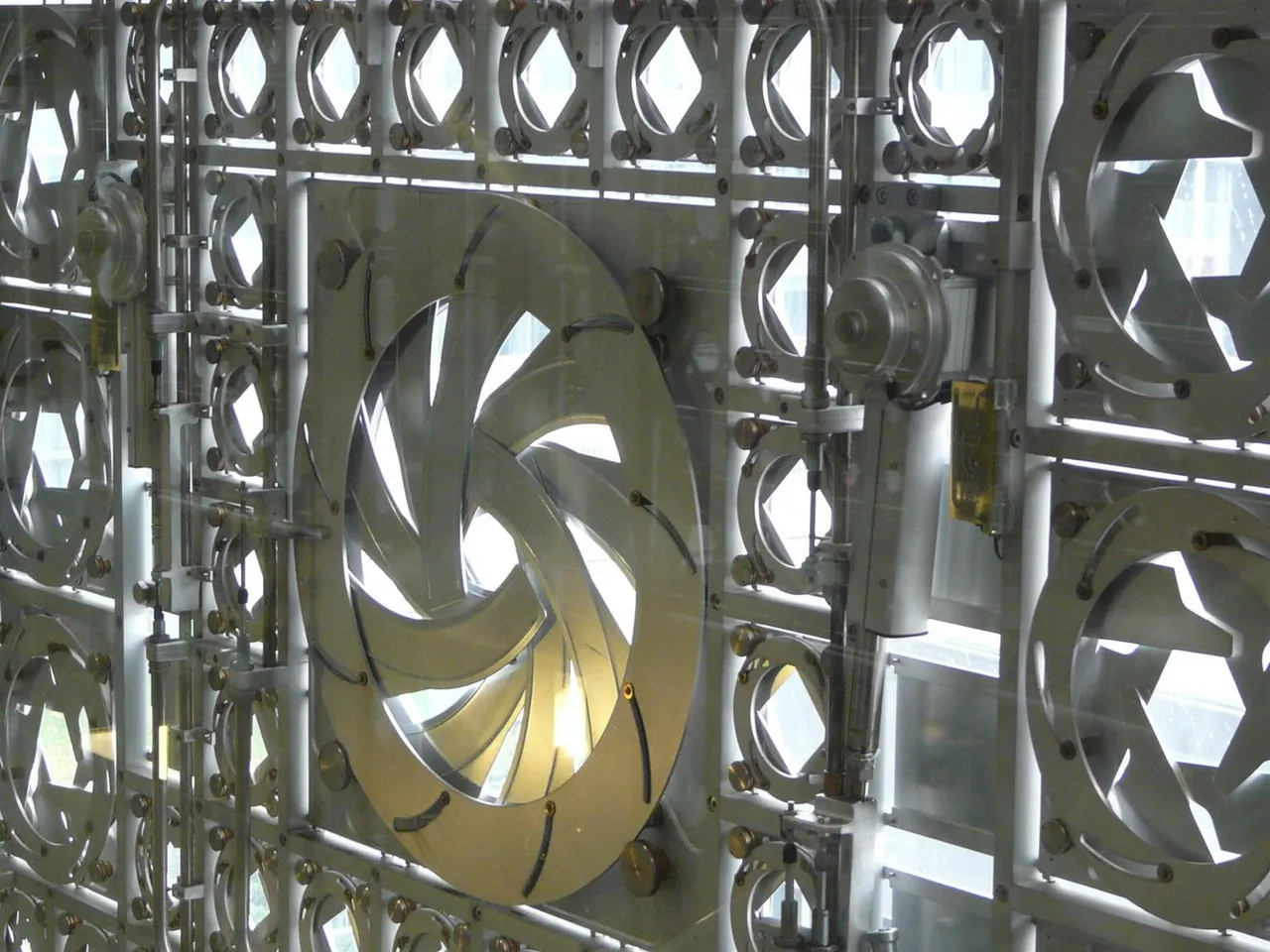

Façade detailing of Institute du Monde Arabe
The institute placed several hundred light-sensitive diaphragms, which regulate the amount of light flowing through the building. Various phases of the lens shift to different geometric patterns of light and void. The interior spaces improve their ambiance as the lens changes and the exterior. It improves the aesthetics of the structure and mitigates solar gains by reducing the aperture size. Nouvel won the Aga Khan Award for Architecture in 1989, and the Equirre d’Argent for French architecture in 1987.
The kinetic architecture provides a unique solution to architectural design, specifically on adaptation to environmental conditions. In contrast, static struggles in providing solutions to problems on adaptation. Kinetic architecture is a design concept that addresses the need for design that adapts to adverse environmental conditions, and for better aesthetic quality.