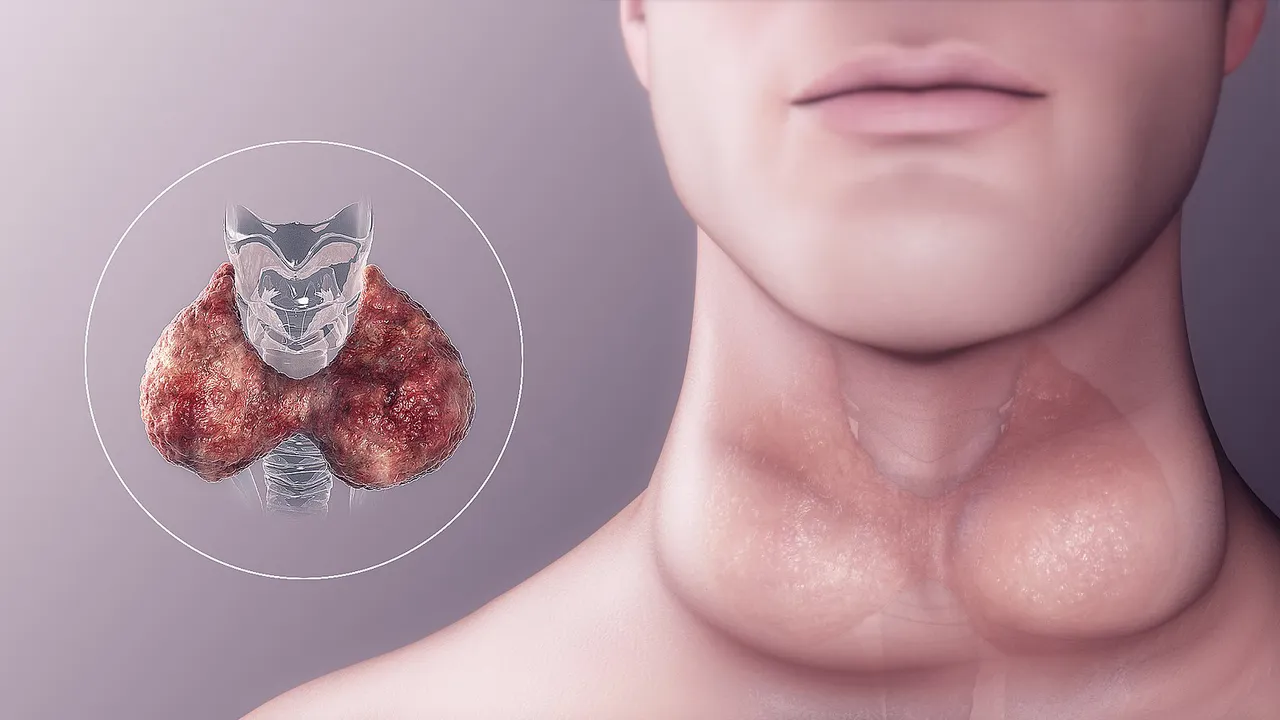
By Scienctific Animations, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia
While in extreme cases, this swelling may result in a life-threatening emergency when the thyroid hormone level gets extremely too high or extremely too low (thyroid storm and myxedema coma). Goiter can occur in both men and women but it occurs more commonly in women. In this post, I will discuss the various presentations of this neck swelling, the causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What is a goiter?
Goiter is simply the enlargement of the thyroid gland which is a gland situated in the front of the neck. The thyroid gland is butterfly in shape, consisting of two lobes joined at the center and located just below the thyroid cartilage commonly called Adam's apple. This gland is responsible for secreting thyroid hormone which is described as the fire of life.
This hormone is very important and affects all parts of the body, that is why its excess or deficiency also manifests in all parts of the body. We will see this when we get to the symptoms of thyroid hormone imbalance.
First, let's look at the functions of the thyroid hormone.
We all eat food every day to get the energy to go about our daily activities. This food is converted into energy and heat by a complex process called metabolism and these metabolic processes are regulated by the thyroid hormone.
Therefore, the thyroid hormone controls the way our body produces and uses energy and heat, it controls the rate of our heartbeat, blood pressure, muscular activities, brain development, body temperature, etc. That is why any excessive production or underproduction of this hormone affects every system of the body.
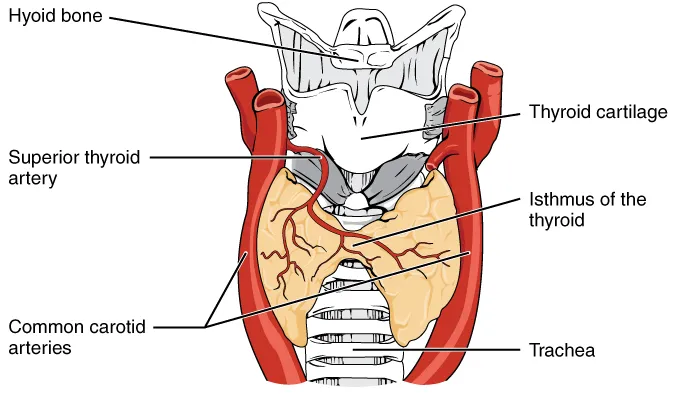
By CFCF - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia
What are the causes of thyroid gland enlargement?
Iodine deficiency is the commonest cause of goiter. But with the use of iodized salts in many parts of the world now, the incidence of goiter from iodine deficiency is on the decline. Iodine deficiency causes goiter because Iodine is an important element used by the thyroid gland to produce the thyroid hormone. So when it is deficient, the thyroid gland has to work harder to produce more thyroid hormone and this overwork causes the enlargement of the gland (goiter).
Another common cause of goiter is autoimmune diseases like graves disease and Hashimoto thyroiditis. In graves disease, the body produces some molecules called thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) which makes the thyroid gland produce excess thyroid hormones leading to hyperthyroidism. The hyperfunctioning of the thyroid gland in this case causes its enlargement.
In Hashimoto thyroiditis, the body's immune system also produces some molecules which damage the thyroid gland leading to a low level of thyroid hormone called hypothyroidism. The gland tries to work harder to compensate for this deficiency and that leads to its enlargement.
Consumption of food referred to as goitrogens like cassava, and cabbage is also a cause of goiter. This disease can also be endemic in mountainous, rocky, and limestone regions with a deficiency of iodine. Other causes can also be Inflammatory diseases and malignancies. It might also be normal changes in pregnancy, breastfeeding, puberty or menses.
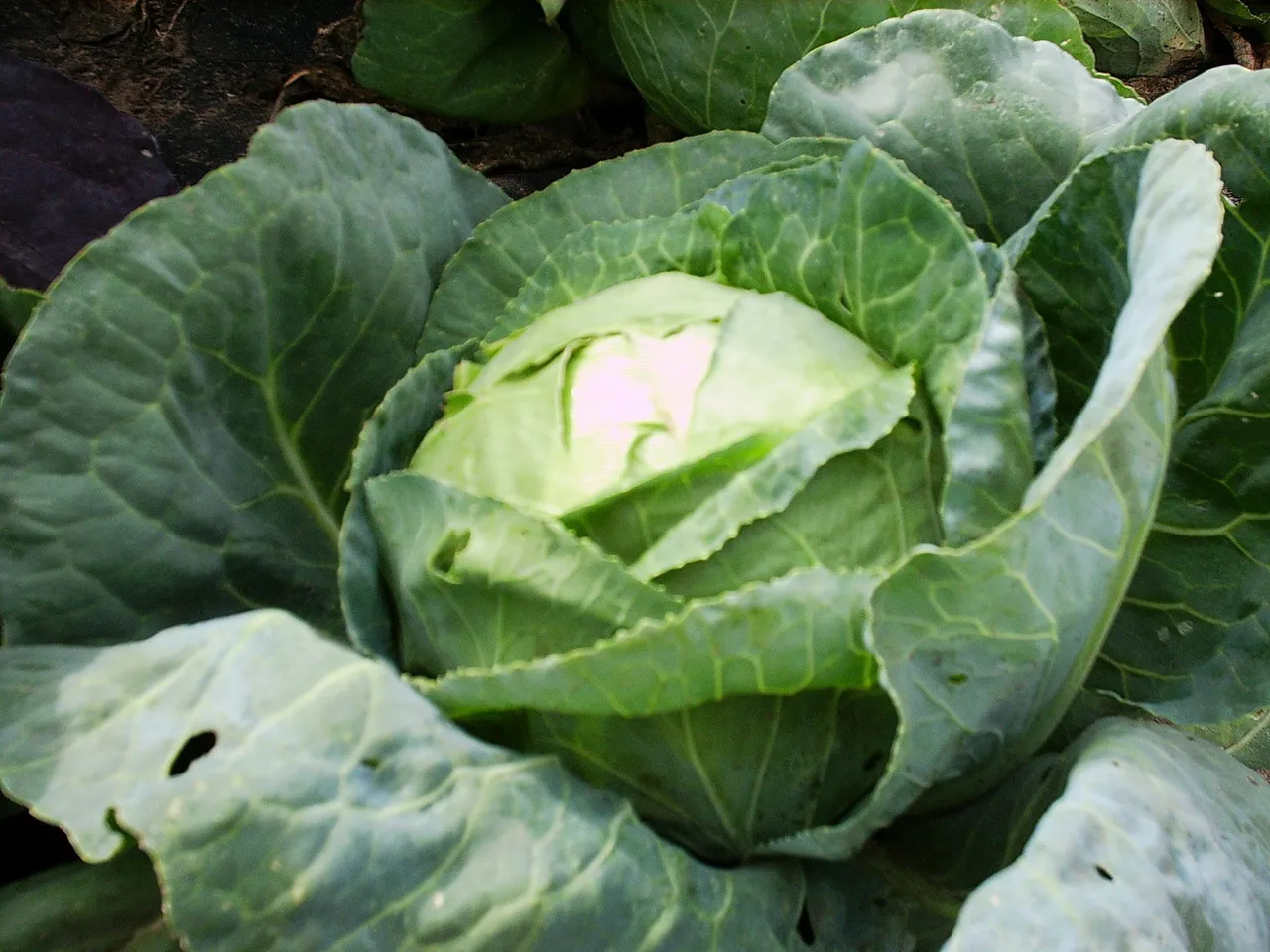

By Steve Block - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia
Clinical manifestations
As I briefly stated at the beginning, goiter in some individuals may have no toxic symptoms. These are referred to as simple nontoxic goiter. For these persons, treatment is simple with drugs and there may be no need for surgery except in the following conditions; cosmesis, or when the goiter grows so large and starts compressing the food and windpipes in the neck causing difficulty in swallowing and airway obstruction.
Another indication for surgery is to prevent the risk of the swelling becoming cancerous or secondary thyrotoxicosis.
For the toxic goiters, it causes symptoms in these individuals due to the high or low levels of thyroid hormone associated with it (Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism).
HYPERTHYROIDISM
This is a condition when the thyroid gland produces an excessive amount of thyroid hormones. Recall that in the functions of the thyroid hormone above, I stated that the hormone regulates the production and use of energy and heat from the food we eat (metabolism). So when it is produced in excess, the patient will experience the following; excessive sweating, heat intolerance, loss of weight despite increased appetite, diarrhea, and frequent stooling.
The thyroid hormone is the fire of life and when it is in excess, everything in the body will start over firing. So in the heart, the patient will have increased heartbeat, chest pain, and features of heart failure. In the neuromuscular system, the patient will experience shaky hands (tremors), anxiety, irritability, sleeplessness, restlessness, etc.
In the eyes, there will be double vision, protruding eyeballs, and visual disturbance. In the reproductive system, there will be amenorrhea and gynecomastia (enlargement of breast in males).

By Jonathan Trobe, M.D, CC BY 3.0, Wikimedia
HYPOTHYROIDISM
This is a condition where the thyroid gland produces low levels of thyroid hormone. Here, this important hormone, the fire of life is going dim. So everything is low and shutting down. The patient will have weight gain because the food is not digested, there will be cold intolerance because heat is not produced from metabolism, there will be constipation, failing thought, and memory, slowed speech and action, and the patient generally becomes very sluggish. Treatment here involves thyroid replacement therapy (levothyroxine).
What are the necessary investigations to do here?
To make a diagnosis, some investigations will need to be done. First, a thyroid function test is done. This test enables us to know the levels of thyroid hormones (thyroxine and triiodothyronine). An ultrasound scan of the neck is done which shows the size, affected lobes, and consistency of the enlarged gland.
An X-Ray of the neck is also done to check if the trachea is deviated, compressed or if the gland enlarged down behind the breast bone. To check if the enlarged gland is malignant or not, a fine needle aspiration cytology is done.
In preparation for surgery, a test called indirect laryngoscopy is usually done to check the state of the vocal cord. This is for medico-legal reasons. Other investigations include thyroid isotope scans, thyroid antibodies to check for autoimmune diseases like graves disease and Hashimoto thyroiditis, Serum calcium and phosphate, Full blood count, and other routine investigations.
How is this condition treated?
The treatment for hyperthyroidism can either be the use of drugs, which is always the first line of action, the use of radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery when indicated.
The drugs commonly used here are carbimazole and propyl thiouracil (PTU) which block the synthesis of thyroid hormones. This is the preferred treatment option for children, pregnant women, those who have recurrence after surgery, or those who have a high level of thyroid hormone without an enlarged thyroid gland. Other drugs like propranolol and diazepam are given to manage the heart symptoms and reduce anxiety respectively.
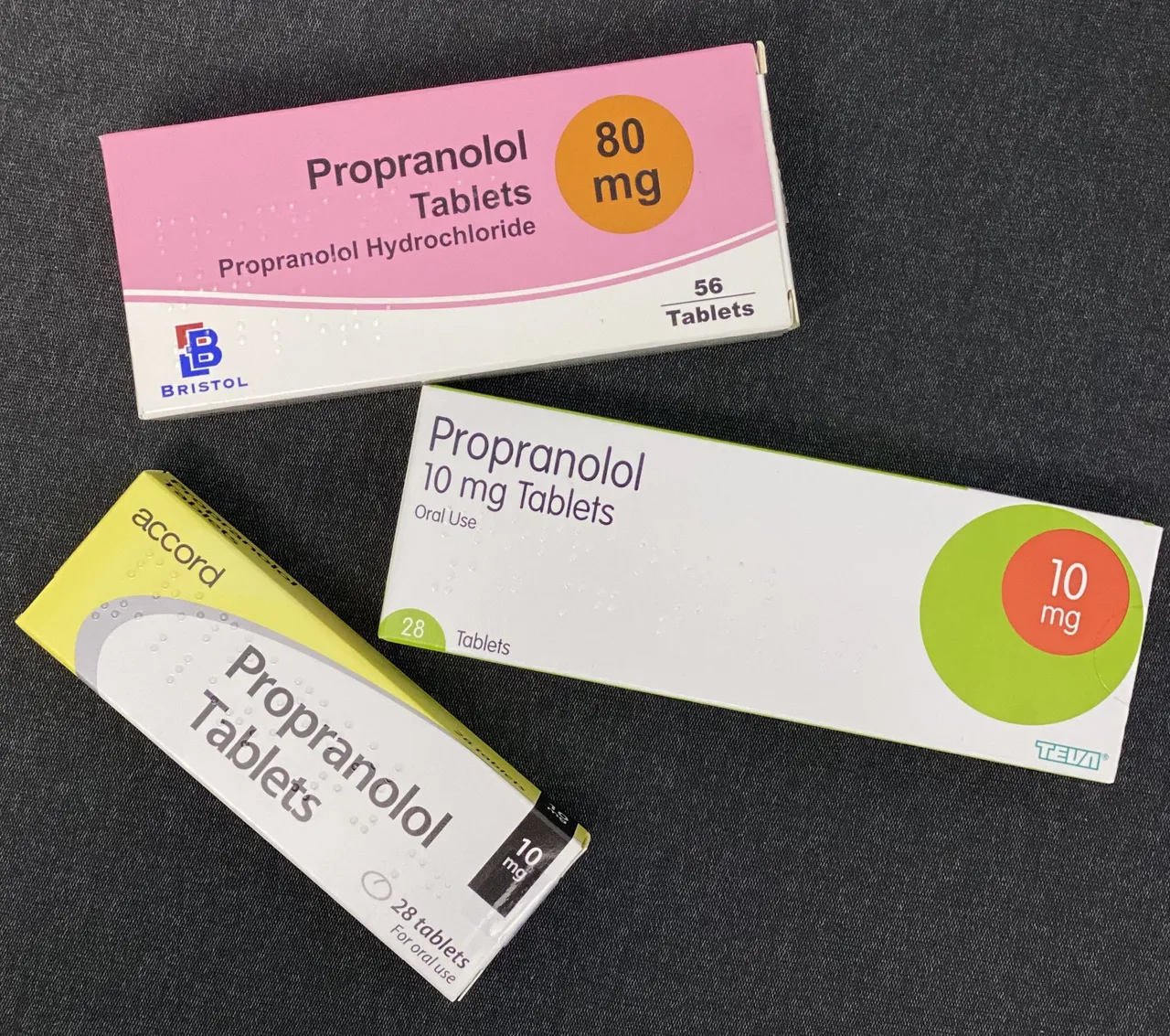
By Whispyhistory - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia
The next treatment option is surgery which is used when the goiter is big enough to cause pressure symptoms, toxic solitary or multinodular goiter or there is relapse after drug treatment or poor drug compliance, etc. A good number of patients go for surgery for cosmesis.
The surgical options can be a procedure called lobectomy where the surgeon just removes a lobe of the thyroid gland or a subtotal thyroidectomy where the surgeon removes the thyroid gland leaving only one-eight of the gland on both sides or a near-total thyroidectomy where the thyroid gland is removed leaving only one eight of the gland on only one side. The one eight glands left in both surgeries will provide the adequate level of thyroid hormone needed by the body for normal functions without problems.
In a total thyroidectomy, the entire thyroid gland is removed without leaving any fraction behind. This is done especially when it is suspected to be malignant. Because the entire gland is removed, the patient has to be placed on the drug L-thyroxine for life since there is no gland again to produce the level of thyroid hormone needed by the body.
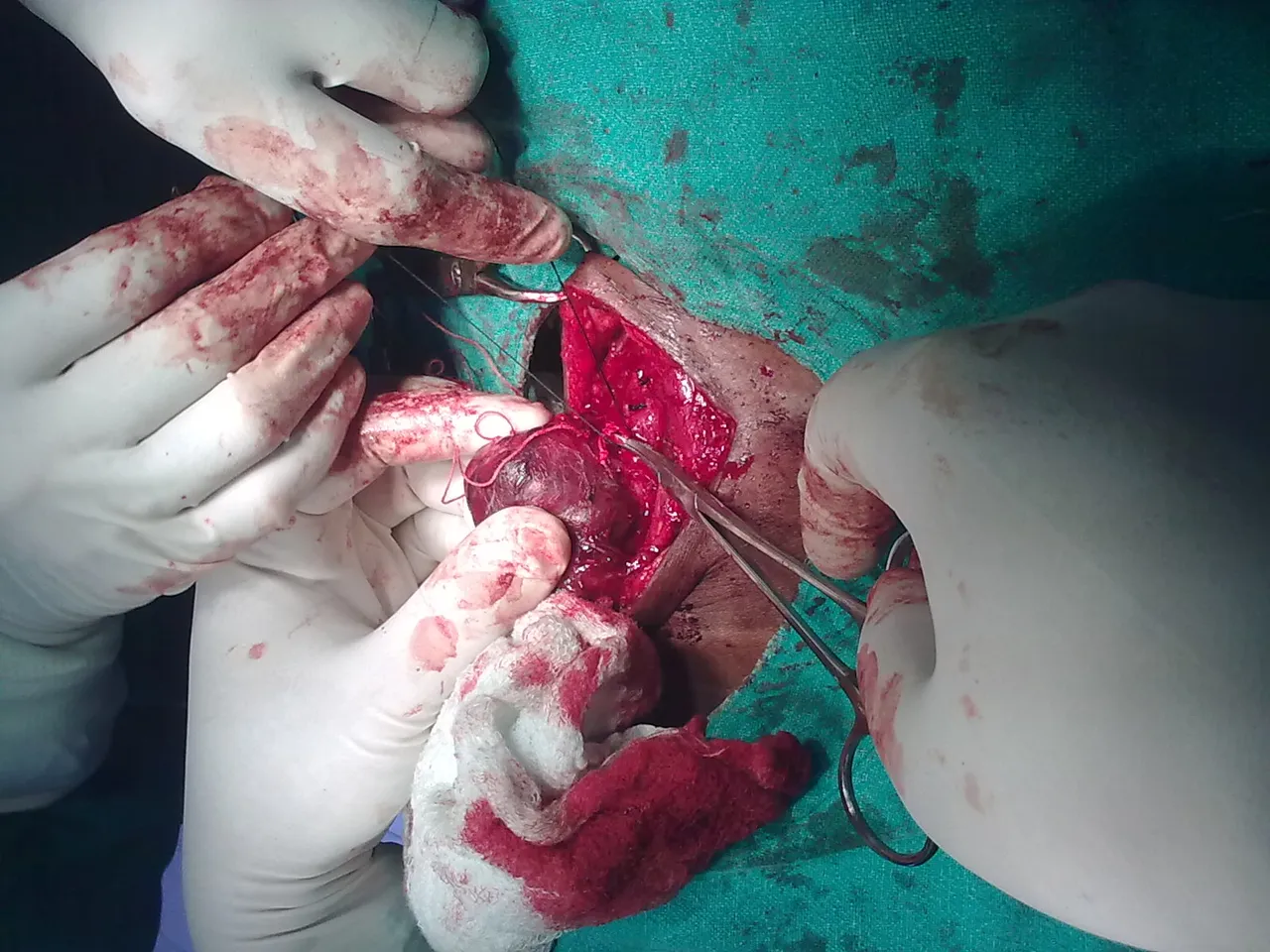
By n.raveender - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia
Thyroid surgeries are always successful but may have some complications to always look out for which include respiratory distress, tension hematoma which occurs from there is bleeding and accumulation of blood at the surgery site, wound infection may occur as well as hypothyroidism, scar formation, thyrotoxicosis crisis, and low calcium levels.
The last treatment option is the use of radioactive iodine therapy which is used to destroy the tissues of the thyroid gland and stop it from oversecreting the hormones. This method can be used when both drugs and surgery options are contraindicated or there is a relapse. However, it cannot be used for children, pregnant and breastfeeding women.
THYROID EMERGENCIES
In some cases, extremely high or low levels of thyroid hormone can present with life-threatening complications which require urgent attention. These are thyroid storm and myxedema coma.
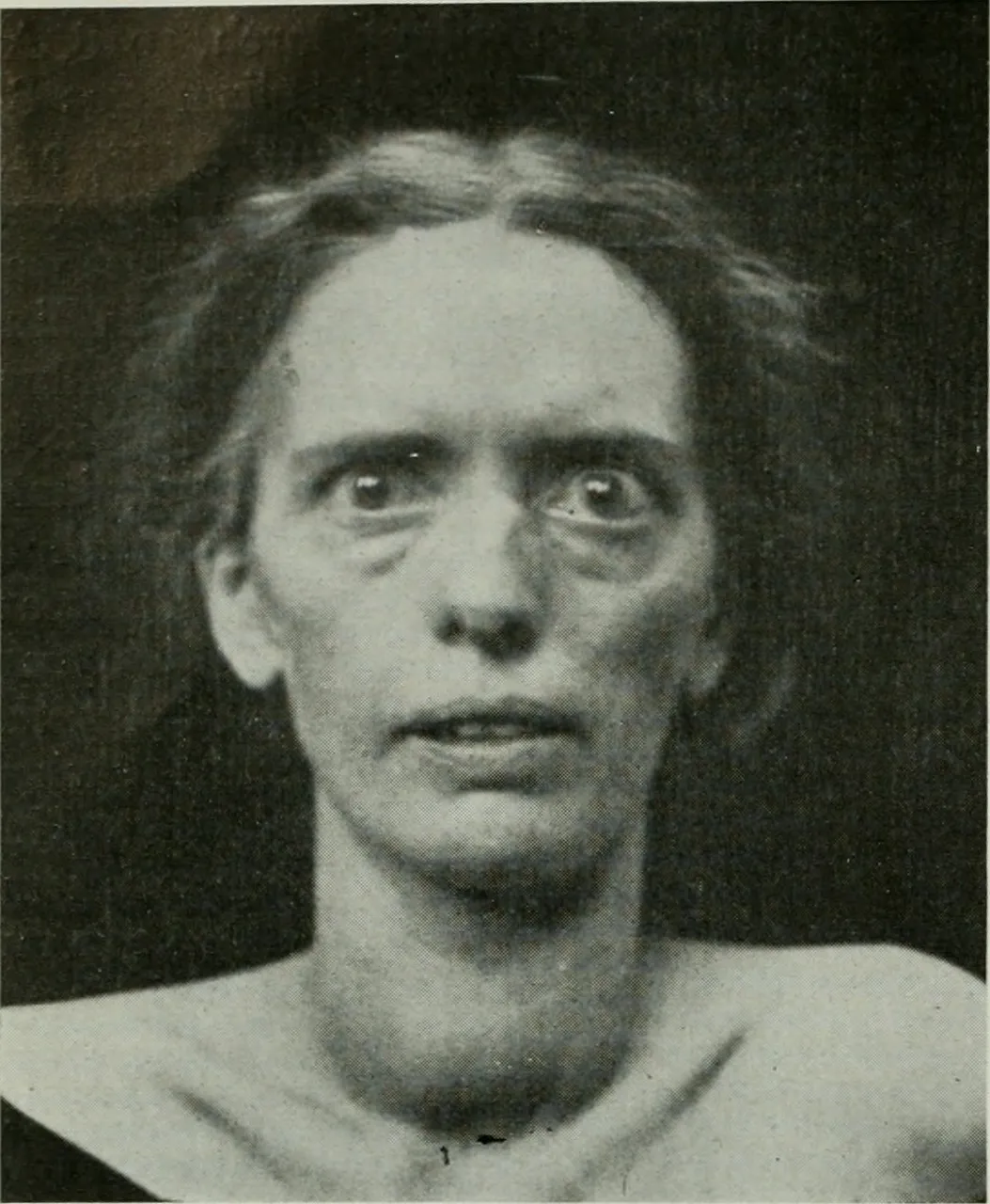
What is a thyroid storm?
This occurs at an extremely high level of thyroid hormone in the body. It is an exaggeration of all the symptoms we saw in hyperthyroidism and at this point, the fire of life (thyroid hormone) is burning fiercely and the body is going haywire. The patient will feel extremely hot with a high fever (hyperpyrexia), profuse sweating, extremely anxious, severely high heart rate, yellowness of the eye, systolic hypertension, wide pulse pressure, diarrhea, etc.
By Internet Archive Book Images, No restrictions, Wikimedia
When this occurs, it is an emergency and managed in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). The patient is exposed and put in ice packs or cooling blankets, and other medications are given like paracetamol to bring down the high temperature, propranolol, antithyroid drugs, steroids, bile acid sequestrants, plasmapheresis, etc.
Myxedema Coma
This is an extremely low level of thyroid hormone. It is an exaggerated state of hypothyroidism and at this point, the body is almost totally shut down. The fire of life has been extinguished. So in this patient, food cannot even move through the digestive system, they are extremely cold with chills, they have heart failure, narrow pulse pressure, somnolence, and lethargy.
This is also an emergency when it occurs and is managed in Intensive Care Unit. They are given warm blankets, warm fluids, steroids are given and then thyroid hormone to replenish the deficiency.
In summary, even though goiter is now rare in some developed countries like America, it is still a common presentation in endemic regions and in many countries especially in Africa. Therefore we must ensure to supplement our diets with iodized salts and as well, avoid or limit the consumption of food or drugs which are goitrogens and can predispose us to goiter.
Thanks so much for reading.
For references and further reading: