Image Source
Brain tumors are a serious and potentially life-threatening medical condition. They occur when abnormal cells form in the tissues of the brain and can range from benign to malignant. Understanding brain tumors and the various symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options available is essential to combat this medical issue. Early diagnosis is key, as timely treatment can often significantly reduce the risk of long-term damage or even death. With the right knowledge, you can be better informed and prepared to take the necessary steps to protect your health. In this article, we will examine the various symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options available to help you better understand brain tumors.
What is a brain tumor?
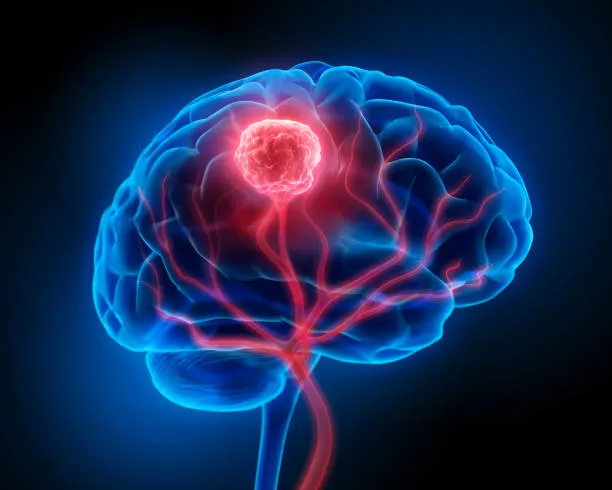
A brain tumor is a mass of abnormal cells that grows in the brain, spinal cord or the tissues surrounding these vital parts of the body. Brain tumors occur when cells in the brain begin to grow out of control and form new masses called tumors. Brain tumors can be either malignant or benign. Malignant brain tumors are cancers that can spread to other parts of the body. Benign brain tumors do not spread outside the brain. However, benign brain tumors can cause serious symptoms and problems, and must be treated. Malignant brain tumors can be life-threatening. Benign brain tumors may also cause serious problems, but they are not likely to spread outside the brain and are not life-threatening. Brain tumors are one of the most common cancers in children, but they can also occur in adults. Brain tumors can affect people of any age, gender, race and ethnicity, but are most frequent in children under the age of 15. It is estimated that each year, approximately 15,000 people in the US will be diagnosed with a brain tumor. The most common types of brain tumors include - Anaplastic Astrocytoma, Astrocytoma, Ependymoma, Glioblastoma, Childhood Brain Tumors
Reference Source
Symptoms of a brain tumor:
The symptoms of a brain tumor vary depending on the type of tumor and location of growth in the brain. Some of the most common symptoms of a brain tumor include -
- headaches
- seizures
- persistently feeling sick (nausea), being sick (vomiting) and drowsiness
- mental or behavioural changes, such as memory problems or changes in personality
- progressive weakness or paralysis on one side of the body
vision or speech problems.
Reference Source
Diagnosing a brain tumor:
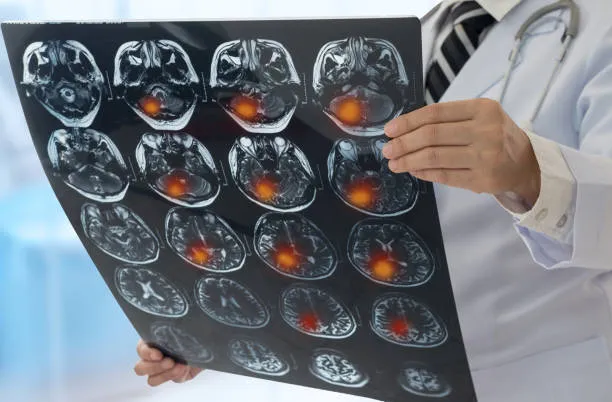
A doctor will perform a physical examination and discuss your medical history to rule out the possibility of a brain tumor. They will take note of any signs and symptoms that you report, as well as perform a neurological exam to assess mental status, motor skills and reflexes. The neurological exam will help determine whether the condition is related to an existing condition or a new onset medical issue. Based on the results of the exam, as well as your medical history and symptoms, a doctor may conduct additional tests to rule out the possibility of a brain tumor. The following tests may be used to diagnose a brain tumor - Laboratory tests - Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans are the most common tests used to diagnose brain tumors. You will lie down on a table and the technician will slide you into a long, narrow tube that contains an extremely strong magnet. The magnet causes the metal in your braces, artificial joints, implanted metal devices, metal in stents in heart arteries, and metallic clips and wires used during surgery to become temporarily magnetized. This allows the technician to move the metal objects away from the area being examined. Brain tumors can be difficult to diagnose due to the lack of specific and consistent symptoms. Imaging tests may reveal certain abnormalities in the brain. These may include -
Reference Source
Types of brain tumors
Brain tumors are typically classified based on their tissue of origin, location and clinical behavior. The most common types of brain tumors include - Meningioma, Childhood Brain Tumors
Treatment options for brain tumors:
The treatment options for brain tumors vary depending on the type and grade of the tumor. Your doctor may suggest surgery, chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy to treat a brain tumor. It is important to note that, in most cases, a combination of the three treatment options will be recommended. Depending on the type and grade of the tumor, doctors may also recommend observation. Treatment options for brain tumors include
- Surgery - Surgery may be recommended to remove the tumor or a part of the brain where the tumor has grown. The surgery may be performed to remove the entire tumor or only a part of the tumor. Special tools may be used to remove a tumor, including lasers, microwaves, electromagnets and ultrasound waves.
Surgery for brain tumors:
Surgery may be recommended to remove the entire tumor, or a part of the tumor, in order to provide relief from symptoms. A neurosurgeon may perform surgery using a craniotomy (the removal of a tumor or a piece of the tumor from the skull) or an endoscopic surgery (a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed with a small camera called an endoscope).
Radiation therapy for brain tumors:
Radiation therapy may be recommended to treat a tumor that cannot be removed surgically. Radiation therapy is a treatment that uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells. In most cases, external-beam radiation therapy is used to treat brain tumors. However, internal radiation therapy may be used in certain cases. External-beam radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send high-energy rays into the brain to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy may be used to treat a tumor in the brain, skull, spine or the nerves around these areas. The type of radiation therapy used to treat a brain tumor depends on the type of tumor.
Chemotherapy for brain tumors:
Chemotherapy may be recommended to treat a high-grade tumor that cannot be removed surgically. Chemotherapy is a treatment that uses anti-cancer drugs to kill cancer cells and stop them from growing. It is important to note that chemotherapy kills both cancerous and healthy cells. It can take time for the healthy cells to grow back after chemotherapy. During this time, you may experience some side effects from the treatment. These side effects may include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fatigue, weight loss and hair loss.
Targeted drug therapy for brain tumors:
Targeted drug therapy for brain tumors is a treatment that uses certain drugs to target specific molecules in cancer cells that help the cells grow and spread. These types of drugs are called targeted therapy. They are designed to treat specific types of cancer rather than treat the symptoms associated with the cancers.
Clinical trials for brain tumors:
Clinical trials are research studies that test new ways to prevent, find, diagnose and treat diseases. Clinical trials are done to find better ways to care for people and sometimes to find new treatments for diseases. Clinical trials are done in phases to find out if new treatments are safe and effective. If you are interested in joining a clinical trial, you should speak to your doctor to find out if you qualify.
Summary:
Brain tumors are a serious medical condition that affects many people each year. Brain tumors are typically classified based on the type of tissue in which they originate and the location of the tumor. The most common types of brain tumors include meningioma, glioblastoma and childhood brain tumors. To diagnose a brain tumor, a doctor may perform various tests such as an MRI, CT scan or blood tests. Treatment options for brain tumors vary depending on the type and grade of the tumor. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy and targeted drug therapy. You may also be able to participate in a clinical trial. With the right knowledge and information, you can better understand brain tumors and their symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options.
Reference:
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brain_tumor
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/brain-tumours/
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/brain-tumor/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350088#:~:text=Magnetic%20resonance%20imaging%20