Fat has received a lot of attention throughout history, and in recent times, it has garnered even more focus. Often viewed as the villain of the body due to its association with various health issues, fat is essential for human survival.
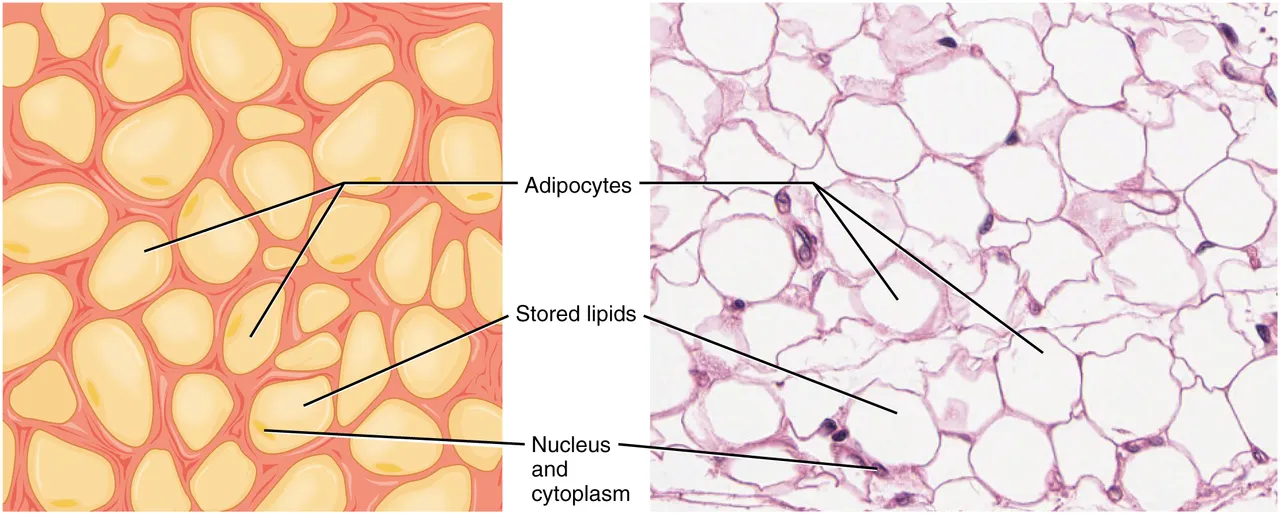
Fat, also known as adipose tissue, is a type of connective tissue composed of adipocytes that store energy as triglycerides. It serves several important functions, including energy storage, heat production, insulation, hormone production, and protection as a cushion for organs.
Our early ancestors had no means of storing food, so they needed to consume large quantities to ensure they had enough to eat during lean times. When the body digests food, any excess is stored as fat, which was crucial for the survival of our hunter-gatherer ancestors.
A healthy lean male typically has a body fat percentage of about 10-15%, while a healthy lean female usually has a body fat percentage of around 20-25%. These differences can be attributed to hormones like testosterone and estrogen, where testosterone helps reduce body fat and stimulates muscle protein synthesis while estrogen increases fat deposition in the areas of the hips, thighs, and breast. Females need more fat for the survival of both mother and child while males don't need much as their job is hunting and protection, so the stored fats are being used for muscle mass instead of building up fat storage for energy reserves in times when food will be scarce.
Have you heard that low fat in women can cause menstrual disruption and this is the body's way of saying there isn't enough fat stored for pregnancy? Depending on the color and location, fat can be categorized. In the aspect of color, fat can be categorized as white fat or brown fat, and we adults have the majority of our fat as white fat. Brown fat on the other hand is found in infants and children and it is rich in red blood cells and has mitochondria. Both fats are involved in thermal regulation. White fat doesn't produce heat, it prevents the heat from leaving whereas brown fat can produce heat.
Depending on location, we have the subcutaneous fat and visceral fat, with the subcutaneous fat found beneath the skin, between the epidermis and the dermis of the skin. Both visceral and subcutaneous fat are white fats responsible for preventing heat from leaving the body.
If fat has been spelled out to you in the past negatively, it is time you begin to understand the good part about it, so do not begin to work towards zero fat in your body in the guise to lose body fat.
REFERENCE
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3648822/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555602/
https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/eat-well/food-types/different-fats-nutrition