The wc command in Linux is a simple tool that allows you to count the number of words, lines, and characters in a file or output. Here are the basic steps to use the wc command.
The first thing you need is to open a terminal window in Linux. This can often be done by using the CTRL-T combination.
Type the following command to count the number of words, lines, and characters in a file:
wc /path/to/file
Replace "/path/to/file" with the path to the file you want to count. For example, to count the number of words, lines, and characters in a file called "file.txt" in the home directory, you would type:
wc /home/file.txt
If you want to count the number of words, lines, and characters in the output of a command, you can use a pipe to send the output to the wc command. For example, to count the number of words, lines, and characters in the output of the "ls" command, you would type:
ls -l | wc
This will list all files in the current directory, and then count the number of words, lines, and characters in the output.
Once you've entered the appropriate command, press "Enter" to execute it. The wc command will count the number of words, lines, and characters in the file or output and display the results.
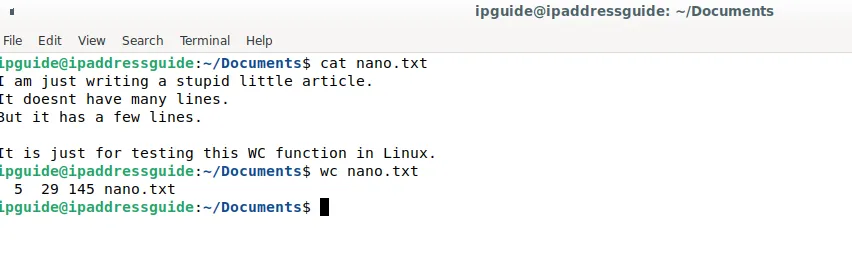
By default, the wc command displays the number of lines, words, and characters in that order. You can also use various options to display only the counts for specific fields or to count only certain types of characters. For example, the "-l" option will display only the number of lines, and the "-c" option will display only the number of characters. To find out more about the options available for wc, you can type "man wc" in the terminal to view the manual page for the command.