Articulating the distinction between cognition and metacognition is the key to understanding metacognition
Image Source
Metacognition characterized by Nelson as the scientific study of a person's cognitions about his or her own cognitions. It is a subset of cognition, a specific sort of cognition. Garner and Alexander distinguished cognitive procedures as exercises for cognitive improvement and metacognitive methodologies as exercises for monitoring cognitive procedures.
Cognitive skills encourage assignment accomplishment, and metacognitive skills help to regulate undertaking accomplishment. Some exploration has upheld the refinement amongst cognition and metacognition. For instance, there is prove that metamemory shortfalls can exist without memory debilitation, so memory and metamemory are particular.
Swanson gave proof to the autonomy of metacognition from general inclination by discovering students with large amounts of metacognitive skill outflanked students with low levels of metacognitive skills on critical thinking assignments paying little heed to general bent.
In spite of the fact that Hacker alluded to the easy refute issue of whether contemplations that were at first metacognitive yet are currently nonconscious and programmed can in any case be thought about metacognition, he recommended that most analysts view metacognitive idea as cognizant and deliberate thinking.
Paris and Winograd restricted their origination of metacognition to knowledge about cognitive states and capacities that can be shared among individuals. Another essential refinement is that amongst metacognition and self-regulation. Paris and Winograd noticed that a few specialists likewise incorporate an emotional part in their meanings of metacognition, for example, metacognitive convictions or attributions.

Image Source
3 Interrelated parts of metacognition by Borkowski
- Knowledge
- Judgments and monitoring
- Self-regulation
Borkowski's perspective of metacognitive knowledge compares to Flavell's classes of individual, errand, and methodology. Judgments and monitoring allude to forms happening while at the same time playing out an undertaking, for example, a sentiment knowing or understanding monitoring. Self-regulation alludes to adjusting skills and techniques to meet evolving requests.
Zimmerman, in any case, contended that self-regulation includes more than metacognitive knowledge and skill, it includes a basic feeling of self-efficacy and individual agency and the motivational and behavioral procedures to put these self convictions into impact.
A learner could have very much created metacognitive knowledge yet be not able self-regulate in a particular setting. Self-regulated learning alludes to the ability to assemble, coordinate, and maintain one's instructional endeavors. In this manner, self-regulated learning is more than metacognitive knowledge and skill.
Individual impacts of self-regulated learning:
- Emotional process
- Behavioral
- Social environment
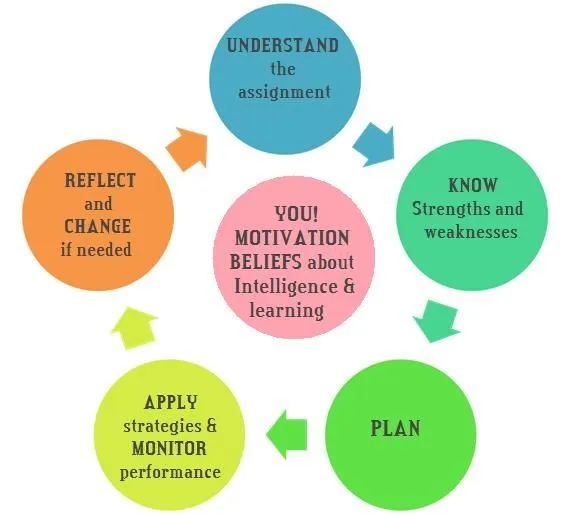
Image Source
How does the idea of metacognition fit into hypotheses of cognitive advancement?
In spite of the fact that the fundamental thought of metacognition, thinking about thinking, has been generally connected with Piaget's phase of formal activities, the idea has pertinence for other hypothetical points of view in cognitive advancement.
The centrality of metacognition to cognitive advancement was featured by Flavell when he contended that the nature and improvement of metacognition and of cognitive monitoring and regulation is right now rising as an intriguing and promising new zone of examination.
He depicted young children as being restricted in their knowledge about cognitive phenomena and as neglecting to screen memory and cognizance. He built up a model of cognitive monitoring that he sought would fill in as an objective after advancement.
Cognitive improvement happens through;
- Interactions among metacognitive knowledge
- Metacognitive experiences
- Goals
- Actions
Metacognitive knowledge is stock knowledge about individual, undertaking, and methodology factors. Metacognitive encounters are the things of metacognitive knowledge that have entered cognizance. Through metacognitive encounters, the stock metacognitive knowledge can be adjusted by including, erasing, or overhauling data Paris and Winograd explained on the vital part of metacognition in cognitive advancement by belligerence that metacognition is both a product and producer of cognitive improvement.

Image Source
References:
Katherine Nelson's
Functional Approach to Language and Cognition
Metacognitive Theories
The concept and Instruction of Metacognition
Metacognition: Theory or Chapter Heading?
Metacognition Flavell