Probably you've heard that HIV virus can't infect some people; here's the three major reasons some people are resistant to HIV virus.
Unarguably, the word HIV/AIDS has been known by 60% of the human race, and
a little knowledge of this virus has reached 2/3 of adults humans world wide. This is because of World Health Organization (WHO), Government, Non Governmental Organizations (NGOs) and individual effort to raise campaign and create awareness over this deadly immuno virus.
HIV; simply means, Human Immune Virus, in this effect it's a virus that attack the body immune system, (it attack the immune cells and mechanism)
This virus was discovered in the year 1983 in by scientists at the Pasteur Institute in France.
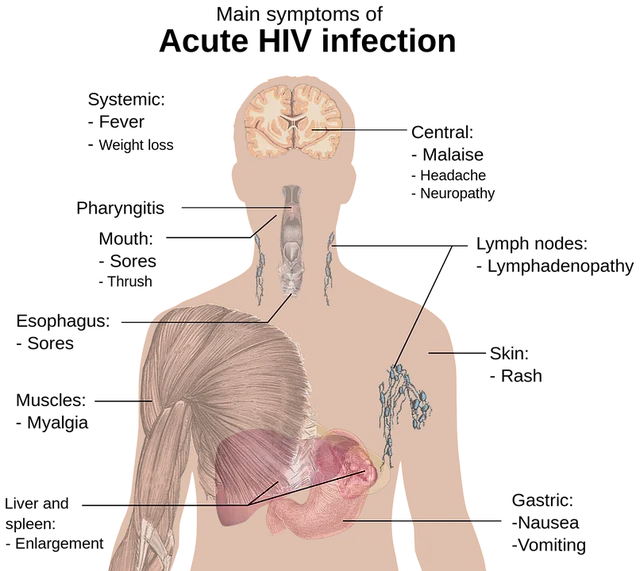
HIV on it own doesn't cause any diseases in the body, it only focus on degenerating the body defense mechanism (immune system), there by exposing the body to a wide range of opportunistic infections which develops with many visible symptoms, as may be in the figure below, (listed as symptoms of acute HIV infection).
The progressive degeneration of the body immune system enhances the situation referred to as Chronic HIV infection, at the stage the viral load in the body has increased and CD4 cells gone low below normal range. At this stage the the case is referred to as AIDS
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. (AIDS):
At this stage the viral load is assumed to be above 100,000 copies and CD4 cells below 200/mm³.
The symptoms that follows include;
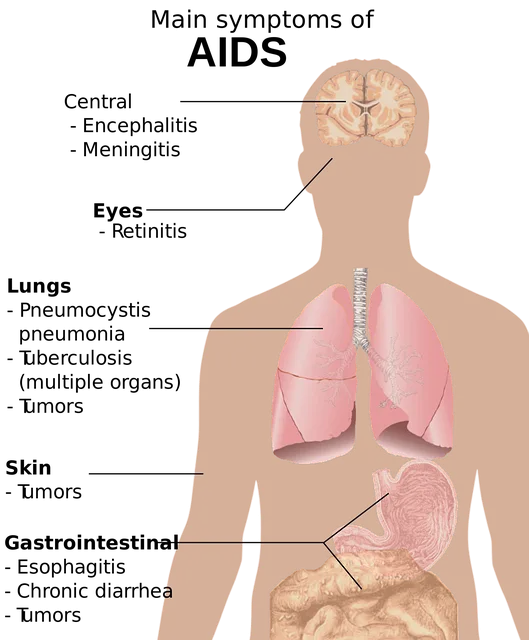
The above image is a brief description of what happens during this stage
Note before that; Viral load is the amount of the virus in the body.
CD4 count is the measure or the estimate of the immune cells there's in the body fighting against this virus.
From here, we go straight to the main topic of this article, the three reasons why HIV virus can't infect some people.
For the sake of the audience, especially those in other field of study outside medical field, I will make it concise so that they can follow through and appreciate it as well
You probably have heard that some people can't contract this deadly virus, is this really true ??, Yes of course.
There is a little population among the human race that can't get infected by HIV virus, because they are resistant to the virus
Let's devour the secret behind this claim.
Strong immune system:
For the purpose of this study, I'm making reference to first line of body defense here, (natural barriers) and the homoral secretions.
In immunology, the natural barriers include the skin, the hairs, nails etc.
Homoral secretions include the; the saliva, tears, mucous, and even the blood rushing out at the sight of injuries.
All this constitute the first line of body defense, during exposure to infection. By this the body resist the virus entrance into the body, the secretions, help to trap bacteria and viruses, and prevent them from entering in to blood stream. Recall that a virus must get attached with it's specific receptor cell before expression of the virion and replication. By implication, on the effective resistance by the first line of body defense to this virus, the person becomes resistant to the HIV virus on this very exposure to the virus.
High cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and Cytokines :
Cytotoxic cells are also referred as "cell eating cells or killer cells". The Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes eat up tumor cells, bacteria cells and virus infected cells at their contact, because this cell are toxic to foreign bodies, they're cell mediated.
They include; CD8+ cell, CD4+ cell, T-helper cells, Regulatory T-cells, and Cytokines.
I will take it one by one for further understanding, but please don't get lost or confused along the line.
CD8+ cells
This is known as "killer T-cells, they're able kill virus infected cell, as well as cancer cells.
CD8+ also make use of Cytokines to recruit and interact with other cells during immuno response.
CD4+ cells: it serves as a co-receptor found on other immune cells like "macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells and T-helper cell, it has wide range of functions in the body especially at engulfing of diseases body.
T-helper cells: send signal to other immune cells including the CD8 cell to attack antigenic cells. They generally have the function on activating the B-LYMPHOCYTE and T-LYMPHOCYTE over antigenic stimulations to increase immunological response.
They are also referred to as CD4 cells, (because of the attachment of CD4 cells as co-receptor on the surface of this cell)
Regulatory T-cell: prevent auto-immune attack, they distinguish the body cell from the invading cells thererby preventing the body from attacking itself. It's also called a suppressor cell.
Dysfunction of this cell results to auto-immune diseases.
Cytokines; are very important cell signaling agent, very important in immune system, acting through cell surface receptors.
Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling as immunomodulating agents. Their definite distinction from hormones is still part of ongoing research.
Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell.
They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the balance between humoral and cell-based immune responses, and they regulate the maturation, growth, and responsiveness of particular cell populations. Some cytokines enhance or inhibit the action of other cytokines in complex ways. They are different from hormones, which are also important cell signaling molecules.
The high production and release of this Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and Cytokines protect the body against HIV virus, the Cytokines acting on the surface receptors, reduce the viral entry and attachment in the CD4 cells (note that; HIV has a specific receptors in CD4 cells), where the virus is attacked by other T-cells on recognition.
This whole mechanisms make some people with very high amount Cytotoxic T-cells and Cytokines in there body resistant on exposures to this virus.
Mutation (The CCR5 delta 32 mutation):
Mutation is the change in the genetic make up of a cell (body).
The HIV has a specific receptor on the CD4 (white blood) cell called CCR5, this enable it to bind with the white blood cell.
The "CCR5 delta 32 mutation" is a mutation found on the surface of the white blood cells (CD4) too that disables the CCR5 receptor on the surface of the white blood cells.
This mutation CCR5-delta 32, hampers the ability of HIV virus to infiltrate immune cells.
The recent discovery of the mutation on some individual has raised so much light and arguments too in the modern medicine.
The mutation literally disables this virus attachment by changing the position of the CCR5 co-receptor on the surface of the immune cell and making it to develop smaller than normal.
Study has also shown that only a little population of individuals has this mutated Gene in Europe and the United States.
The CCR5 delta 32 mutation, which was discovered over 20 years ago, disables the CCR5 receptor on the surface of white blood cells. HIV uses this receptor almost like a key -- it latches onto it to get into the cell. Without a working version of CCR5, HIV is essentially locked out of person's immune system. The mutation is most common among people of Northern European descent. Approximately 10% of people in Europe and the United States have inherited this from one of their parents, but it is only protective in the 1% who are homozygotes -- meaning they inherited a mutated gene from both of their parents. Studies have shown that these individuals are 100 times less likely to contract HIV if exposed to the virus
This however make it possible for individuals who're homozygous to this mutated gene to be resistant to HIV virus even on repeated exposure to this virus.
I'm sure I have done justice to this topic, you can leave your comments below.
Thanks very much for your time.
Reference
illustrations/hiv-aids-png-1-2-human-body-study