The brain is the control center of the body, responsible for numerous commands, including movement, thoughts, processing visual commands, and so on. A lot can go wrong when there is an issue with the brain, such as a stroke. So what happens when there is a stroke, and how does it affect the brain?
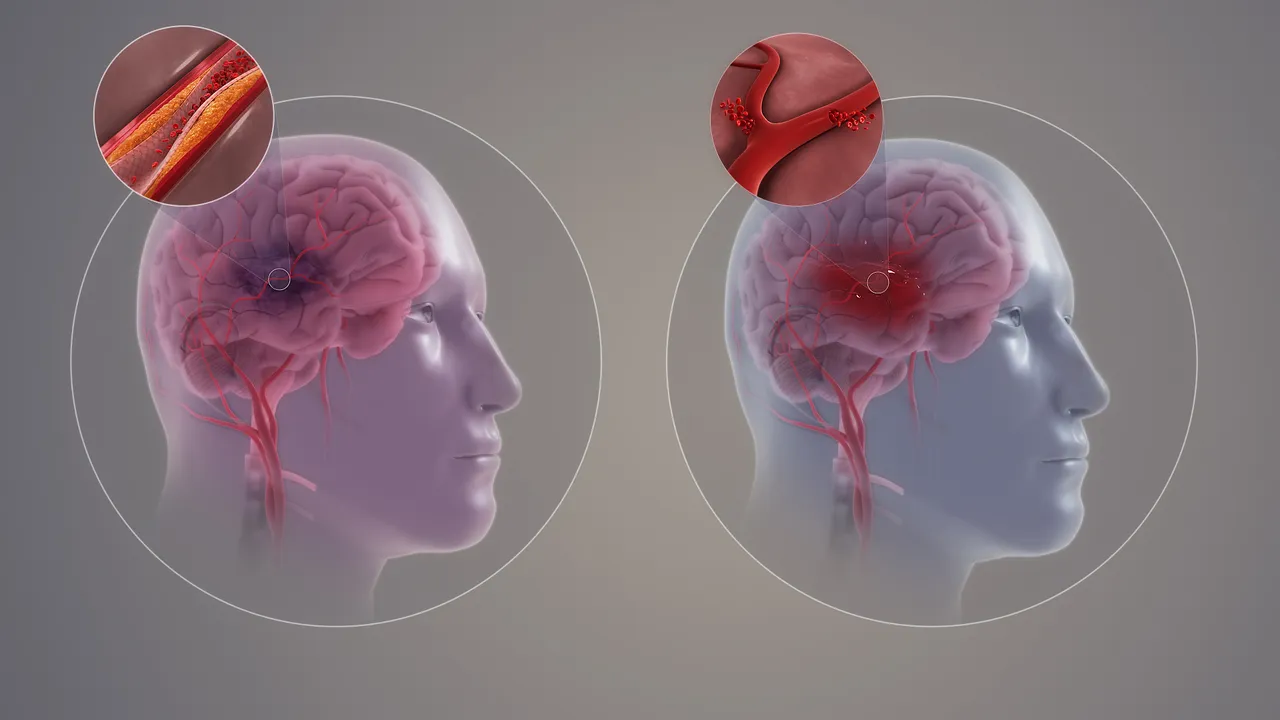
Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and disability. A stroke occurs when there is a disruption to blood flow to part of the brain causing brain cells to be starved of oxygen and nutrients. Within 4 to 6 minutes, brain cells begin to die. This stroke can be ischemic or hemorrhagic with the first being a blockage in the vessels and the other being a burst in the vessel. Hemorrhagic strokes are less common with an occurrence of about 15% of the time, but they are very severe when they happen. On the other hand, ischemic strokes are very common.
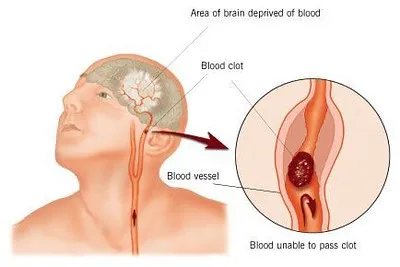
The carotid artery supplies the head with blood with the external carotid artery supplying the face with blood while the internal carotid artery supplies the brain. When the vessel enters the brain, it becomes smaller capillaries supplying blood to every part of the brain. With ischemic stroke, a blood clot prevents the flow of blood to the brain. The blood clot could be a thrombus or an embolus with the first being a clot forming in the artery while the other being a clot that travels from elsewhere to block the passage.
When there is a blockage, the brain tissue around the blocked area starts to die immediatellly but around the penumbra, there is damage as a result of reduced blood flow, and these tissues can be saved within a short time if properly attended to. With stroke, the internal cerebral artery is the most commonly blocked artery during an ischemic stroke. The artery supplies a large portion of the cerebrum which is responsible for motor function, sensation, and language skills. This is why you would have seen that the majority of the stroke incidents you see suffer weakness or paralysis on one side of the body, diminished sensation, trouble speaking, and loss of vision.
A major cause of blockage with stroke is atherosclerosis is plaque built up in the arteries. This plaque is made up of cholesterol, fat, and calcium, narrowing the vessels. A rupture of the plaque leads to a clot in the area of the vessel. A blood clot breaking loose from somewhere else could move from another part of the body like the heart to get to the brain.
People who suffer a stroke might not be able to raise one of their hands, suffer from drooling, slurred speech, nausea, sudden confusion, dizziness, and severe headaches, and the faster one acts, the better it is at saving brain tissue. The goal when treating a stroke is to restore blood flow as soon as possible so the use of clot-busting drugs can be used. In all you do, try to keep your blood pressure low because high blood pressure is the number 1 risk factor for both stroke.
Read More
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/stroke/
- https://www.cdc.gov/stroke/signs-symptoms/index.html
- https://www.stroke.org/en/about-stroke
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/stroke
- https://www.stroke.org/en/about-stroke/types-of-stroke/ischemic-stroke-clots
- https://dpuhospital.com/blog/blood-clot-in-brain-risks-symptoms-treatments-prevention/
- https://psrihospital.com/causes-symptoms-treatment-of-blood-clot-in-brain/
- https://www.nanavatimaxhospital.org/blogs/blood-clot-in-brain-symptoms-diagnosis-and-treatment
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/cerebral-venous-sinus-thrombosis