Spacetime is a mathematical concept that combines space and time into a single, unified entity. It is a fundamental part of the theory of relativity, which was developed by Albert Einstein in the early 20th century.
In everyday life, we experience space and time as separate and distinct entities. We move through space and experience the passage of time as we age. However, Einstein's theory of relativity showed that these two concepts are actually interconnected and cannot be thought of as separate from one another.
According to the theory of relativity, the laws of physics are the same for all observers, no matter how fast they are moving. This means that the passage of time and the distance between objects can change depending on the observer's frame of reference.
For example, if an object is moving at a high speed, time will appear to pass more slowly for that object compared to an object at rest. This phenomenon, known as time dilation, has been confirmed through experiments and is an important aspect of spacetime.
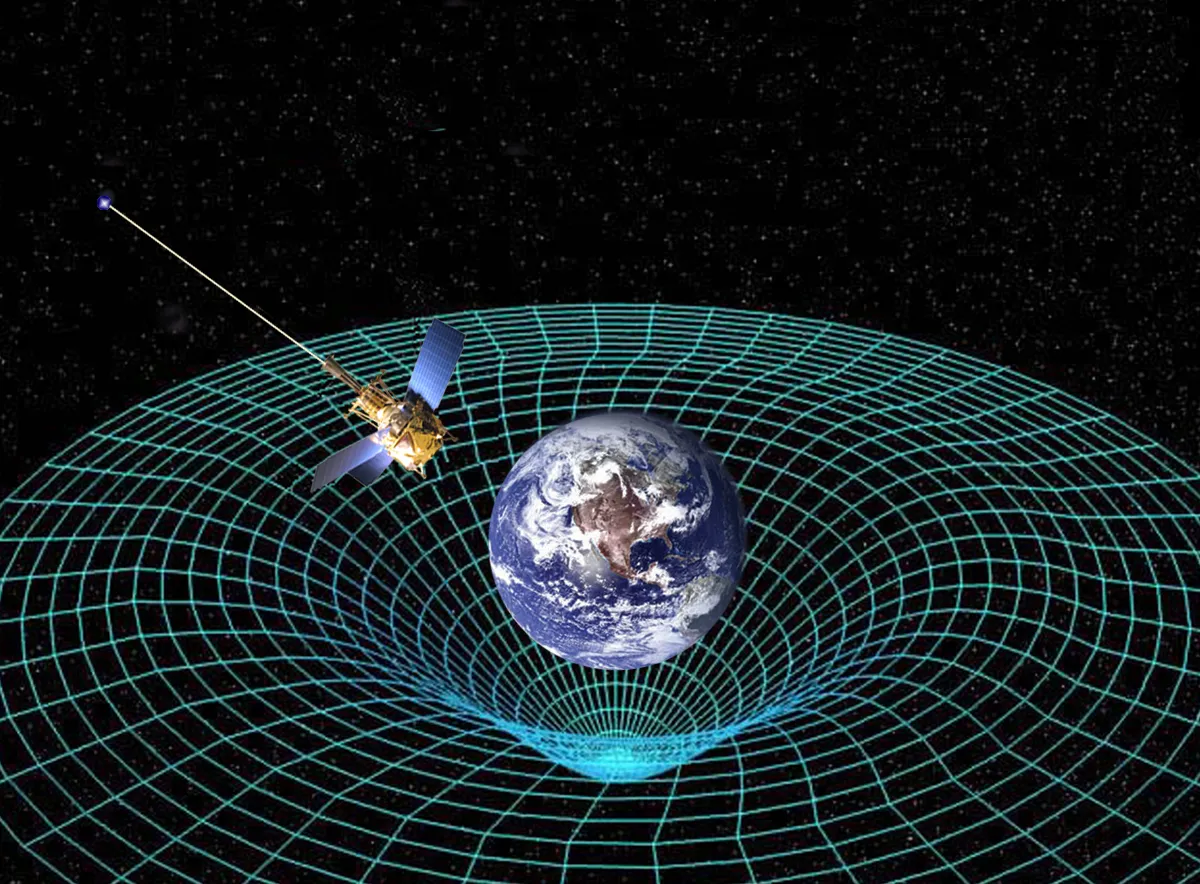
Another key aspect of spacetime is the concept of curvature. In Einstein's theory, the presence of mass or energy causes spacetime to curve. This curvature can affect the paths of objects moving through spacetime, causing them to follow a curved path rather than a straight line.
One of the most famous examples of this curvature is the way that light bends as it passes through a gravitational field, such as the one created by a planet or a star. This phenomenon, known as gravitational lensing, has been observed and measured in numerous experiments.
Spacetime is a complex and fascinating concept that has changed our understanding of the universe and the way we think about time and space. It continues to be an active area of research and exploration in physics and astronomy.