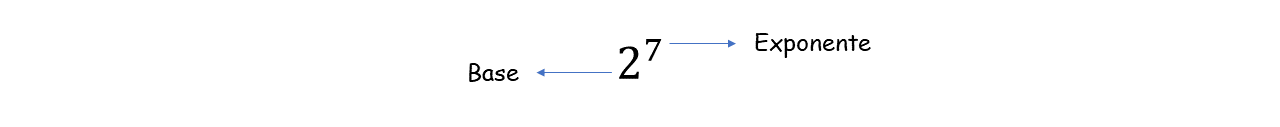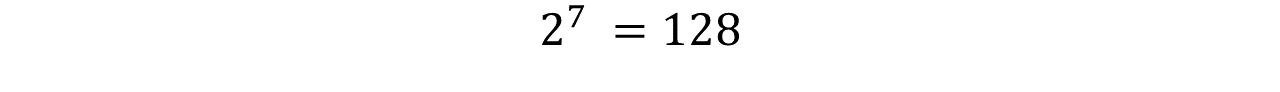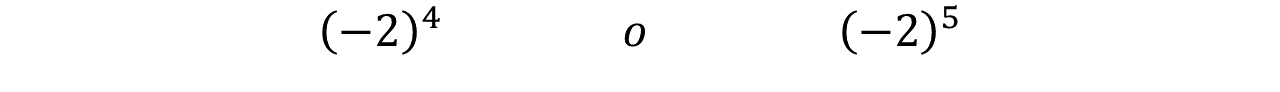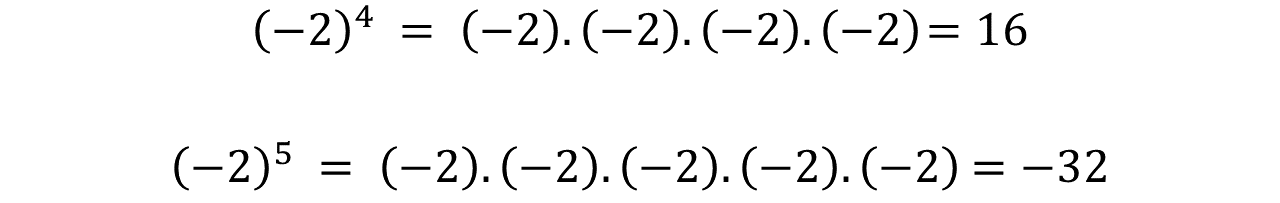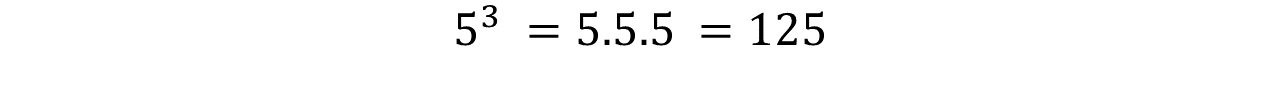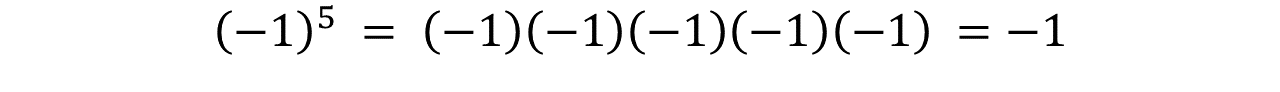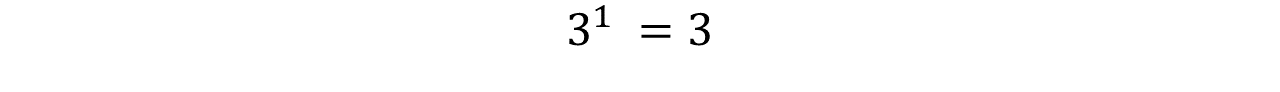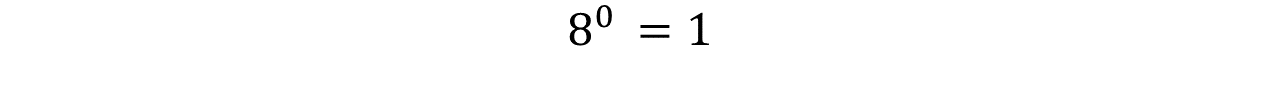¡Hola querida comunidad científica de #Hive, reciban todos un cordial saludo!🖐
Hello dear #Hive scientific community, receive warm greetings from all of you!🖐
La Potenciación es uno de los principios básicos de la matemática, con diversas aplicaciones. Es necesario conocer de ello para la conversión de unidades, la formulación de modelos matemáticos aplicados en diferentes ramas de la Biología, el estudio de funciones polinómicas, exponenciales y logarítmicas. También es necesario conocer de este tema para comprender contenidos de Biomecánica, Electroquímica, Termodinámica Biológica, Naturaleza Atómica de la materia, entre otros.
Potentiation is one of the basic principles of mathematics, with various applications. It is necessary to know this for the conversion of units, the formulation of mathematical models applied in different branches of Biology, the study of polynomial, exponential and logarithmic functions. It is also necessary to know this topic to understand contents of Biomechanics, Electrochemistry, Biological Thermodynamics, Atomic Nature of matter, among others.
Imagen realizada con la página web de diseño gráfico y composición de imágenes Canva // Image made with the graphic design and image composition website Canva.
La verdad, es que son innumerables las diferentes aplicaciones que la Potenciación tiene en las ciencias naturales, y no solo en ciencias sino en la cotidianidad, ya que su objetivo de alguna manera es simplificar operaciones como la multiplicación.
Pero, ¿Qué es una potencia? Una potencia es una operación matemática que consiste en multiplicar un número por sí mismo, la cantidad de veces que lo indique otro número llamado exponente. Esto quiere decir que, para que exista la Potenciación se deben considerar dos cifras.
Cómo acabamos de mencionar la Potenciación es una operación que relaciona a dos números, una base y un exponente, como se logra observar el siguiente ejemplo:
The truth is that there are innumerable different applications that potentiation has in the natural sciences, and not only in science but also in everyday life, since its objective is to simplify operations such as multiplication.
But, what is a power? A power is a mathematical operation that consists of multiplying a number by itself, the number of times indicated by another number called exponent. This means that, in order for a power to exist, two numbers must be considered.
As we have just mentioned, potentiation is an operation that relates two numbers, a base and an exponent, as we can see in the following example:
La base es el número de tamaño normal, el cuál indica que será multiplicado por sí mismo, mientras que el exponente, es el número más pequeño encargado de decidir cuantas veces debe multiplicarse.
Según él ejemplo propuesto, se debe multiplicar el número 2 por sí mismo 7 veces, de ésta manera: 2 . 2 . 2 . 2 . 2 . 2 . 2 Cuando se hace la multiplicación, se obtiene que el resultado es 128 y se puede escribir de la siguiente manera:
The base is the normal size number, which indicates that it will be multiplied by itself, while the exponent is the smallest number in charge of deciding how many times it must be multiplied.
According to the proposed example, the number 2 must be multiplied by itself 7 times, in this way: 2 . 2 . 2 . 2 . 2 . 2 . 2 . 2 . 2 . 2 . 2 When the multiplication is done, the result is 128 and can be written as follows:
Otro ejemplo puede ser 3 . 3 . 3 . 3 la cual también se puede escribir como 3 elevado a la 4, lo que significa que el número 3 ha sido multiplicado por sí mismo cuatro veces. Esta expresión se lee como “tres elevado a la cuarta potencia, o simplemente tres elevado a la 4.
Cabe resaltar que existen varios tipos de potencia, en esta ocasión desarrollaremos Potenciación de enteros, tanto positivos como negativos, así como potencias de números racionales.
En la Potenciación de números enteros pueden ser positivos y negativos, así que se puede presentar potencias cuya base sea un número negativo. ¿Cómo se trabaja la Potenciación cuando la base es negativa? Estas potencias se caracterizan por tener un número negativo en la base y un paréntesis que los encierra.
Por ejemplo:
Another example might be 3 . 3 . 3 . 3 which can also be written as 3 to the 4th power, meaning that the number 3 has been multiplied by itself four times. This expression is read as "three raised to the fourth power, or simply three raised to the 4th power.
It is worth noting that there are several types of power, this time we will develop Powering of integers, both positive and negative, as well as powers of rational numbers.
In the powering of integers they can be positive and negative, so we can present powers whose base is a negative number. How do we work with powering when the base is negative? These powers are characterized by having a negative number in the base and a parenthesis enclosing them.
For example:
Sin embargo, cuando la potencia presenta una base negativa hay que tener claras dos propiedades:
- Si el exponente es un número par la potencia es positiva
- Si el exponente es un número impar la potencia es negativa.
Veamos los ejemplos señalados anteriormente:
However, when the power has a negative base, two properties must be clear:
- If the exponent is an even number the power is positive.
- If the exponent is an odd number the power is negative.
Let us look at the examples given above:
Efectuaremos las siguientes potencias:
We will perform the following powers:
Para el primer ejercicio, tal como lo indica la definición de potencia, vamos a multiplicar la base tantas veces como indique el exponente.
For the first exercise, as the definition of power indicates, we are going to multiply the base as many times as the exponent indicates.
Cómo la base es positiva el resultado es positivo.
As the base is positive, the result is positive.
En el segundo ejemplo podemos ver qué la base es un número negativo cómo la definición dice que se multiplica la base tantas veces lo indica el exponente. Está regla también aplica para el signo que acompaña la base.
In the second example we can see that the base is a negative number as the definition says that the base is multiplied as many times as the exponent indicates. This rule also applies to the sign that accompanies the base.
Al aplicar las leyes de los signos podemos demostrar que cuando la base es negativa y el exponente impar el resultado es negativo.
Continuando con el tema, es recomendable conocer sobre las potencias con exponentes 0 y 1. Este tipo de potencias hacen parte de un grupo de potencias especiales, las cuales tienen algunas reglas que facilitan encontrar el resultado.
- Toda potencia con exponente 1, es igual a su base
Ejemplo:
By applying the laws of signs we can show that when the base is negative and the exponent is odd, the result is negative.
Continuing with the topic, it is advisable to know about powers with exponents 0 and 1. This type of powers are part of a group of special powers, which have some rules that make it easier to find the result.
- Any power with exponent 1, is equal to its base.
Example:
Toda potencia con exponente 0, es igual a 1
Ejemplo:
Any power with exponent 0 is equal to 1.
Example:
Ya para despedirme, agradezco a quienes se tomarnos unos minutos de su tiempo para leer mi publicación y me encantaría poder leer en los comentarios sus opiniones e impresiones sobre el tema.
In closing, I would like to thank those of you who took a few minutes of your time to read my publication and I would love to read in the comments your opinions and impressions on the subject.
Referencias
Baldor, A. (1941). Algebra. México, Publicaciones Cultural.
Hinds, J. (2002). Matemática 8. Caracas, Editorial Premier.
References
Baldor, A. (1941). Algebra. Mexico, Cultural Publications.
Hinds, J. (2002). Matemática 8. Caracas, Editorial Premier.
Translator Deepl