This ensure that at least one of this conditions can not cope by preventing occurrence of a deadlock.
- MUTUAL EXCLUSION
Not require for shareable resources must hold for non-shareable resources. - COLD MUD
This must guarantee that when ever a process requests a resources, it does not hold any other resources. - NO PREMPTION
If a process that is holding some resources request another resources, that can not be immediately allocated to it, then all the resources currently being hold are released. - CIRCULAR WAIT
Impose in total ordering of all resources types and require that each process request resources in an increasing order of enumeration.
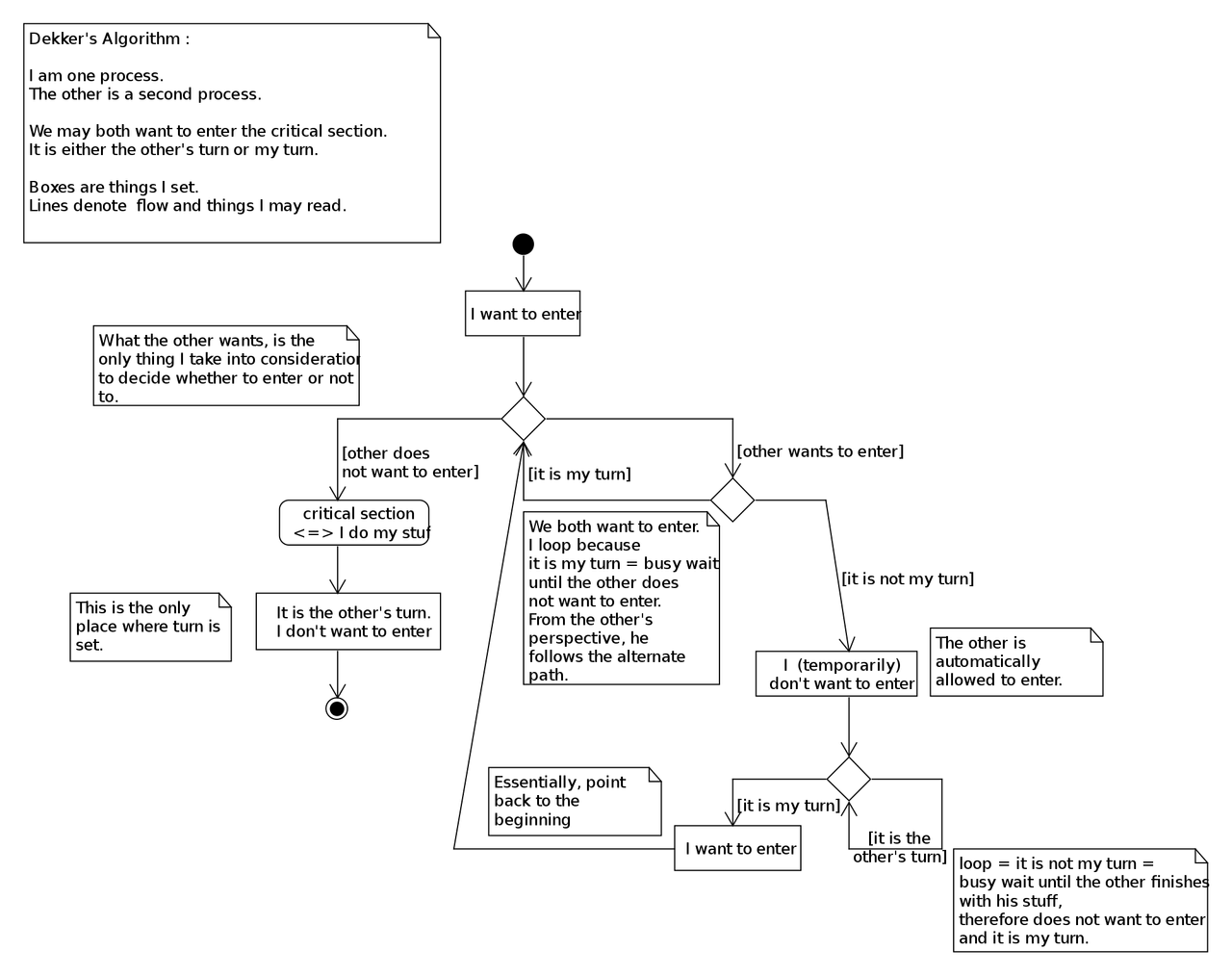
Image credit: Wikimedia Commons, public domain
- Simplest and the most useful model requires that each process declare the maximum number of resources of each type that it may need.
- The deadlock avoidance algorithm dynamically ex-ermines the result allocation state to the ensure that there can never be a circular wait condition. Resources allocation state as defined by the number of available and allocated resources and the maximum demands of the processes.
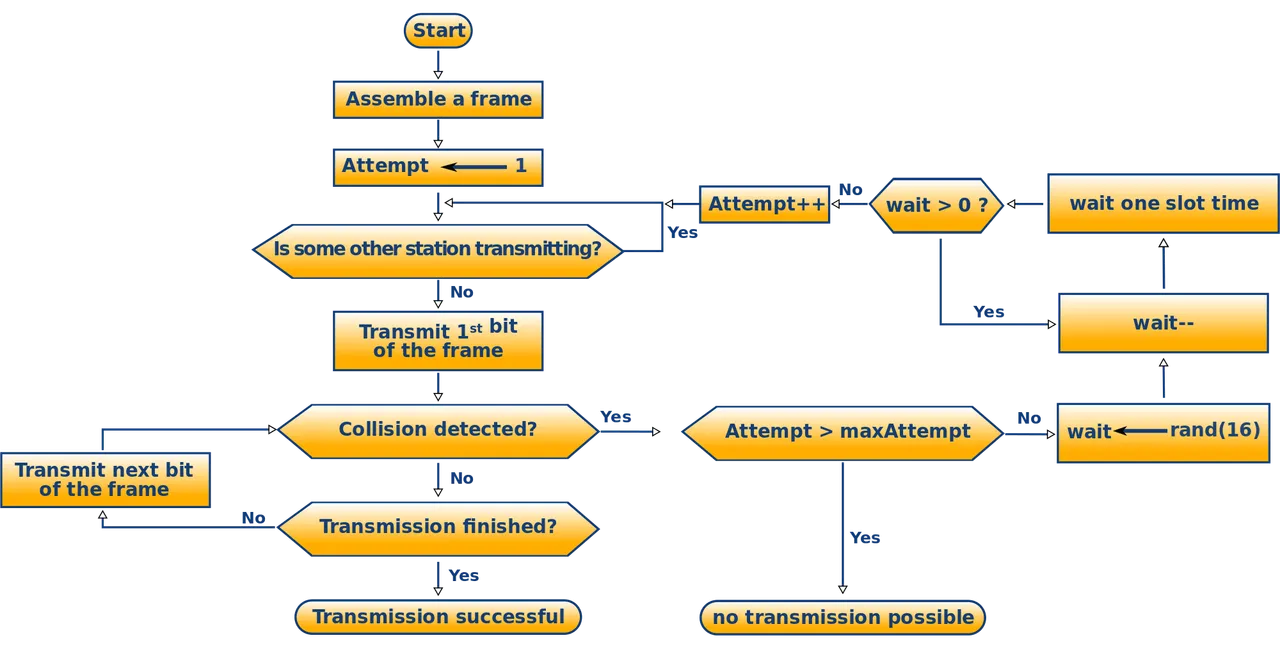
Image credit: Wikimedia Commons, public domain
If the system doesn't employ a deadlock prevention or a deadlock avoidance. An algorithm then a deadlock situation may occur. In those environment the system must be able to provide.
- An algorithm that ex-ermine the state of a system to determine if a deadlock has occurred.
- An algorithm to recover from a deadlock.
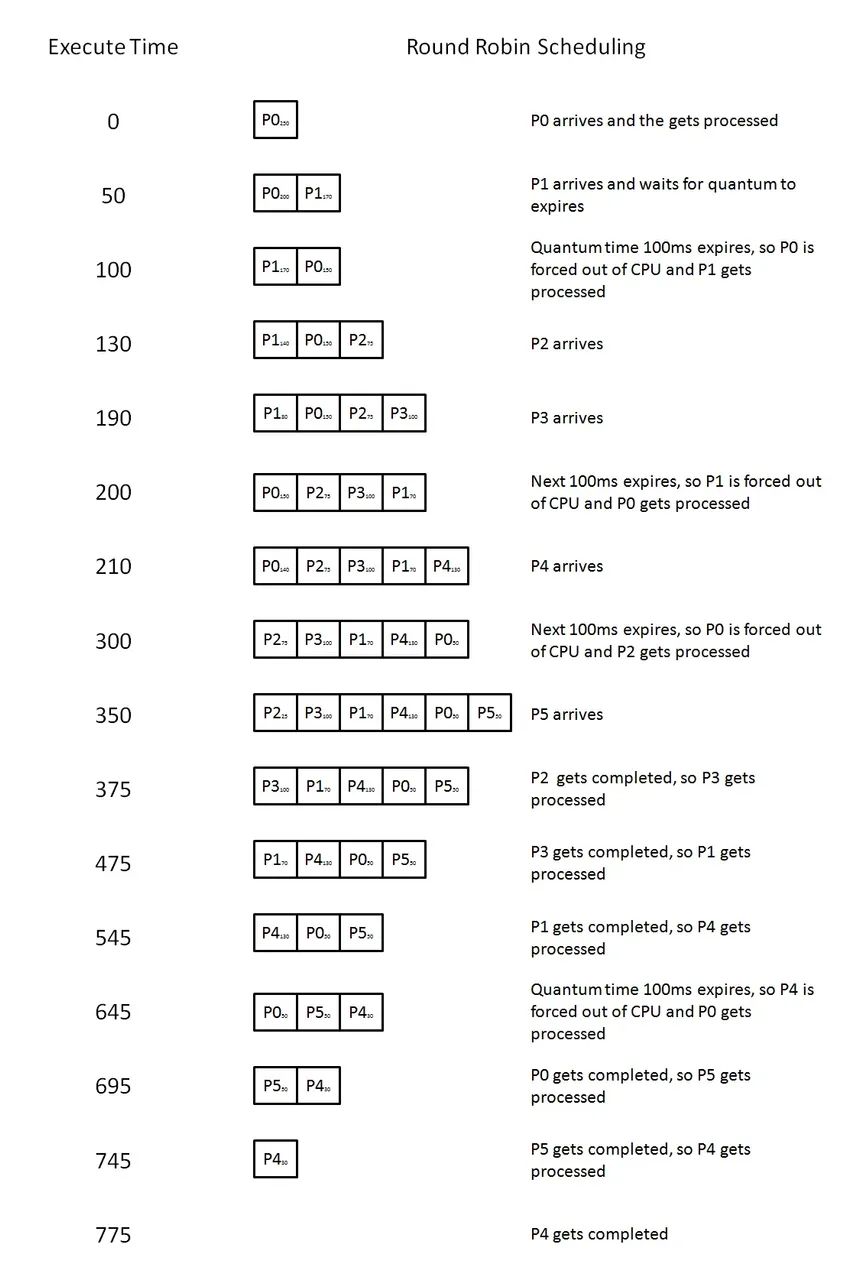
Image credit: Wikimedia Commons, public domain