Greetings Steemians, welcome to my blog
I am sure you have seen or heard of wireless charging and the possibility of transmitting electric power from one location to another without connecting wires. This has gone beyond proof of concept and several companies have demonstrated it with significant results using different techniques mostly for short range transmissions. But the obvious questions now are: Why is it not yet applied on a large scale for long distance transmission? What are the present limitations and future possibilities? Can we really transfer power through the air using microwaves and its devices as in the case of telecommunication and radio engineering? Do read on to find out.
 CCO Creative Commons: Microwave tower
CCO Creative Commons: Microwave tower
Let me quickly talk about wireless power transmission in general as microwave power transmission is just one of its many techniques.
There has been a long standing interest in the area of transmitting “power through the air”. In fact, it is a long time technological dream. This concept is popularly known as Wireless Power Transmission (WPT). WPT also called inductive or electromagnetic power transfer uses time-varying magnetic, electric or electromagnetic fields.
As the name implies, WPT is the transmission of electric power from one location to another without connecting wires as a physical link.
It is mainly divided into two broad categories namely: Near-field (non-radioactive) and far-field (radioactive) techniques. The near field techniques is simply used for appliance not far from the power source while the far-field techniques involves the use of electromagnetic radiation such as microwaves or laser beams for energy transmission over a longer distance. There are also other recent technologies but our central focus today is on microwaves as a mechanism for WPT.
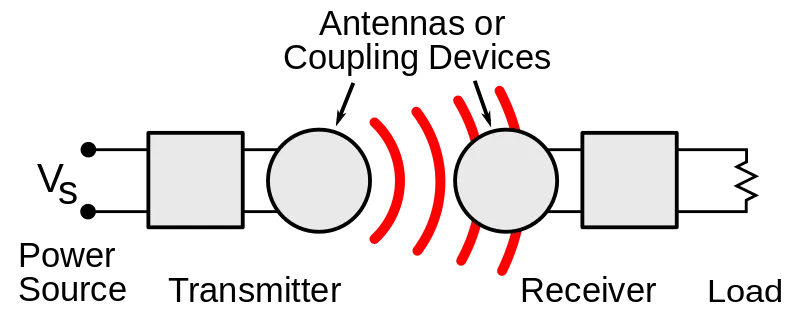 Creative Commons CCO:wireless power system
Creative Commons CCO:wireless power system Now that you have a little penetration into what WPT entails, let us go back to the business of the day
MICROWAVE POWER TRANSMISSION (MPT)
MPT is the transmission of power through space by means of microwaves. Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation whose wavelengths are conveniently measured in small numbers of centimeter.
This part of radio spectrum ranges across frequencies of roughly 1.0 GHz to 30GHz.
MPT is a far- field technique used in wireless power transmission. In particular, MPT is suitable for long range transmission.
In simple words simply put, a MPT system converts direct current (DC) power to microwaves energy by microwaves generator, transmits that microwave radiation into space through a transmitting antenna to a receiver called rectenna, and the receiver converts the microwave radiation back to DC power. In this technology, Alternating Current (AC) is first converted to DC; the DC is then converted to microwaves energy for transmission and thereafter the microwaves is converted to DC at the receiving end. In the final step, DC will be converted back to AC. This is because AC cannot be directly converted to microwaves energy.
Component of MPT System
- Microwave Generator:
These are microwave transmitting devices classified as Microwave Vacuum Tubes such as magnetron, klystron, Travelling Wave Tube (TWT) etc. Magnetron is widely used for MPT systems and it generates microwaves by passing electrons through a magnetic field.
- Transmitting antenna: All antennas can be applied for MPT system but the slotted waveguide antenna is best suited due to its over 95 % efficiency and good directivity to avoid power losses.
- Rectenna: As its name implies, it is a combination of a rectifier with an antenna. A rectifier is a device used to convert alternating current to direct current while an antenna is a transducer whose job is to convert radio frequency fields into alternating currents and vice versa. Therefore, a rectenna converts microwave power received into dc power
HISTORICAL MILESTONE
Nikola Tesla is popularly considered the father of wireless power transmission because of his experiment in the late 18th century on wireless lighting using the near field inductive and capacitive coupling. After several successful demos, Tesla attempted to build a large high- voltage wireless power station for the transmission of radiotelegraphy and wireless power but the construction was never completed and the project ultimately failed. Even though he could not make a commercial product, his findings are currently being applied in short- range wireless transmission.
 wikimedia creative commons CCO: A model of Tesla tower
wikimedia creative commons CCO: A model of Tesla tower CURRENT STATUS
In recent times, there have also been lots of developments and demonstrations using MPT over longer distances. Ten years ago, a long- range transmission was recorded on the main island of Hawaii. 20 watts was transmitted over 145km. In 2015, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) also demonstrated MPT by transmitting 1.8 kilowatts wirelessly over more than 50 meters to a small receiver and in the same year Mitsubishi Heavy industry announced transmitting 10kw using microwaves over 500meters. Many researches have been done and are still ongoing. The Qi technology has moved from demo to the market and more than 50 million wireless chargers have been sold.
LIMITATIONS
19th century to 21st century is a long time and it is still as though this concept has continued to elude reality especially the area of long distance wireless transmission. Some of the reasons for this are highlighted below:
- Safety concern: Humans and the whole biological environment can be dangerously affected when exposed to harmful levels of radio-frequency electromagnetic fields.
Therefore, government regulation set limits on the power levels that humans may be exposed to.
In an attempt to comply with this regulation, the maximum power output of MPT needs to be reduced and indirectly the achievable transmission distance is also limited. This is because unlike the traditional microwave transmission used in telecommunication, the power level in MPT is slightly higher. Some researchers said the power level for MPT will be almost equal to the leakage from a microwave oven and slightly greater than that of a cell phone.
- Line of sight issues: MPT is based on the transfer of microwave from a source to the target. The path between the source and the receiver is referred to as the line of sight. Thus, the clearer the line of sight, the more efficiently power transmission can be achieved. Factors such as weather and physical obstructions can affect MPT. Most of the demos are majorly done on a clear path. Even with that the intensity received at the rectenna is low. For instance, during the 1975 NASA JPL gold stone transmission, 500kw was actually transmitted and just 34kw was received at the rectenna. MPT provides the efficiency in energy conversion but it is slightly difficult to focus the beam in a small region.
FUTURE POSSIBILITIES
Despite these limitations, it will interest you to know that work is still ongoing to limit the adverse effect of this technique and even another technique called highly resonant WPT which is capable of overcoming the limitations of MPT has been recently proposed for long range transmission. Imagine a world without electric grids, towers, and sub-stations etc. where our lives can be truly wire-free and power can be transmitted with negligible losses.MPT is most commonly proposed for the transmission of energy from solar power satellite or other space- based sources to the earth surface. With the inception of electric cars and its battery technology set back, many researchers have also envisioned MPT to be used in the charging of electric cars. There are several other applications that can be possible with MPT.
CONCLUSION
Dr Neville of NASA said:
You don’t need cables, pipes, or copper wires to receive power. We can send it to you like a cell phone call- where you want it, when you want it, in real time.
The truth is that the potential applications of this technique are numerous and so are the negative impacts. This technique is still quite far from the finish line but based on these current progressive trends, one cannot completely overrule the possibility of microwaves as a mechanism of WPT in the decades to come.
Thank you for reading. I hope I was able to bring you up to date on the happenings in MPT.
REFERENCES AND FURTHER READING
- http://www.iosrjournals.org/iosr-jeee/Papers/Vol4-issue5/D0452428.pdf
- https://www.wirelesspowerconsortium.com/blog/246/dreaming-of-power-through-the-air
- https://www.slideshare.net/rudrasbanerjee/wireless-power-transfer-using-microwaves
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wireless_power
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microwave_transmission
- Mohammad, S., Hooman, S & Mohammad A. (2014). Wireless Power Transmission Trends. 3rd International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision
- Kuchipudi, D.P. & Kuntigorla, S. (2015). Wireless Power Transmission and Reception using Rectenna. International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering. 2(3): 145-157
- Venkateswara, R.M., Sai, H.M. & Venkat M. (2013). Microwave Power Transmission- A Next Generation Power Transmission System. Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering. 4(5): 24-28

