Let us learn about the basic theory of contactless energy transfer and how the charger works via wifi / wireless? How It utilizes the concept of wireless power transfer.
Many of us might have seen the wireless charger technology , which relieves us from using the power cord to recharge the battery. This technology is incorporated into various modern devices and systems.

A symbolic image of wireless power transfer (WPT)
The electricity in our house goes into the connecting box for, then the power cord sends current to the equipment and the AC (Alternating Current) electric devices that we use every day to turn on the lights, kitchen utensils, chargers, and so on.
Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) makes it possible to supply electricity through an air gap, without the need for a current-carrying cable. WPT can provide power from an AC source to a battery or compatible device without a physical or wired connector. WPT can recharge mobile phones and tablets, drones, cars, even transportation tools.
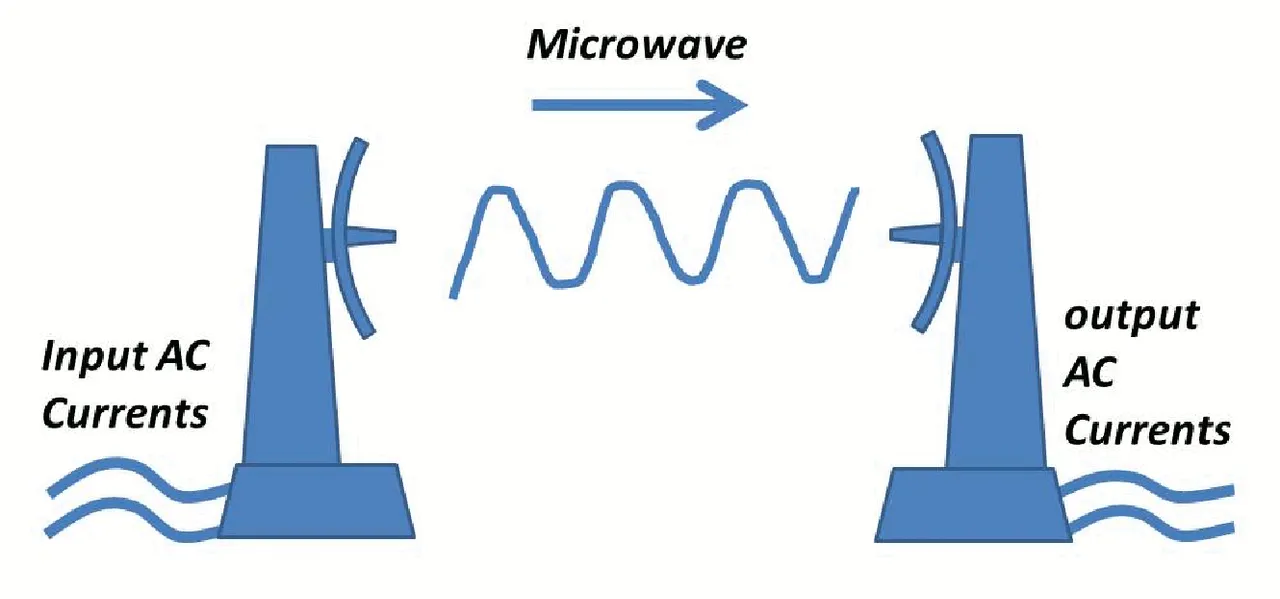
Wireless energy transfer
The concept of wired power transfer (Wireless power), has been around since the late 1890s. Nikola Tesla was able to light the bulbs wirelessly at his Colorado Springs Laboratory using electrodynamic induction (resonant inductive coupling).
Three light bulbs placed 60 feet (18m) from the power source are turned on, and demonstrations are documented. Tesla has a big plan and hopes that the Long Island-based "Wardenglyffe Tower" will transmit wireless power across the Atlantic Ocean. It never happened because of difficulties, including funding and time of its realization.
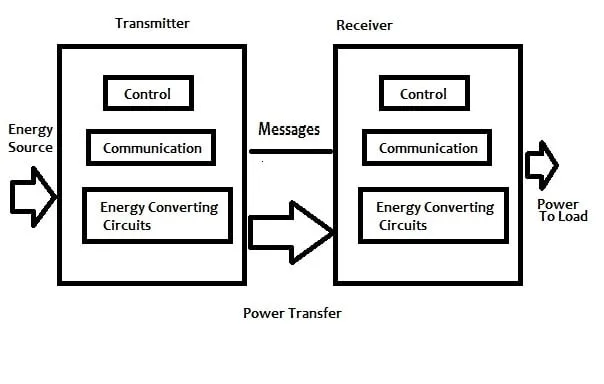
Principle of wireless power transfer
WPT uses a field created by charged particles to bring energy between the transmitter and the receiver through the air gap. The air gap is bridged by converting energy into a form that can propagate through the air. The energy is converted into an oscillating field, transmitted over the air, and then converted into electrical current that can be used by the receiver. Depending on strength and distance, energy can be transferred effectively through an electric field, magnetic field, or electromagnetic wave (EM) such as radio waves, microwaves, or even light.
The following figure shows the various technologies of WPT as well as the form of power transfer.
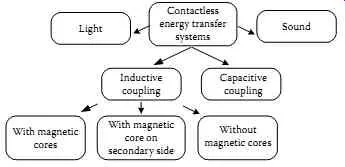
classification of wireless power transfer methods
Qi Charging, Open Standard for Wireless Charging
While some companies that promise WPT are still working on delivering the product, Qi (pronounced "chee") is standard charging, which is already available today. Wireless Power Consortium (WPC), established in 2008, developed the Qi standard for battery charging. This standard supports both inductive and resonant charging technologies.
Inductive charging has the energy that passes between the transmitting and receiving coils at close range. The inductive system requires the coils to be near and parallel to each other; Usually the device is in direct contact with the charging pad. Resonant charging does not require careful alignment, and the charger can detect and charge the device at a distance of up to 45mm; Thus, resonant chargers can be embedded in furniture or mounted on the shelf.
When first introduced, Qi charging low power, about 5W. The first smartphone to use Qi charging was introduced in 2011. By 2015, Qi expanded to include 15W, which allows fast charging.
Here is a Block diagram that shows the Qi method of energy transfer.
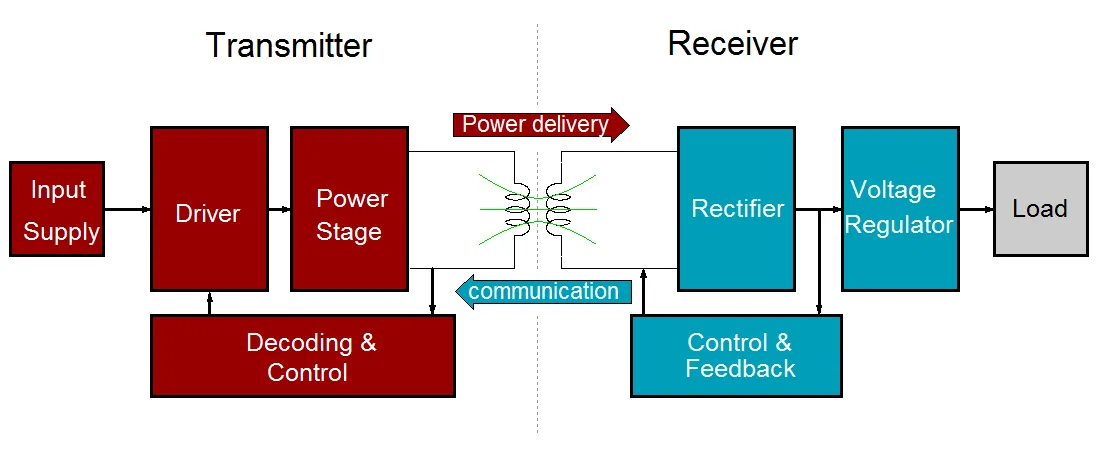
Qi charging
Only devices registered in the Qi Registration Database are guaranteed to provide Qi compatibility. Currently there are more than 700 products listed. It is important to note that products with the Qi logo have been tested and certified; The magnetic fields they use will not cause problems for sensitive devices like cell phones or electronic passports. Registered devices are guaranteed to work with all registered chargers.
WPT for consumer devices is a growing technology, but its basic principles and components are not new. Maxwell's equations still apply wherever electricity and magnetism are involved, and transmitters send energy to the receiver as in other forms of wireless communication. WPT is different, though, because its primary purpose is to transfer the energy itself, rather than information encoded in energy.
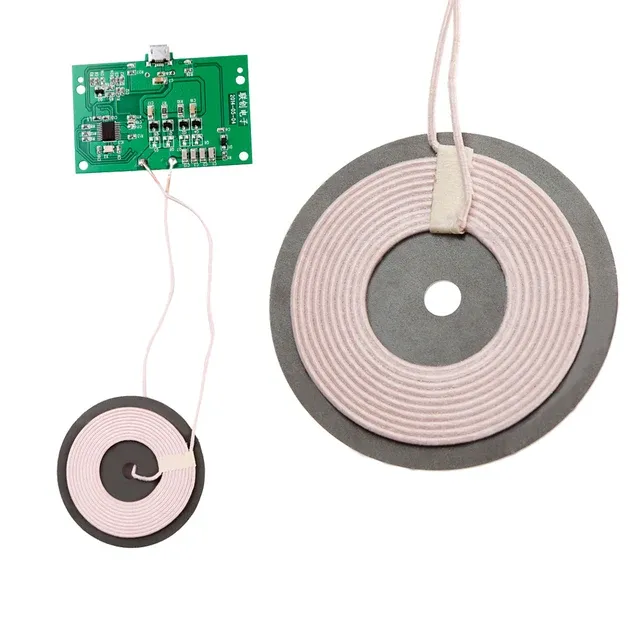
The electromagnetic fields involved in WPT can be very powerful, and human safety must be taken into account. Exposure to electromagnetic radiation can be of concern, and there is also the possibility that the fields generated by the WPT transmitter may interfere with usable medical devices.
The transmitter and receiver are embedded inside the WPT device, as well as the required battery. The actual conversion circuit will depend on the technology used. In addition to the actual energy transfer, the WPT system must enable the transmitter and receiver to communicate. This ensures that the receiver can notify the charging device when the battery is fully charged. The communication also allows the transmitter to detect and identify the receiver, to adjust the amount of power delivered to the load, and to monitor conditions such as battery temperature.

The near-field concept vs mfar-field radiation is relevant to WPT. The transmission technique, the amount of power that can be transferred, and the proximity requirements are influenced by whether the system utilizes near field radiation or far field.
Locations that are far from the antenna far less than one wavelength are in a closer area. The energy at nearby locations is nonradiative, and the oscillating magnetic and electric fields are independent of each other. Capacitive (electric) and inductive (magnetic) coupling can be used to transfer power to a receiver located at a location near the transmitter.
Locations whose distance from the antenna is greater than about two wavelengths are in far field. (The transition region exists between the near location and the remote location.) The energy in the far field is typical electromagnetic radiation. Remote field power transfer is also referred to as power beaming. Examples of remote field transfer are systems that use high-power lasers or microwave radiation to transfer remote energy.
Application of Wireless Charging
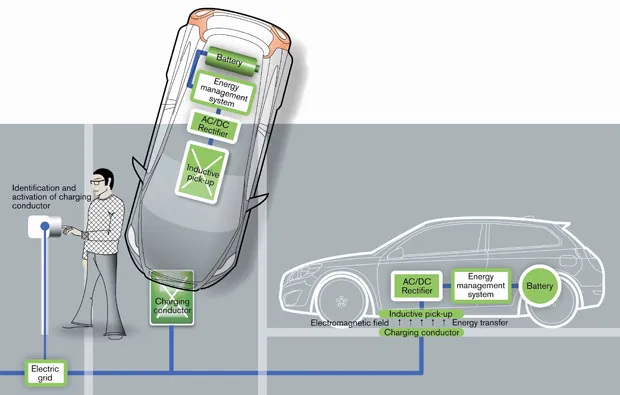
Electric car's wirless charging
There are inomerous applications of wireless power charging. Many are there in practice today.
Using WiTricity, discovered by MIT scientists, electric cars can be used to charge wirelessly, and they can charge your phone wirelessly (Using Qi charging). This convenient wireless technology, of course, allows also to charge the car faster than plug-in charging.
Don’t expect this solution to become available anytime soon. "There is not yet any common standard for inductive charging.This is a smart technolgical solution that is some way into the future.

References sourced:
- http://large.stanford.edu/courses/2010/ph240/ma1/
- https://spaceforest.pl/wireless-power-transfer/
- http://www.pcbheaven.com/opendir/index.php?show=7962jo9161add5232667
- http://www.electromagnetics.unisalento.it/?page_id=543
- http://www.plugincars.com/volvo-explores-wireless-electric-car-charging-built-road-107205.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wireless_power_transfer
Support @steemstem and the #steemstem
project - curating and supporting quality STEM
related content on Steemit
