Weather symbols, source :wikimedia commons
There are various weather/climatic hazards that affect agricultural productions. These hazards vary from one climatic zone to another and occur at different times. These weather hazards depends on the position /latitude of the place on the world map. These hazards affect crops and agricultural productivity negatively if they are not checked. Every agricultural zone has one particular hazard that is associated with it and in most cases affect the crop productions and reduce the annual crop yield. In this article, we will look at the various hazards in agriculture one after the other.
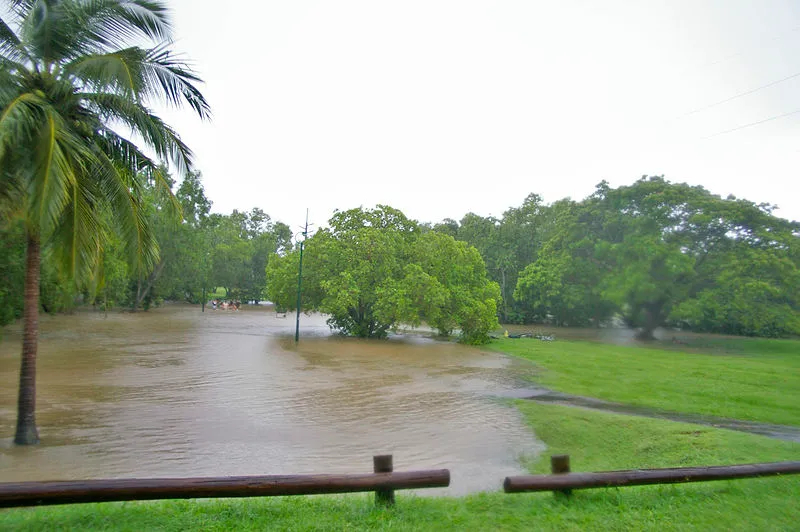
Floods
Floods occur almost every part of the world, it may occur as a result of excessive rainfall, overflow of river banks, discharges from pipes, high water table and fluctuations in ground water tables. Foods tend to cover the entire farmlands with water thereby destroying economic crops as they are washed away by flood. Flood tends to cause sheet, rill and gully erosion, makes the land unfit for crop productions, impairs the movement of machines, washes away valuable soil nutrients, leads to land degradation and causes environmental pollutions.Droughts
The drought is said to occur when there exist period of little or no rainfall. At this period, the supply of moisture from the precipitation (rainfall) or those stored in the soil are said to be insufficient to fulfil the crop water needs or meet the optimum water needs of plants. Drought is a wind -induced menace since the prevailing winds crossing the affected zone cannot induce rainfall as they are said to be dry. Droughts are classified into different types which are; permanent drought, seasonal drought, contingent and invisible drought. Wherever drought occur usually have a negative effects on the crops. It leads to an increase in water demand, water stresses in plants, the crops may wilt during the period, it causes higher evapotranspiration and leads to poor agricultural yields.Frost actions
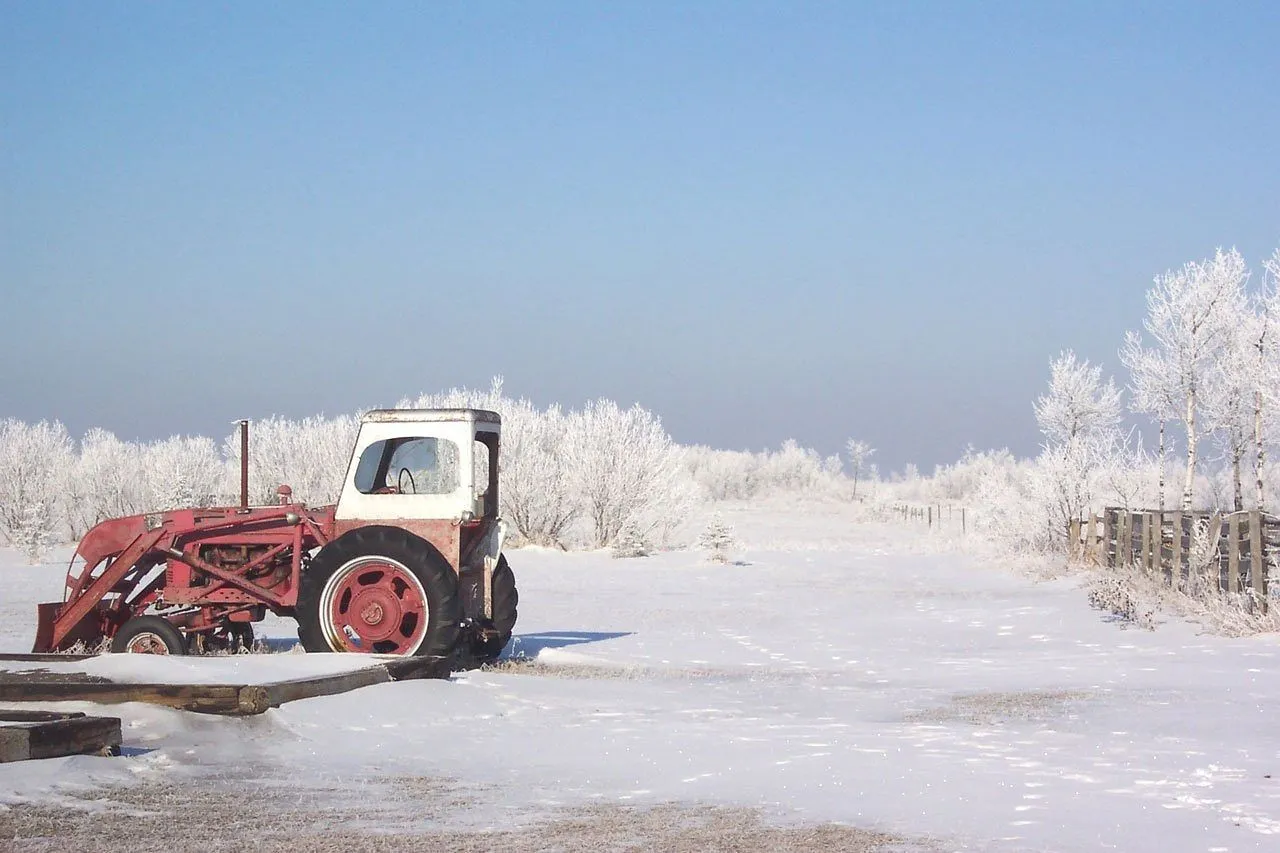
Frost are water induced hazards which occur as a result of lower environmental temperature which force the water to form ice blocks they may not be easily removed. It is associated with the Polar regions of the world with daily temperature of less than 6°C. The entire agricultural lands are covered with frozen particles of water or ice clouds. Frost actions do affect agricultural productions in the in a way that it prevents early tillage operations, proper development of the crops, inaccessibility of farmlands to the farmers and excess water which can result to flooding.Winds
Excessive winds occurs in agricultural zones with little or no vegetation cover or wind breakers /shelter belts. Strong winds affect maize crops in most southern parts of the world particularly during the winter /raining seasons. While in most Northern parts of the world excessive winds are common during the summer /dry/harmattan season. Excessive winds velocities encourage the destruction of stems of mostly maize crops, detach/transport/deposit the soil at will, washes away soil nutrients from the agricultural lands and dries up the seeds and grains.
Extreme temperatures and Excessive rainfall
Extreme temperatures refers to the conditions of higher environmental temperatures that is not convenient to crops, man and his animals. Extreme temperatures levels encourage the multiplication of pests and diseases in an environment.
It leads to an increase in water requirements of crops and crops can also suffer from water stresses.Excessive rainfall is the occurrence of many rainfall events which leads to an increase in rainfall depths. Excessive rainfall is not beneficial to crops since plants have optimum depth of water required for their metabolic activities. Excessive rainfall washes away the essential nutrients in the soil, floodings,poor physical development of the growing crops and accelerates the decay of the growing crops after maturity.
Weather Aspects of Crop Pests and Diseases
We must take into considerations the climate and it's roles while planning for agricultural operations and development. The temperature and rainfall (climate) influence agricultural productions directly or indirectly. In the tropics for example, higher temperatures encourage the rapid breeding of pests and diseases. These pests and diseases attack and destroy these crops at every stage of the crops growth. The multiplications of pests and diseases are at higher levels during the periods of higher environmental temperatures. Lower environmental temperature regimes do not favour the growth of pests and diseases. For grains, particularly maize, the absorption of water through rainfall do accelerate the rate of decays of the crops and reduce the market value. It has been reported that extreme temperatures and higher periods of rainfall do lower the performance of agricultural crops particularly during the early stage of growths of such crops.Conclusion
Agricultural production is completely dependent on the availability of climate and water and it is adversely affected by weather catastrophe. Crops do not do well at extreme weather conditions but under favourable weather conditions. Weather hazards can result to deficiencies in the supply of macro and micro nutrients in the soil. Which will yield little or no agricultural produce.
Reference
[1] Types of Weather Hazards
[2] Weather Hazards
[3] Weather-related hazards and risks in agriculture
[4] Natural Disasters and Extreme Events in Agriculture
[5] category: weather hazards -Wikipedia