A recent malware campaign targeting Google Chrome & Firefox has just switched gears; instead of afflicting victims' systems with Locky ramsomware it now installs a RAT (Remote Access Tool, "NetSupport Manager" specifically), giving attackers much greater influence over the victim who may remain unaware of the situation indefinitely.
| TL;DR: |
|---|
| ⚠️ DO NOT INSTALL Font_Chrome.exe It is malware executable code that installs NetSupport Manager Remote Access Tool. ⚠️ DO NOT INSTALL Win.JSFontlib09.js It is a JavaScript file that downloads and installs Locky ransomware ⚠️ The Google Chrome variant has only changed its final payload, it has not replaced the Firefox variant; Both HoeflerText variants, Google Chrome RAT installer and Firefox ransomware, are currently active, the Firefox variant may yet change payload and previous methods could be reactivated at any time. ℹ️ JavaScript (.JS) and executable code (.EXE) are not fonts. Read on for more info. |
Attack Method
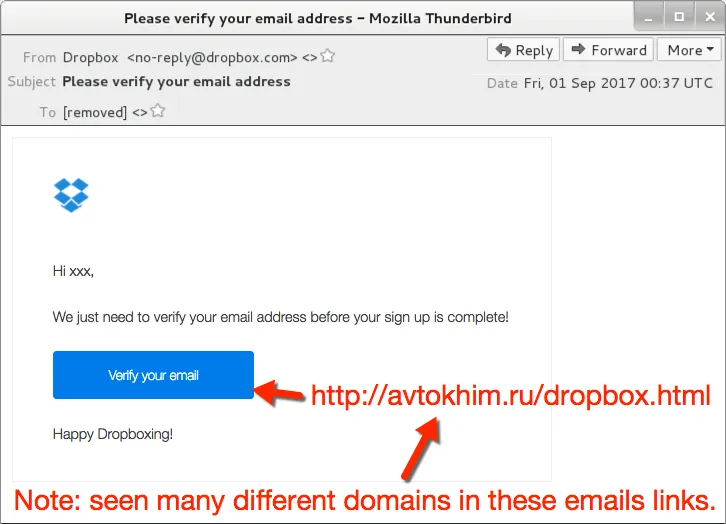
The infection chain employs the use of malicious scripts and a payload added to web pages, either fake or legitimate but compromised, sometimes in conjunction with spam email campaigns (see below) featuring spoofed identities such as Dropbox to drive unsuspecting potential victims towards the boobytrap. But these email lures are not required if the user stumbles upon a legitimate page that has been compromised due to poor or outdated server security.
Scripts inserted on bogus or compromised pages trigger when loaded into browsers meeting specific criteria (see below), replacing page data between HTML tags with the non-existent ISO character “�”, causing the browser to use the substitute character � and creating the semblance of an error requiring user intervention.
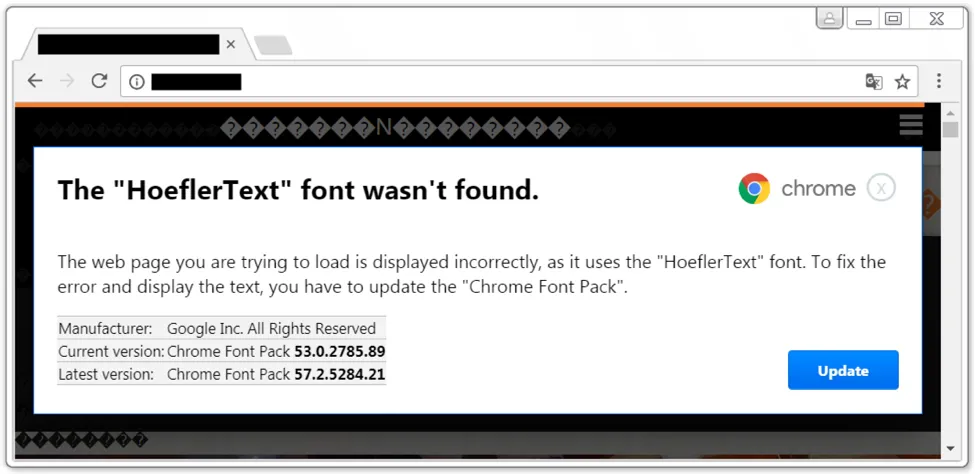
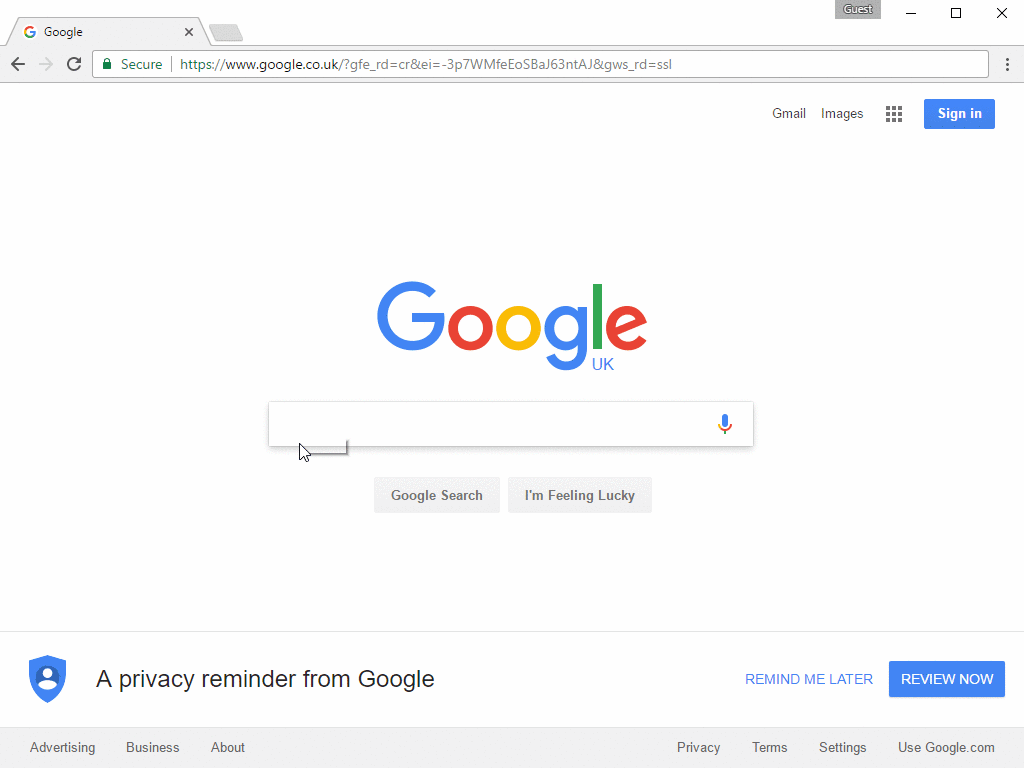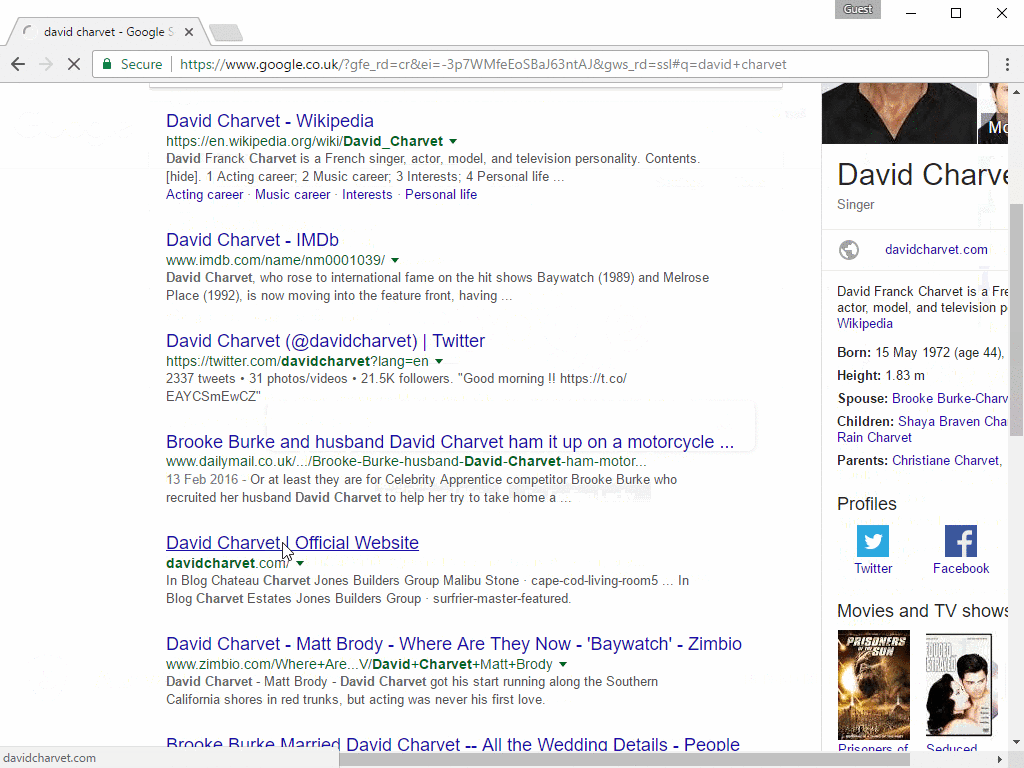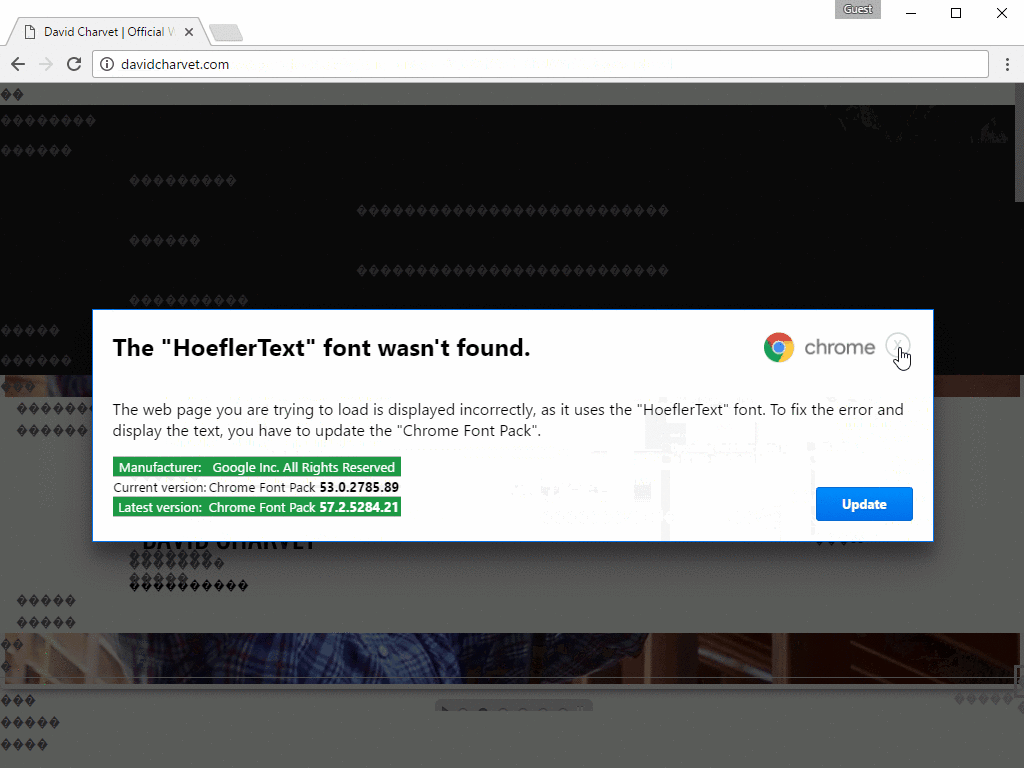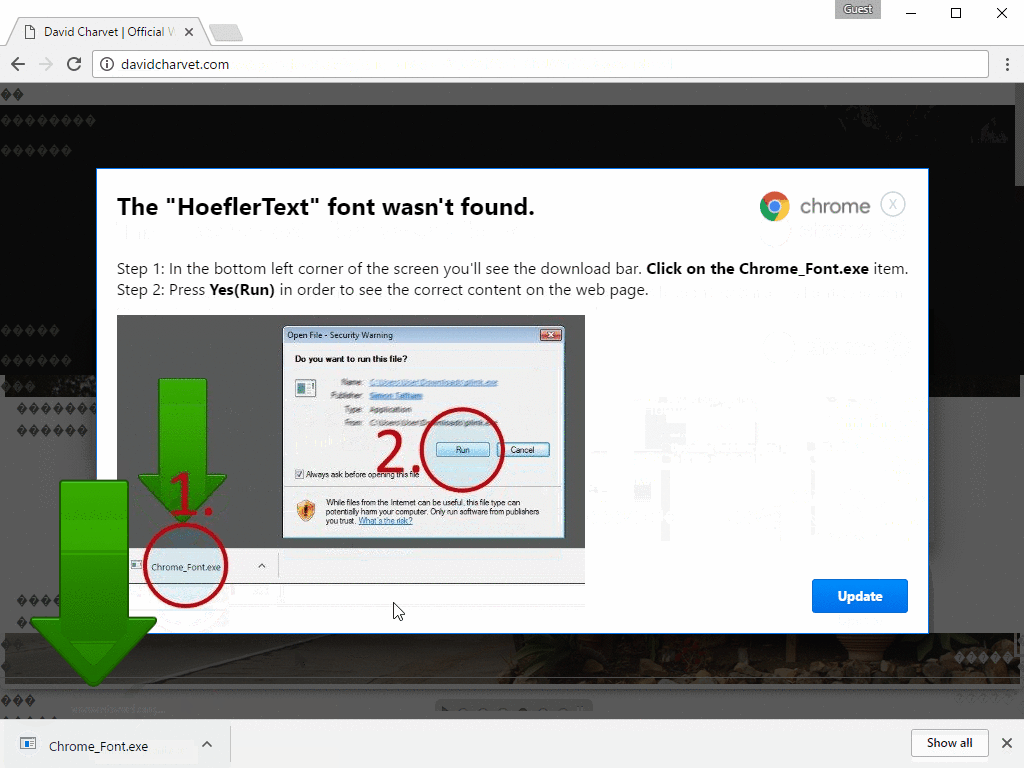
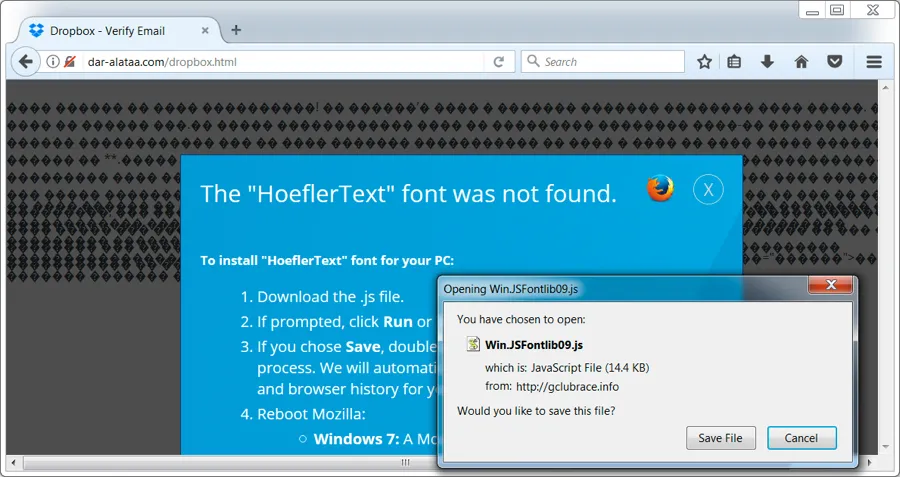
The illusion is further supported by the display of Base64 encoded images in a CSS overlay styled to resemble a modal browser notification declaring 'The "HoeflerText" font wasn't found.' complete with Google Chrome or Firefox logo and directs the user to "update" the missing component.

Finally, the payload installation stage begins when the downloaded file, be it Chrome_Font.exe or Win.JSFontlib09.js, is run by the unsuspecting victim. After that it's goodnight and good luck a case for detection and removal processes.
“In recent days, I’ve noticed multiple waves of malspam every weekday. It gets a bit boring after a while, but as 2017-08-31 came to a close, I noticed a different technique from this malspam,”
“If you viewed the pages in Chrome or Firefox, they showed a fake notification stating you don’t have the HoeflerText font. These fake notifications had an “update” button that returned a malicious JavaScript (.js) file.”
- Brad Duncan, SANS Internet Storm Center & Palo Alto Networks' Unit 42
An animated overview from Proof Point of the two step process for Google Chrome RAT installation:
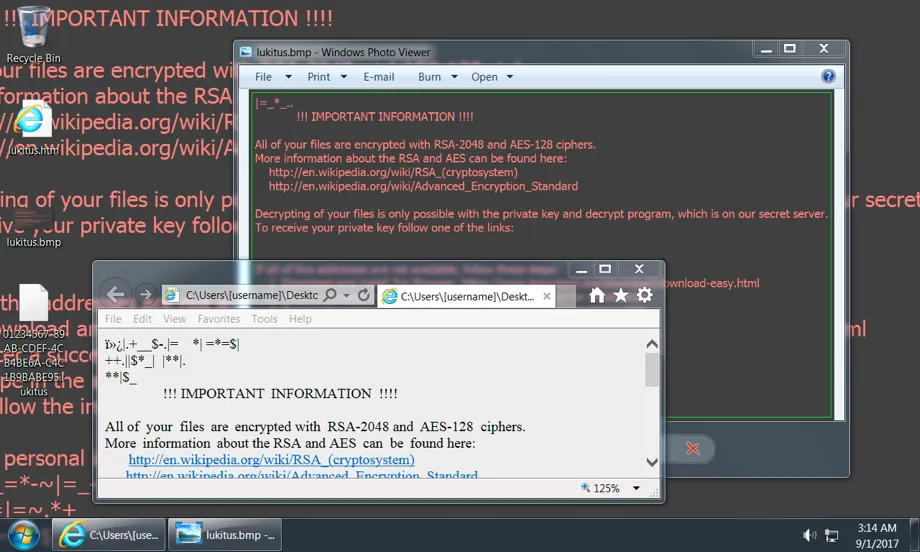
Screenshot of "Lukitus" Locky variant crypto-locked system:
Users of IE/Edge browsers that meet selection criteria will be presented a fake anti-virus alert with a tech support scam phone number.
Lure emails that were sent out were done so from botnets with various IP addresses around the world using the following message details:
- Sender (spoofed): "Dropbox" no-reply@dropbox.com
- Subject: Please verify your email address
But, as previously noted, the email lure is not required to encounter a compromised web page and trigger the initial delivery mechanism.
Evolution
It's important to be aware of the history of this developing attack method as the criteria, paths, and payloads could be changed, deactivated, or reactivated at any time.
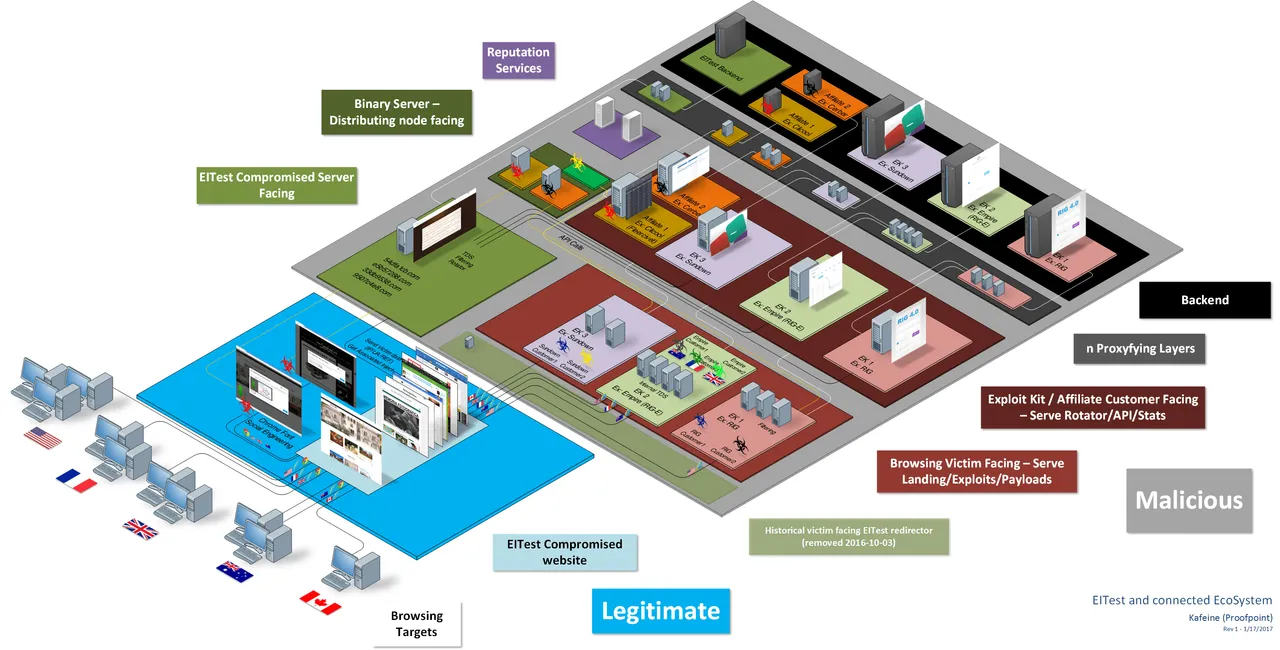
The HoeflerText attack uses the EITest infection method, a combination first identified in December 2016. EITest itself is a complex framework with evidence of its use dating back to 2014 but potentially using elements dating back as far as 2011.
EITest malware campaign began using HoeflerText popups to distribute the Win.JSFontlib09.js JavaScript file to Firefox users and Chrome_Font.exe to Google Chrome users as a means of delivering the Locky variant cryptolocker ransomware.
However in late August 2017 the Chrome_Font.exe had its payload switched from Locky crypolocker ransomware to the NetSupport Manager RAT, specifically targeting Chrome users.
The current criteria used to trigger scripts on a compromised web page:
- target country
- specific referrer
- specific User-Agent, currently: Windows Google Chrome for RAT variant, Windows Firefox for Locky variant, Windows IE/Edge for tech support scam variant
Other paths have previously been added to the EITest infection chain, in December 2014 ElTest used redirected victims to an Android “Police” Browser locker. More paths and payloads could in future be added to this complex ecosystem, of which a partial diagram produced by Proof Point is shown below:
GENERAL ADVISORY
Be vigilant! Don't follow lures to install files from unknown internet sources. Scrutinise apparent email senders and web link targets, especially when confronted by the unexpected, unfamiliar, or unusual. Hover your mouse cursor over a link without clicking it to see the link target, use a search engine to investigate, or if in doubt simply exercise caution and raise your concerns with appropriate parties, ie: contact the apparent email sender via known and trusted means, raise your concerns with your IT staff if you have them, communicate your find with other staff.
And remember: JavaScript (.JS) and executable code (.EXE) are not fonts, nor are they images, nor joke of the day but you may be if you blindly execute them.
You will find good advice about malicious scripts on compromised websites here: https://www.welivesecurity.com/2016/06/28/malicious-scripts-compromised-websites-protect/
Be safe, and as always STEEM ON!
Sources: https://researchcenter.paloaltonetworks.com, https://isc.sans.edu, https://www.proofpoint.com.
^vote, resteem, and comment below. Considerable effort has gone into researching, testing, and formatting for this article.