What Will I Learn?
- Logical operators
- Bitwise operators
- Xor operation
Difficulty
- Basic
Tutorial Contents
We have learned many operators so far. At this tutorial we're going to learn Bitwise operators and Conditional operators and do some examples.
Logical Operators
In the previous tutorials, i gave some login examples. The comparisons that we were doing there was operating by logic operators. The gate transactions used in the logic circuits are also done with these operators. These operators can be use with different needs. At the login process, ID and Password have to match with each other. We can do this with conditional operators. There are different areas to use.
Let's make an example;
package com.org.operator;
public class Operators {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int password=1234;
String name=" John" ;
if (password==1234 && name==" John" )
system.out.prinln(" login successful" );
}
}
The screen will show;
login successful
At this example, if the password and name match, login process is working. To do this, we are using "&&" operator. We can multiply the examples like this. If we want to do something if just one of them are right, we have to use "||" operator.
Let's make a big example now;
package com.org.operators;
public class LogicalOperators {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
boolean x=false;
boolean y=true;
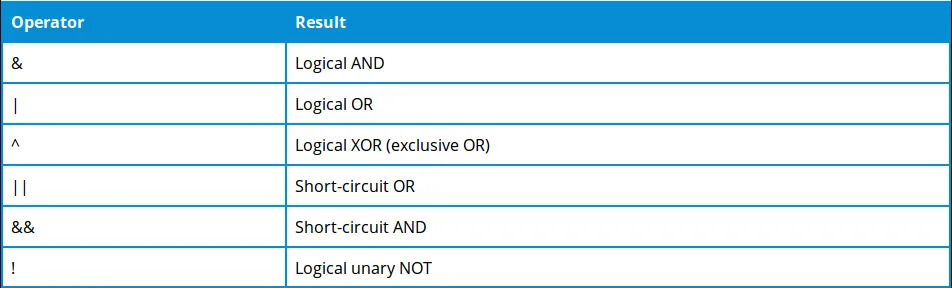
System.out.println(" x&y = " + (x&y) ) ;
System.out.println(" x|y = " + (x|y) ) ;
System.out.println(" x&&y = " + (x&&y) ) ;
System.out.println(" x||y = " + (x||y) ) ;
System.out.println(" x^y = " + (x^y) ) ;
System.out.println(" !x = " + (!x) ) ;
System.out.println(" (x&y) || (x^y) = " + ( (x&y) || (x^y) ) ) ;
On the screen wee see;
x&y = false
x|y = true
x&&y = false
x||y = true
x^y = true
!x= true
(x&y) || (x^y) = true
__
At this example, if we write "false" instead of "x", "true" instead of "y", we can find the results easily. For this, we have to know the accuracy table of "AND, OR and XOR" transactions.
Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operators that are not used much in programming are used for operations such as shifting bits and inverting.
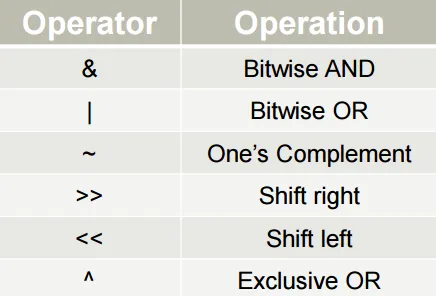
For example;
Think the number "3". This number is "0011" on the binary system. And for another example, think the number "14". It's "1110" on binary. If we process numbers 3 and 14 into "and", the corresponding bits of those numbers are subjected to a single "and" operation.
Which means a number doesn't go to process directly. This numbers binary type goes to the process.
Basic Bitwise operators
I told you which operator is doing what. Now let's take a look at those on the examples. The numbers we'll be process will be 3 and 14. So we have to know their binary type.
AND Process
number1 = 0011 (3)
number2 = 1110 (14)
Result = 0010 (2) - (&-AND Process)
...at the example;
package com.org.operator;
public class Operators {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println (3&14) ;
}
}
The screen will show;
2
At this example, we made an AND process to the 3 and 14 numbers with & operator. And now, we have 2.
Let's take a look at the "^" operator that makes XOR process.
XOR Process
number1 = 0011 (3)
number2 = 1110 (14)
Result = 1101 (13)
...with the example;
package com.org.operators;
public class Operators {
public static voic main(String [] args)
{
System.out.println(3^14) ;
}
}
The screen will show;
13
At the XOR process, if the bits on the process are different result is 1, if those are different it's 0. XOR process took the numbers binary types and changed those to the base 10 and gave us the result; 13.
***Reversing the bits with ~ ***
Number = 1101 (13)
Result = 0010 (2)
Let's make an example for this too;
package com.org operators;
public class Operators {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(~3) ;
}
}
Screen will show;
-4
Our number was 3. At binary system its 0011. If we reverse it, it'll be 1100. first bit means the negative so our number become a negative number. 100 bit means 4, so our number become -4.
After the next step, i'll teach shift and type comparison operators in Java. Those are the last operators and after that you'll learn operator primary. Than the operator topic will be finish.
Curriculum
- Partitioning the number using "_" - Boxing/Unboxing and Local Variables on Java
- Basic and Other Assignment Operators, Multiple Assignment Process and Variable Swap at Java
- What is Relational Operators on Java? -With examples
- Arithmetic operators and various operations we can do with them on Java
Posted on Utopian.io - Rewarding Open Source Contributors