
Repository
https://github.com/dart-lang/sdk
What Will I Learn?
- You will learn about Abstract Classes
- You will learn about Class Inheritance
- You will learn about Class Interfaces
- You will learn about Type Casting
- You will learn about Mixins
Requirements
System Requirements:
- IDEA intellij or Visual Studio Code with the Dart Plugins
- The Dart SDK
OS Support for Dart:
- Windows
- macOS
- Linux
Required Knowledge
- The Dart SDK
- A Dart supported text editor (Dart Pad can be used)
- A little time to sit and watch a video and some patience to learn the language
Resources for Dart:
- Dart Website: https://www.dartlang.org/
- Dart Official Documentation: https://www.dartlang.org/guides/language/language-tour
- Dart GitHub repository: https://github.com/dart-lang/sdk
- Awesome Dart GitHub Repository: https://github.com/yissachar/awesome-dart
- Pub website: https://pub.dartlang.org
Sources:
Dart Logo (Google): https://www.dartlang.org/
Difficulty
- Beginner
Description
In this video tutorial, we continue to look at Object Oriented and Class based Programming in the Dart programming language. To fully understand why Classes and Objects are useful in a programming context, we need to understand inheritance and the Dart single inheritance model. This includes looking at Abstract Classes, Class Interfaces, Mixins and Type Casting. Along the way, we also look at importing libraries and the logical switch statement.
Abstract Classes and Interfaces
An abstract class is a type of class that doesn't allow for object instantiation. This tool exists so that developers may further generalize their class blueprints into interfaces. As such, abstract classes are used to define methods and properties without including implementation details. These methods, properties and other details make up the interface of the Class. Dart makes use of these class interfaces to create a description of the complex relationships between classes. This enables Inheritance, Implementations and Mixins despite the language only allowing a single inheritance model.
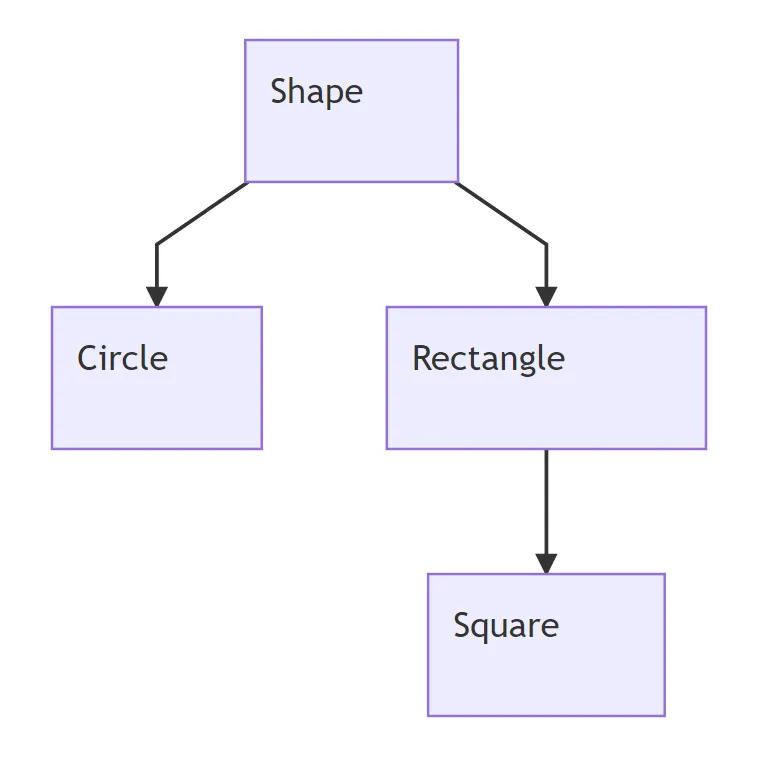
In the example, we take a look at direct inheritance using an abstract Shape class. The Shape class allows us to define the interface for any other Shape objects in our program. To be a Shape type, an object must implement three getter methods; a name method, a area method and a perimeter method. This graph shows the flow of inheritance between the three main classes that we created in the example. Circle and Rectangle directly inherit from Shape and therefore must have their own implementations of the Shape getters. Square on the other hand inherits from Rectangle which allows us to save writing a new implementation of the Shape Interface. While Square's direct parent class is the Rectangle Class, it still is a Shape type because both implement the Shape interface.
Adding Properties and Methods Without Using Inheritance
Dart's single inheritance model may seem restrictive when compared to multiple inheritance models from other programming languages. Dart provides us with several ways to include attributes from multiple other classes outside of inheritance. Every Dart class automatically exposes its interface and a class can implement multiple interfaces which allows us to build composite classes.

In this image, we have an example of a complex class. This C class implements the interfaces for class A and class B by way of the implements keyword. C must contain the full interface for both A and B to satisfy this call. C also adds a third class called TimeStamp through the use of a Mixin. For a class to be used as a Mixin, it must follow three specific rules. The class must not have a declared constructor, it also can not be a subclass to another class and it must not have any calls to the super keyword. When the class fits these rules, its behavior can be mixed directly into another class using the with keyword.
The Source Code for this video may be found here: https://github.com/tensor-programming/dart_for_beginners/tree/tensor-programming-patch-4
Video Tutorial
Curriculum
- A Beginners Guide to Dart - Methods, Final, Static, and Class Inheritance - Part Four
- A Beginners Guide to Dart - Intro to Classes and Objects - Part Three
- A Beginners Guide to Dart - Control Flow and Low Level Compilation - Part Two
- A Beginners Guide to Dart - Types, Functions, Variables and Objects - Part One