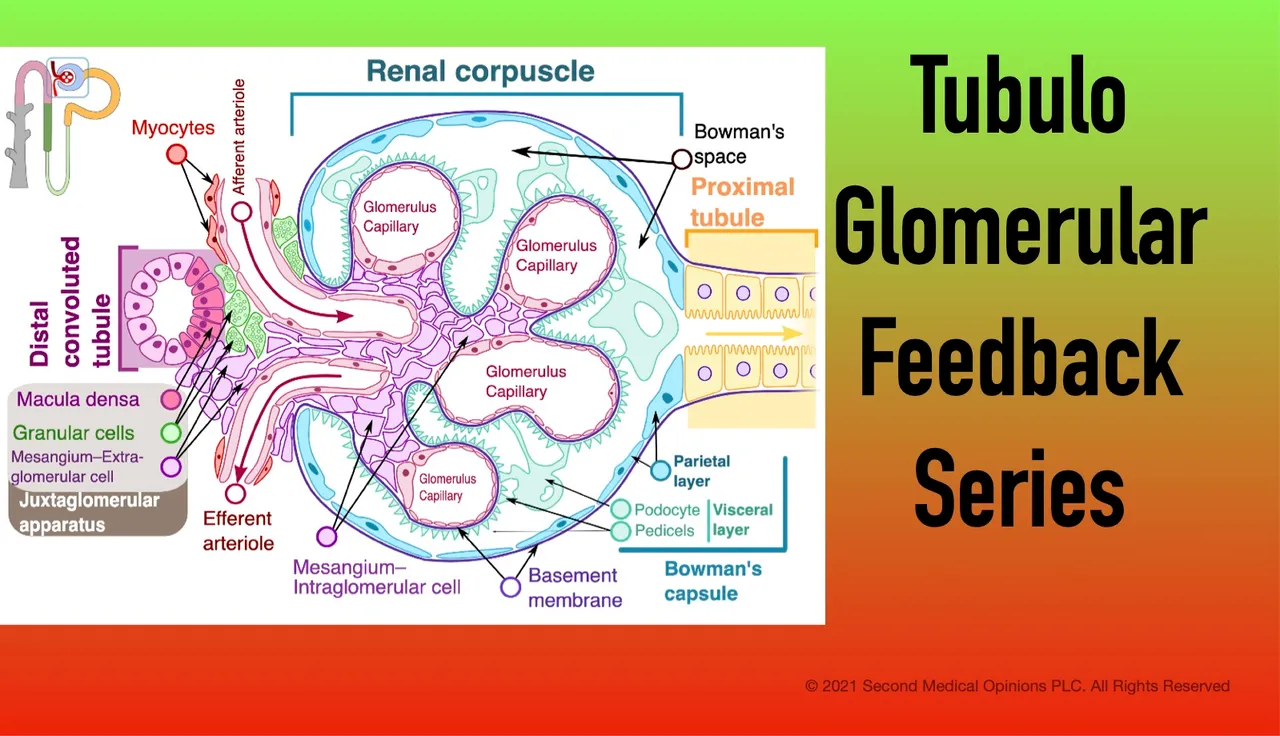
This article is a reference article that, among other things, reports that ecto-5′-nucleotidase is present in the cell membranes of the mesangial cells.
This means that the ATP released from macula densa (MD) cells can be converted into adenosine in the interstitial space by the ecto-5′-nucleotidase.
The produced adenosine can then reach the afferent arteriole in order to constrict it and execute the TGF response.
Credits
Renal Corpuscle Image. 2019. Downloaded under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International License from Wikimedia Commons. Author: Shypoetess. No changes were made.
Posts in this series
The Macula Densa Cells May Sense Tubular Salt Content Using a NHE2 Exchanger
The Macula Densa Cells Also Can Sense Sodium and Chloride Concentrations Using the NKCC2 Transporter
MAP Kinases are Activated by Low Tubular NaCl and Stimulate COX-2 Expression
Inhibition of nNOS in the Macula Densa leads to an Exaggerated TGF Response
The Juxtaglomerular Granular Cells are More Numerous in the Afferent Arteriole
Angiotensin II, Mediated by AT1 Receptors, Stimulates Nitric Oxide Release in Afferent Arterioles
Angiotensin II Effects are Different in the Afferent and Efferent Arterioles
Macula Densa Cell Depolarization Mediates Release of ATP When There is Increase in Sodium Chloride
The Extraglomerular Mesangial Cells Participate in the Signaling of the TGF
ATP is Released Through Large Channels at the Basolateral Membrane of the Macula Densa Cells