Hello Hive-, Java-, node.js-, docker-freaks,
Hello all others,
In my last documentation I showed, how I have connected a REACT node.js server with a simple Java Springboot server via REST API commands.
Now I want to explain, how to send CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete)-commands to the backend.
In the long run I want to create a simple game with the name "Hammurabi", which uses hive content to influence the run of play.

The state was, that we had a simple structure, which allowed us to get some data from Elasticsearch, through Java, to the browser by pressing a button by the user:
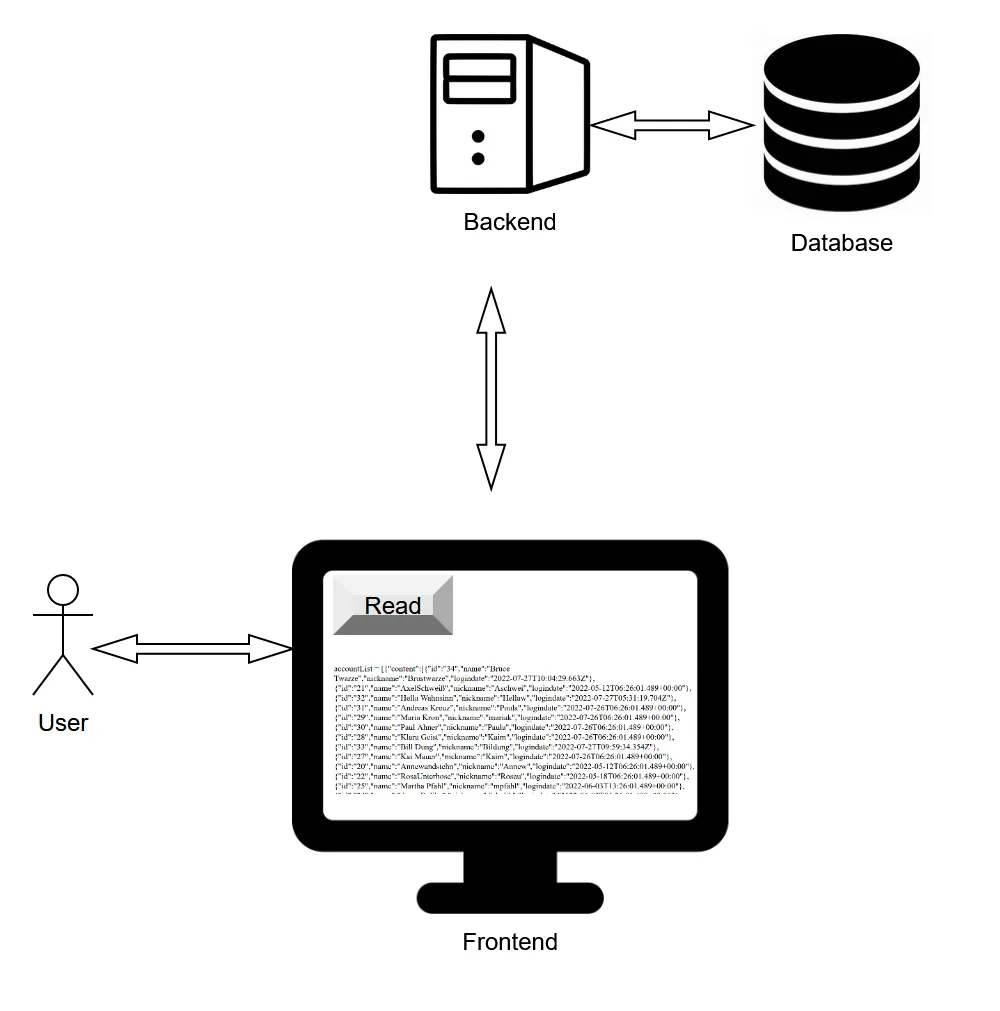
(Origin)
Now we want more. We want to have three buttons, that allows us also to write (create and update) and delete the data.
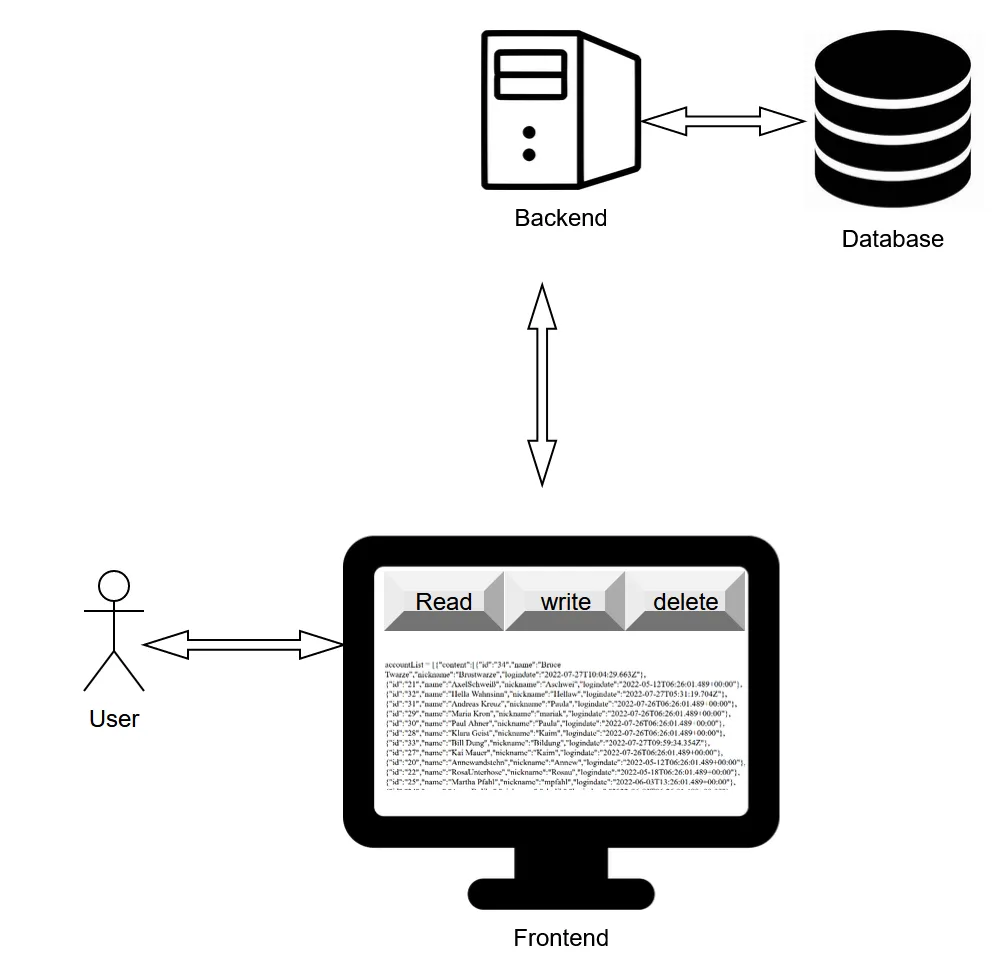
Post Request (Create And Write)
First we need to enhance the React Components with axios:
npm i axios
npm audit fix
Then we start with a first try, by adding this short function into the App.jsx file:
handleSubmitLastname(event){
alert('Yourlastnameis:'+this.state.lastname);
event.preventDefault();
//constfetch=require('node-fetch');
constaxios=require('axios')
letconfig={
headers:{
"Content-Type":"application/json"
}
}
letdata={
"id":"30",
"name":"PaulAhner",
"logindate":"2022-07-26T06:26:01.489+00:00",
"nickname":"Paula"
}
axios.post("http://192.168.2.121:8080/api/account",data,config)
.then(function(response){
console.log(response);
})
}
It works. We see in the debugger and on the Elasticsearch server:
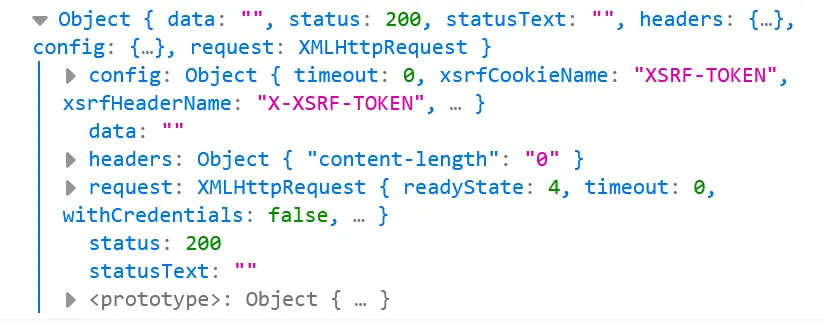

Now we create a button, that executes the function:
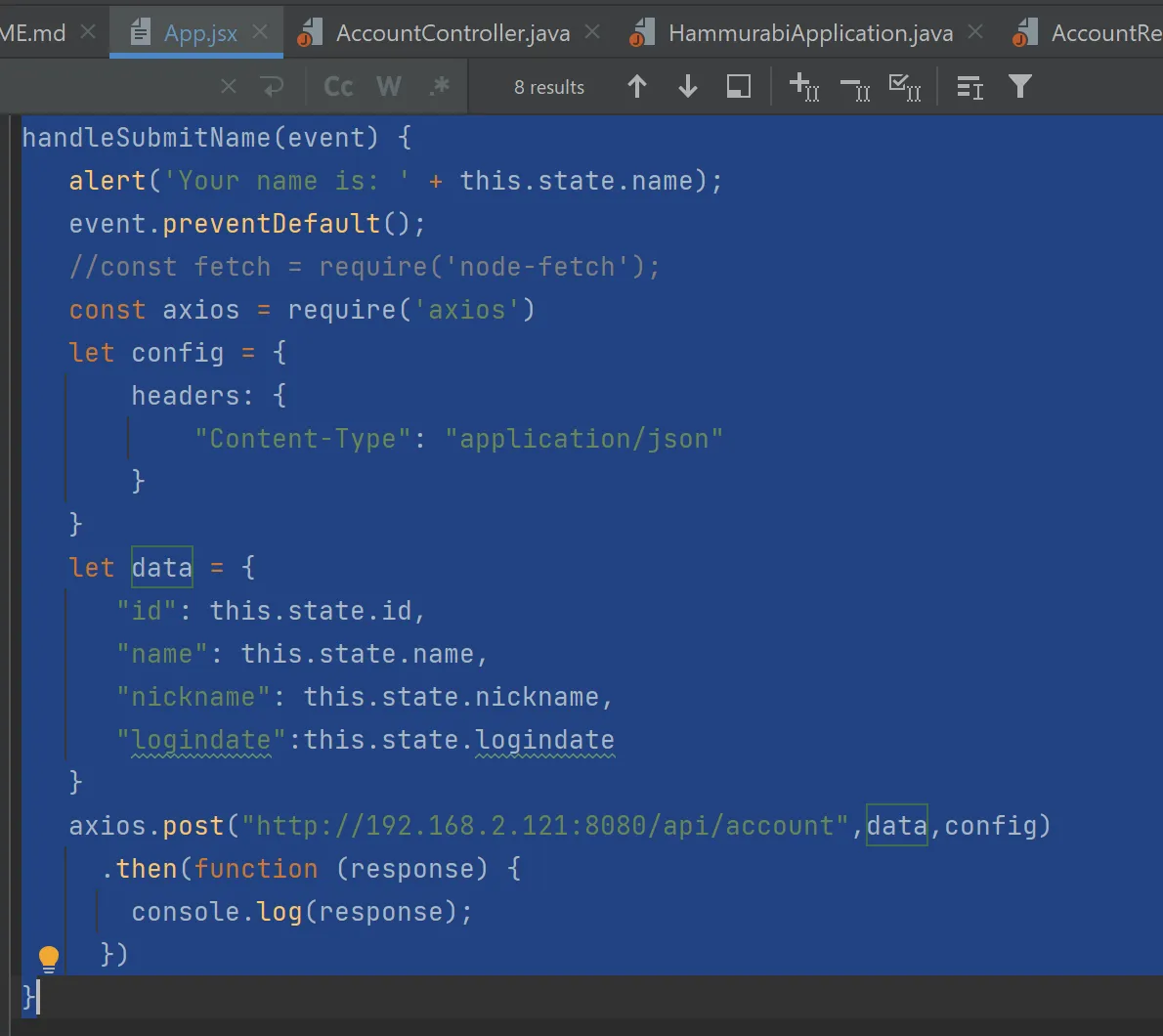

App.jsx:
importReactfrom'react';
classAppextendsReact.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state={
value:'coconut',
id:null,
name:null,
logindate:null,
timestamp:null
};
this.handleChangeId=this.handleChangeId.bind(this);
this.handleChangeName=this.handleChangeName.bind(this);
this.handleChangeNickName=this.handleChangeNickName.bind(this);
this.handleSubmitId=this.handleSubmitId.bind(this);
this.handleSubmitName=this.handleSubmitName.bind(this);
}
handleChangeId(event){
this.setState({id:event.target.value});
}
handleChangeName(event){
this.setState({name:event.target.value});
this.setState({logindate:newDate().toISOString()})
//soll:2022-07-26T06:26:01.489+00:00
//isttoISOString:2022-07-27T05:17:09.385Z
}
handleChangeNickName(event){
this.setState({nickname:event.target.value});
}
handleSubmitId(event){
alert('YourIdis:'+this.state.id);
event.preventDefault();
}
handleSubmitName(event){
alert('Yournameis:'+this.state.name);
event.preventDefault();
//constfetch=require('node-fetch');
constaxios=require('axios')
letconfig={
headers:{
"Content-Type":"application/json"
}
}
letdata={
"id":this.state.id,
"name":this.state.name,
"nickname":this.state.nickname,
"logindate":this.state.logindate
}
axios.post("http://192.168.2.121:8080/api/account",data,config)
.then(function(response){
console.log(response);
})
}
render(){
return(
<divclassName="App">
<formonSubmit={this.handleSubmitName}>
<label>
TypeinyourId:
<inputvalue={this.state.id}onChange={this.handleChangeId}/>
Typeinyourgivenandlastname:
<inputvalue={this.state.name}onChange={this.handleChangeName}/>
Typeinyournickname:
<inputvalue={this.state.nickname}onChange={this.handleChangeNickName}/>
</label>
<buttontype="submit">senden</button>
</form>
<hr/>
The complete content is:{this.state.id},{this.state.name},{this.state.nickname},{this.state.logindate}
<hr/>
</div>
);
}
}
exportdefaultApp;
//See also https://reactjs.org/docs/forms.html
Now we can read, create und update.
See also:
https://reactjs.org/docs/forms.html
https://medium.com/nerd-for-tech/your-first-nodejs-rest-api-client-59467659ab99
Update The Java Code To Get Delete Requests
For the next step we have to enhance our Java code. At first we add the @DeleteMapping endpoint into the controller class:
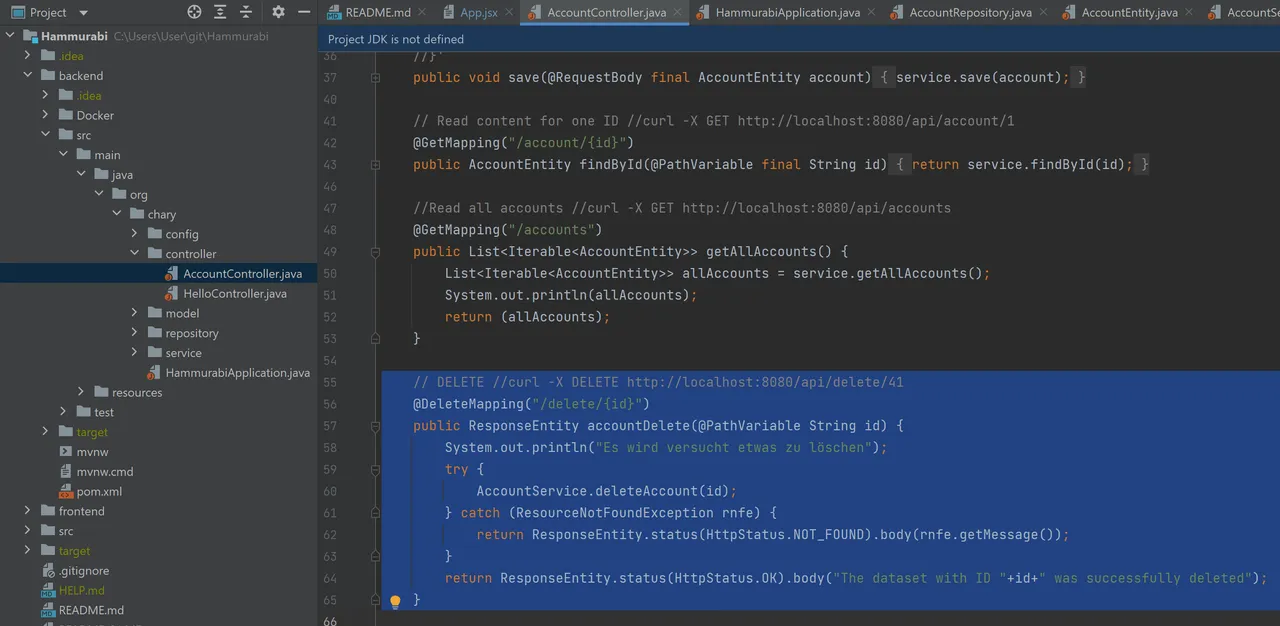
// DELETE //curl -X DELETE http://localhost:8080/api/delete/41
@DeleteMapping("/delete/{id}")
public ResponseEntity accountDelete(@PathVariable String id) {
System.out.println("Es wird versucht etwas zu löschen");
try {
AccountService.deleteAccount(id);
} catch (ResourceNotFoundException rnfe) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND).body(rnfe.getMessage());
}
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body("The dataset with ID "+id+" was successfully deleted");
}
In the service class we create the method, that does the action. The Spring-magic lies in the command "repository.deleteById(ID)":
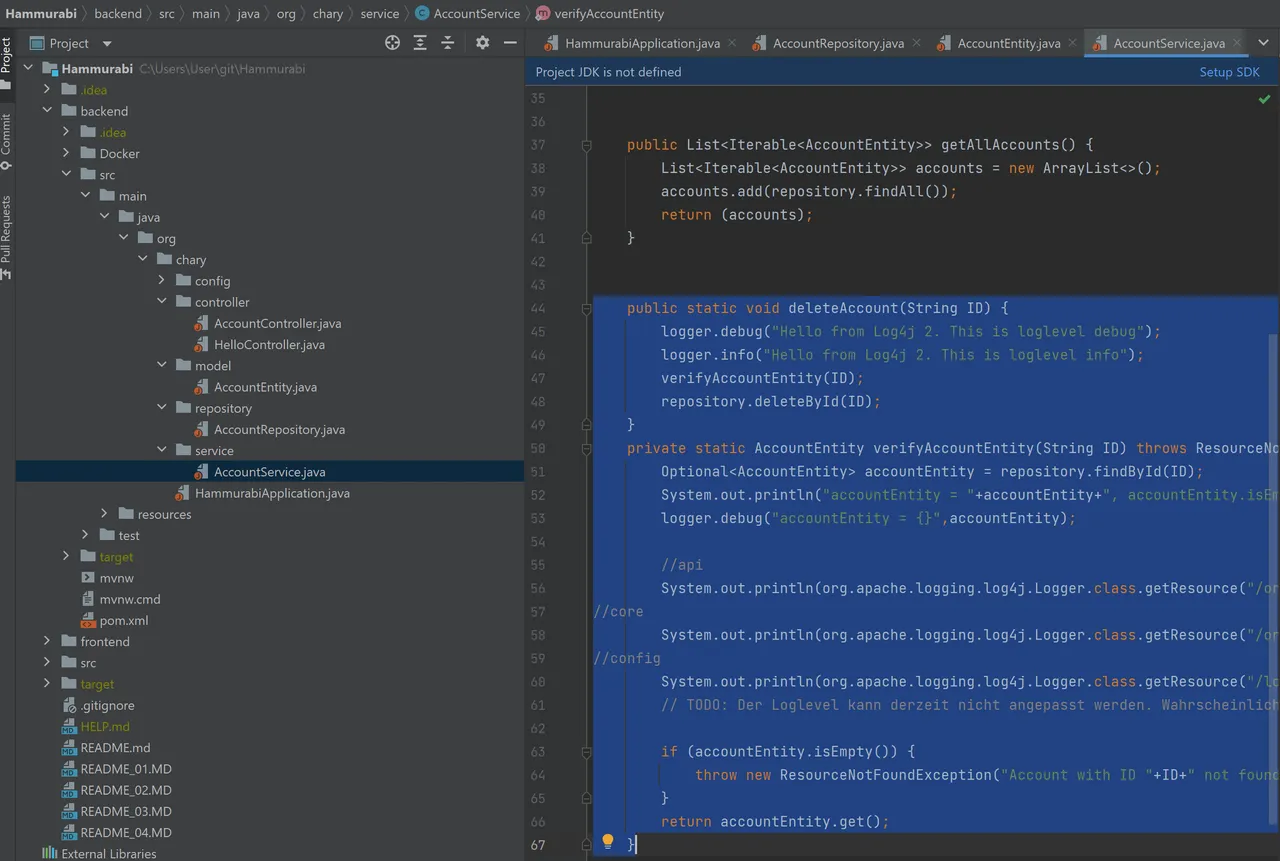
public static void deleteAccount(String ID) {
logger.debug("Hello from Log4j 2. This is loglevel debug");
logger.info("Hello from Log4j 2. This is loglevel info");
verifyAccountEntity(ID);
repository.deleteById(ID);
}
private static AccountEntity verifyAccountEntity(String ID) throws ResourceNotFoundException {
Optional<AccountEntity> accountEntity = repository.findById(ID);
System.out.println("accountEntity = "+accountEntity+", accountEntity.isEmpty = "+accountEntity.isEmpty());
logger.debug("accountEntity = {}",accountEntity);
//api
System.out.println(org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger.class.getResource("/org/apache/logging/log4j/Logger.class"));
//core
System.out.println(org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger.class.getResource("/org/apache/logging/log4j/core/Appender.class"));
//config
System.out.println(org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger.class.getResource("/log4j2.xml"));
// TODO: Der Loglevel kann derzeit nicht angepasst werden. Wahrscheinlich wird log4j.xml nicht gezogen. Nach einem Vormittag Recherche gebe ich erst mal hier auf.
if (accountEntity.isEmpty()) {
throw new ResourceNotFoundException("Account with ID "+ID+" not found");
}
return accountEntity.get();
}
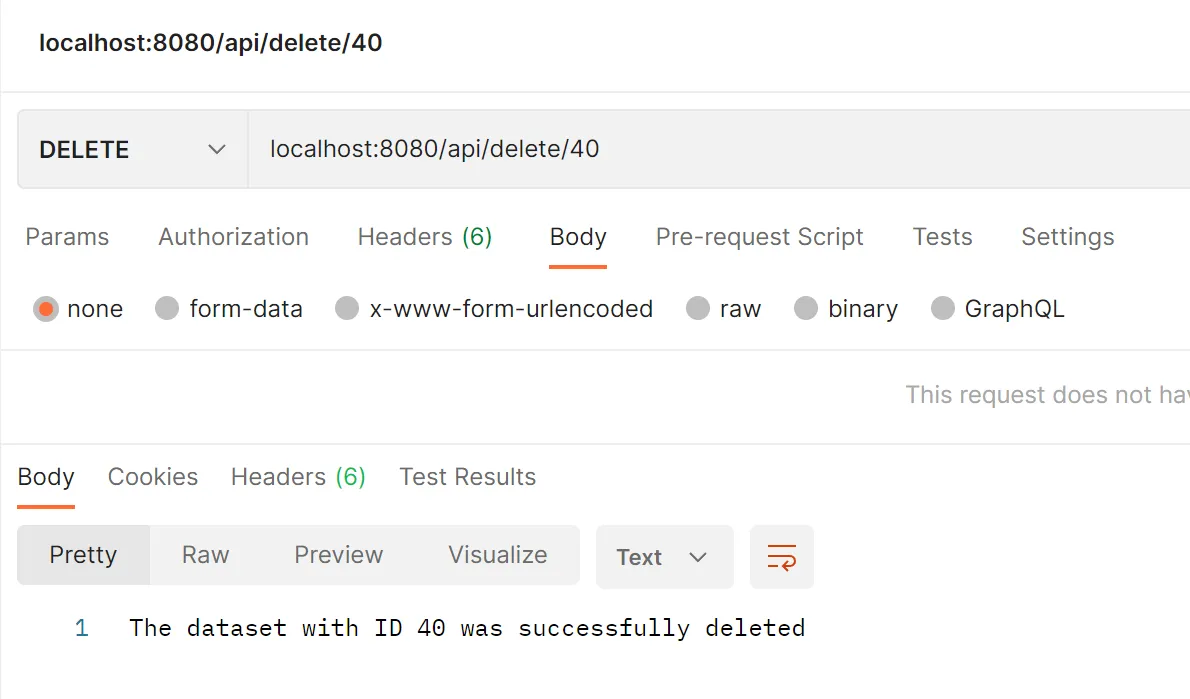
We can test the result with postman:
Or, of course, with curl:
curl -X DELETE http://raspi:8080/api/delete/40

Delete Button in React
The next thing is to create a button in our frontend-code, that collects the information from the ID field and then sends this curl command to the backend.
We create a method with the name "handleDeleteAccount(event). Here lies the React-magic in the command "axios.delete(http://…)":
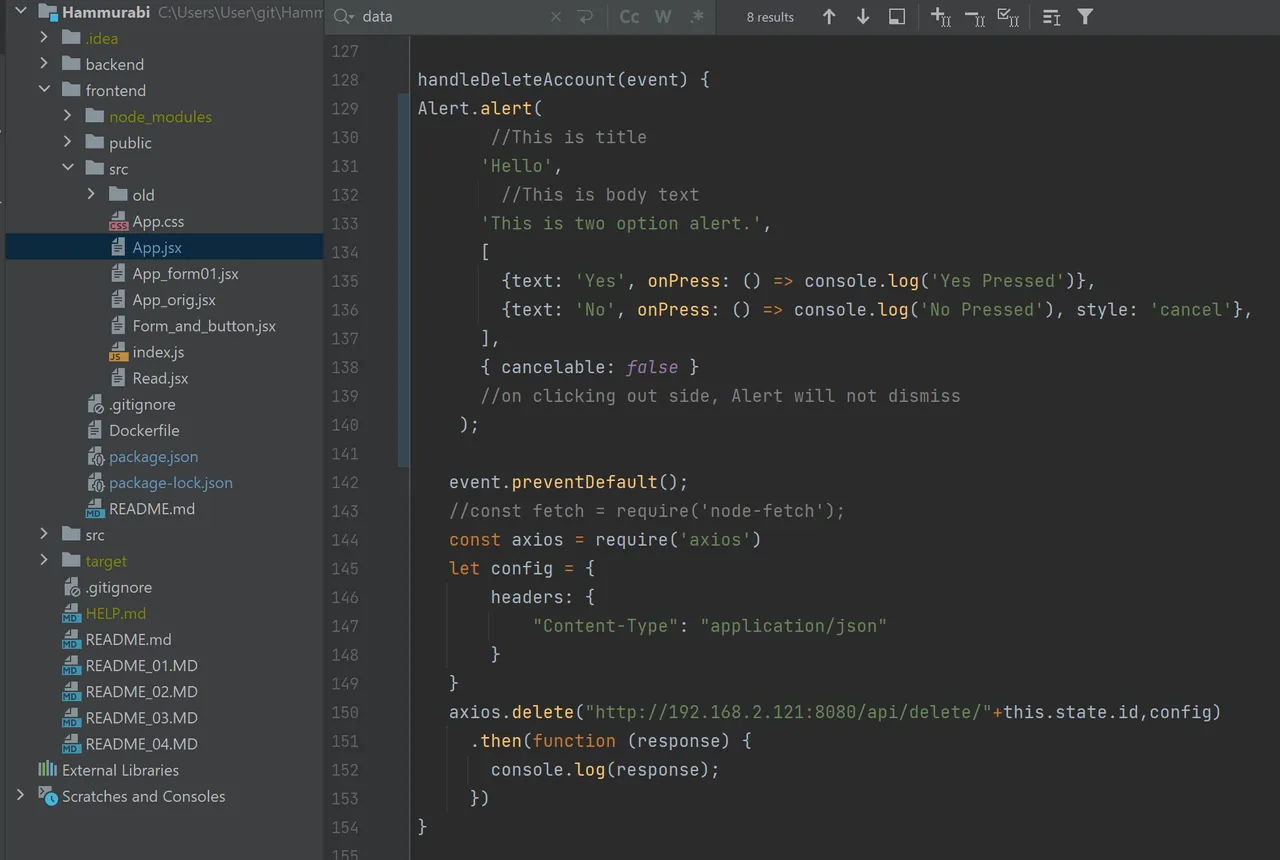
This function is startet via the following form section in the render part.
(I had some problems, because the function was startet permanently without pressing any button. Therefor I had to add the word "bind(this)" in row 184):
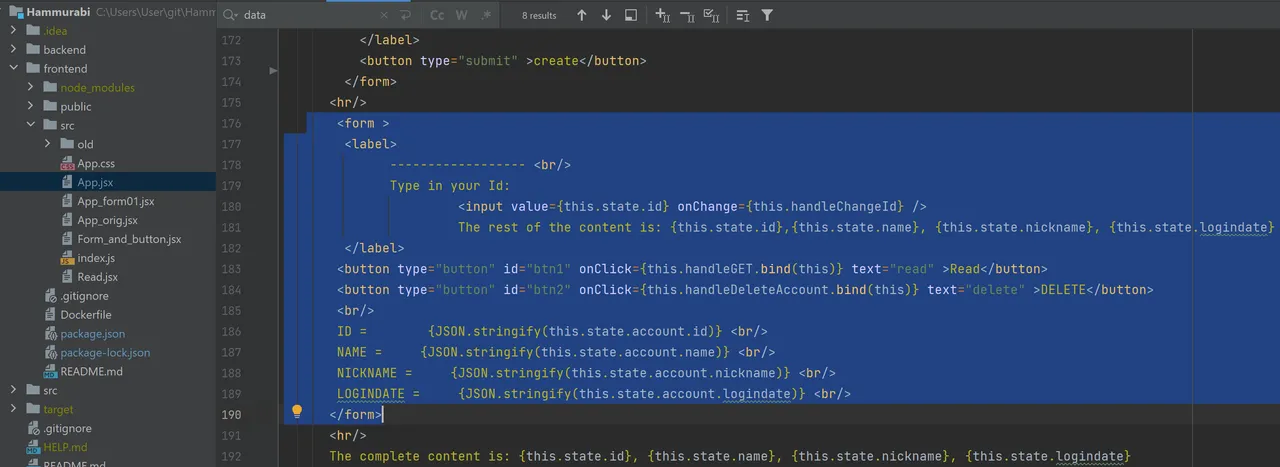
The result is the ID-field, that can import the ID and the delete button, which can delete the corresponding dataset:
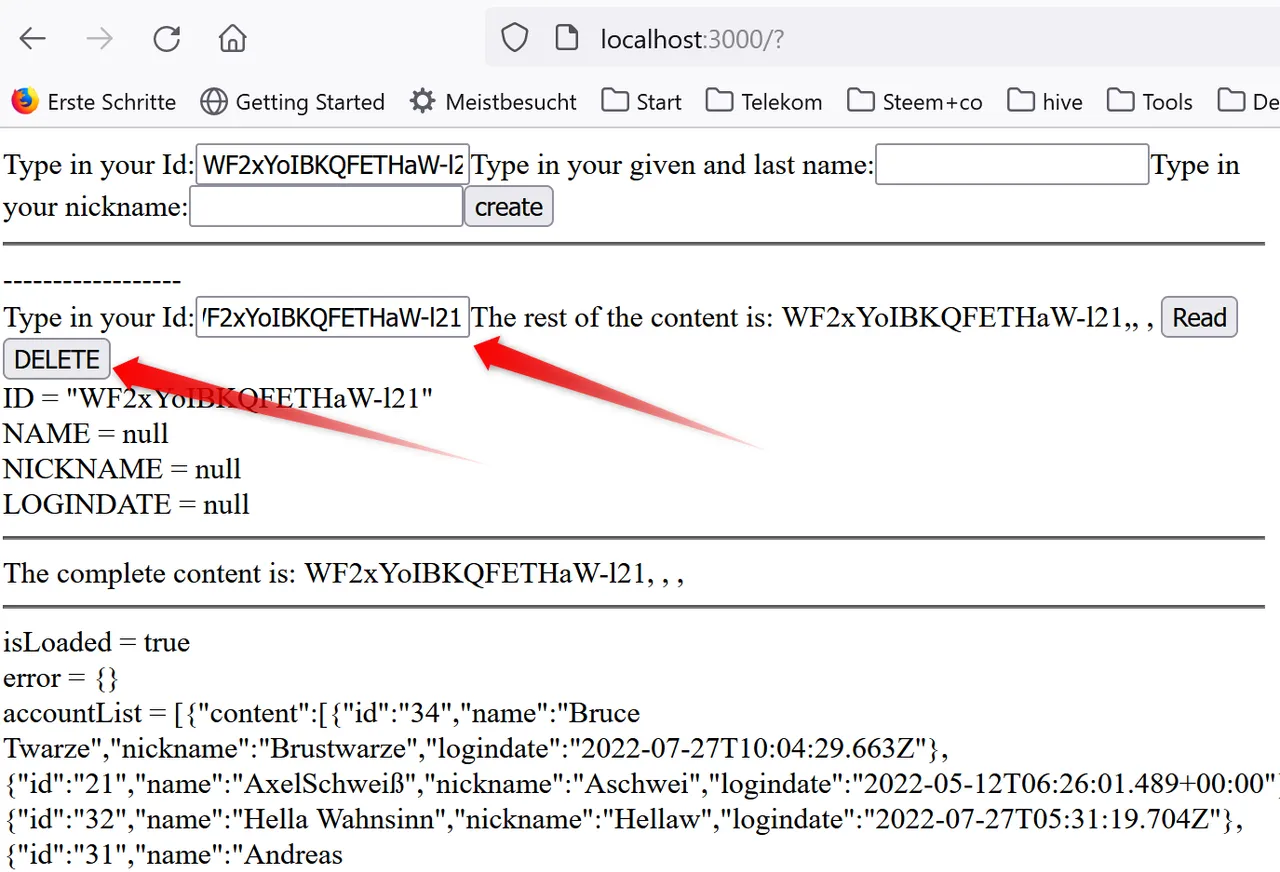
Here is the complete App.jsx:
import React from 'react';
import { Alert, Button, View, StyleSheet } from 'react-native';
//If the module was not found execute: npm install react-native-web
//import Read from './Read.jsx';
//import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
value: 'coconut',
id: null,
name: null,
logindate:null,
timestamp: null,
isLoaded: false,
error: false,
accountList: null,
data: [],
account: "nix"
};
this.handleChangeId = this.handleChangeId.bind(this);
this.handleChangeName = this.handleChangeName.bind(this);
this.handleChangeNickName = this.handleChangeNickName.bind(this);
this.handleSubmitId = this.handleSubmitId.bind(this);
this.handleSubmitName = this.handleSubmitName.bind(this);
this.handleGET = this.handleGET.bind(this);
}
simpleAlertFunction = () => {
//function to make simple alert
Alert.alert('Alert Title','This is Simple Alert');
}
componentDidMount() {
this.handleAccounts()
}
handleAccounts() {
const params = {
method: 'GET',
headers: {
'accept': 'application/json'
}
};
fetch("http://192.168.2.121:8080/api/accounts/",params)
.then(response => response.json())
//.then(response => response.blob()) //mutual exclusive with json
.then(
(data) => {
this.setState({
isLoaded: true,
accountList: data
})
})
.catch(e => console.error(e));
}
handleGET() {
const id = this.state.id
alert('The ID is: '+id);
console.log("handleGET: "+ "http://localhost:8080/api/account/" + id)
fetch("http://192.168.2.121:8080/api/account/" + id)
.then(res => res.json())
.then(
(result) => {
this.setState({
isLoaded: true,
account: (result)
})
},
(error) => {
this.setState({
isLoaded: true,
error
});
}
)
}
handleChangeId(event) {
this.setState({id: event.target.value});
}
handleChangeName(event) {
this.setState({name: event.target.value});
this.setState({logindate: new Date().toISOString()})
// soll: 2022-07-26T06:26:01.489+00:00
//ist toISOString: 2022-07-27T05:17:09.385Z
// this.handleGET();
}
handleChangeNickName(event) {
this.setState({nickname: event.target.value});
}
handleSubmitId(event) {
alert('Your Id is: ' + this.state.id);
event.preventDefault();
}
handleSubmitName(event) {
alert('Your name is: ' + this.state.name);
event.preventDefault();
//const fetch = require('node-fetch');
const axios = require('axios')
let config = {
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
}
let data = {
"id": this.state.id,
"name": this.state.name,
"nickname": this.state.nickname,
"logindate":this.state.logindate
}
axios.post("http://192.168.2.121:8080/api/account",data,config)
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
}
handleDeleteAccount(event) {
Alert.alert(
//This is title
'Hello',
//This is body text
'This is two option alert.',
[
{text: 'Yes', onPress: () => console.log('Yes Pressed')},
{text: 'No', onPress: () => console.log('No Pressed'), style: 'cancel'},
],
{ cancelable: false }
//on clicking out side, Alert will not dismiss
);
event.preventDefault();
//const fetch = require('node-fetch');
const axios = require('axios')
let config = {
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
}
axios.delete("http://192.168.2.121:8080/api/delete/"+this.state.id,config)
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
}
render() {
const { error, isLoaded, data, account } = this.state;
const Button = (props) => {
return (
<button>{props.text}</button>
); }
return (
<div className="App">
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmitName}>
<label>
Type in your Id:
<input value={this.state.id} onChange={this.handleChangeId} />
Type in your given and last name:
<input value={this.state.name} onChange={this.handleChangeName} />
Type in your nickname:
<input value={this.state.nickname} onChange={this.handleChangeNickName} />
</label>
<button type="submit" >create</button>
</form>
<hr/>
<form >
<label>
------------------ <br/>
Type in your Id:
<input value={this.state.id} onChange={this.handleChangeId} />
The rest of the content is: {this.state.id},{this.state.name}, {this.state.nickname}, {this.state.logindate}
</label>
<button type="button" id="btn1" onClick={this.handleGET.bind(this)} text="read" >Read</button>
<button type="button" id="btn2" onClick={this.handleDeleteAccount.bind(this)} text="delete" >DELETE</button>
<br/>
ID = {JSON.stringify(this.state.account.id)} <br/>
NAME = {JSON.stringify(this.state.account.name)} <br/>
NICKNAME = {JSON.stringify(this.state.account.nickname)} <br/>
LOGINDATE = {JSON.stringify(this.state.account.logindate)} <br/>
</form>
<hr/>
The complete content is: {this.state.id}, {this.state.name}, {this.state.nickname}, {this.state.logindate}
<hr/>
<form onSubmit={this.handleAccounts}>
<label>
isLoaded = {JSON.stringify(this.state.isLoaded)} <br/>
error = {JSON.stringify(this.state.error)} <br/>
accountList = {JSON.stringify(this.state.accountList)} <br/>
data = {this.state.data} <br/>
</label>
<button type="submit" >Refresh</button>
</form>
<hr/>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
// See also https://reactjs.org/docs/forms.html
// Read
// <button onClick={() => this.handleGET(this.state.id)} >Read
// Read verhindert, dass es permanent ausgeführt wird.
Conclusion
Now we have a Java backend and a React frontend, which is able to create, read, update and delete (CRUD) some data in the elasticsearch database.
You can find my code on https://github.com/achimmertens/Hammurabi
The next big thing is, that I want to switch from React to Angular, because this will be the software, I need to learn for my job and it seems, that Angular has some advantages to React.
So stay tuned, Achim